![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define what a vaccine is |
A material originating from a micro organism or other parasite that induces an immunological mediated resistance to disease |
|
|
Milk maids didn't get small pox! What is the name and year of the person who looked further into this what did he do? |
Edward Jenner 1796- found that milk ladies were exposed to cows with cow pox which helped them become immune to small pox |
|
|
What Is either side of the window of opportunity |
1. Loss of passive immunity from mother 2.timing of natural exposure to infection |
|
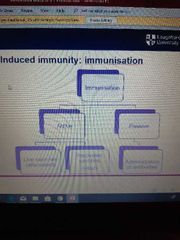
Which is the most effective and induces a cell mediated response? |
Live vaccines |
|
|
What is pertussis and how long does your maternal passive immunity last (generally) |
Declines rapidly |
|

What does this graph show? |
Seroresponders are people that have detected the antigen and started to produce their own antibodies. You can see that ideally 100% would be seroresponders at 11-12 months there is the highest %. This could be due to this being the 'Window of opportunity' for the children |
|
|
Are their benefits of curcumin to infectious diseases in childhood? |
Yes there seems to be a lower likelihood of allergy and auto immune disease e.g. asthma |
|
|
Why is it best to get diseases such as chicken pox when you are younger? |
You have a weakened cell mediated response to infection so less immunopathology |
|
|
What is herd immunity? |
Not needing to vaccinate the entire population but a large enough % so that it cant spread |
|
|
What does EPI stand for and what was its goal by 1990 (starting at 1974) |
The expanded programme on immunization. Vaccines for every child against 6 major diseases |
|
|
EPI failed its initial targets. Name some barriers they came across |
1. Lack of public and government awareness on the seriousness of some of the diseases 2. Bad programme management 3. Inadequate equipment and skills for vaccination storage and handling |
|
|
What is a more current vaccine plan that is still going today |
|
|
|
Is measles bacteria or virus and enveloped or non enveloped? |
Enveloped Virus |
|
|
What is the difference between humoral and cellular immunity? |
|
|
|
What is the Dosage, number of doses, duration of immunity, cell mediated response level and risk of reversion to virulence for live attenuated vaccines |
Low dose, only 1 dose, long lived immunity, good cell mediated response and rarely reverts back to virulence |
|
|
What %of people need to be vaccinated to create herd immunity for measles? |
93-95% this is quite high |
|
|
Does the uk have herd immunity? |
No |

