![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Erythema nodosum causes |
localized inflammatory condition of skin (type of hypersensitivity rxn) think anytime you have red nodules on anterior aspect of legs assoc with preg most common causes: streptococcal infections coccidioidomycoses histoplasmosis sarcoidosis IBD syphilis hepatitis |
|
|
Erythema nodosum presentation |
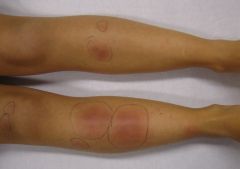
multiple painful, red, raised, nodules on anterior surface of lower extremities tender to palpation do not ulcerate can last ~6 weeks |
|
|
Erythema nodosum next steps |
Want to fig out cause: CXR --> sarcoid, fungal infection further w/u if CXR is negative |
|
|
Fungal infection presentation |
superficial fungal infections of skin, hair, and nails are dx with visual appearance and confirmed with KOH test leading edge of lesion on skin or nail is scraped with scalpel to remove epithelial cells --> KOH dissolves epithelial cells but does not affect fungus |
|
|
Tinea versicolor |
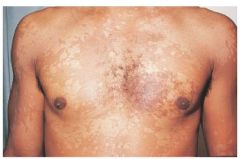
occurs in humid climates or those who sweat perfusely common in adolescents dx with KOH with wood lamp |
|
|
Rx of fungal infection |
Onychomycosis (nail infection): oral terbinafine or itraconazole 6 weeks for fingernails & 12 weeks for toenails monitor LFTs when on terbinafine Griseofulvin for fingernails (6-12 months) less efficasious than terbinafine & no longer rec for toenails Tinea captitis (hair infection): Oral terbinafine or itraconazole Griseofulvin for 6-8 weeks |
|
|
Tinea versicolor vs vitiligo appearence |
Tinea versicolor: lesions of different colors from tan to pink lesions do not tan KOH + Vitiligo: no pigmentation KOH - |
|
|
Vitiligo |
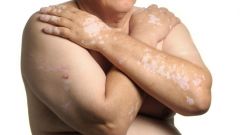
chronic dz with idiopathic pathogenesis assoc with autoimmune dz such as addison's dz, hashimoto thryoiditis, DM1 rx with topical steroids, calcineurin inhibitors, phototherapy |
|
|
Herpes simplex |
Genital infection --> multiple painful vesicles (normally caused by HSV2 but can also be HSV1) Many ppl infected are asympt Oral infection --> vesicles are usually visible & rx should be started immediately (oral acyclovir, famciclovir, or valacyclovir) w/o test confirmation (usually caused by HSV1) |
|
|
Herpes simplex diagnosis |
dx is done with active lesions only if dx not clear, best initial test is Tzanck smear of lesion --> detects multinucleated giant cells (technique is similar to pap smear) most accurate diagnostic test is viral cx (takes 1-2 days) serology NOT useful (just distinguishes acute vs chronic) |
|
|
Herpes zoster |
occurs in elderly or immunocompromised pts vesicles follow dermatone distribution with erythematous base pain occurs prior to vesicle appearance Can dx with appearance but Tzanck prep is best initial test & viral cx is most accurate test rx with oral acyclovir (800mg 5x/day for 10 days), valacyclovir, famciclovir aluminum acetate soaks can be comforting for skin lesions disseminated herpes zoster (multiple dermatones) --> IV acyclovir postherpetic neuralgia --> analgesics (eg gabapentin, amitriptyline, lidocaine patch, pregabalin) |
|
|
Ramsay hunt syndrome |
Zoster affects geniculate ganglion of sensory branch of facial nerve vesicles and pain appear on external auditory canal pts lose their sense of taste in anterior 2/3 of tongue w/ipsilateral facial palsy facial palsy + pain = zoster facial palsy w/o pain --> something else (eg Lyme dz) |
|
|
Syphilis presentation |
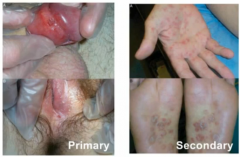
primary syphilis --> chancre- an ulcertaion with heaped up indurated edges that is painless (but can also be in oral area) secondary syphilis --> generalized copper-colored, maculopapular rash on palms and soles of feetcan also have mucous patch, alopecia areata, or condylomata lata secondary syphilis is infectious and VDRL & RPR is only positive in secondary syphilis |
|
|
Syphilis dx & rx |
Primary syphilis: best initial test --> darkfield exam (false neg rate of 25% for both VDRL & RPR) Secondary syphilis: VDRL and RPR have ~100% sensitivity followed by treponemal specific testing (eg fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption (FTA-ABS) rx with single IM dose of penicillin but if allergic, can give orally dox for 2 weeks rx with pencillin causes rapid death of treponemal & can cause Jarisch-Herxheimer rxn (fever, chills, rigor, hypotension, headache, tachy, vasodilation, myalgia) |
|
|
Lyme dz |
caused by Borrelia burgdorferi transmitted by deer tick (Ixodes scapularis) >85% develop a erythematous rash (erythema migrans) with central clearing that occurs 7-10 days AFTER tick bite --> if seen, can start treatment with no further w/u rx with oral dox, amox, or cefuroxime once rash is seen with no rx, rash goes away in a few days to weeks with 2/3 of pts eventually develop monoarthritis or rarely migratory arthritis & smaller number of pts develop neurologic or cardiac d/o neurologic (b/l facial nerve palsy) or cardiac sxs (AV block, PR interval incr)--> IV ceftriaxone 2-4 weeks |
|
|
Melanoma |

L melanoma R normal superficial spreading melanoma is most common type (2/3 of cases) |
|
|
Types of melanoma |
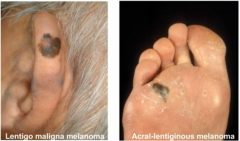
Lentigo maligna melanoma --> sun exposed body parts in the elderly Acral-lentiginous melanoma --> palms, soles of feet, and nail beds |
|
|
Melanoma dx & rx |
Bx is with full thickness sample bc tumor thickness is most important prognostic factor rx with excision |
|
|
Squamous cell carcinoma |
develops on sun exposed skin in elderly 10-25% of skin cancers are squamous cell common on lip (more common with tobacco use) ulceration of lesion is common dx with bx rx with surgical removal and RT can be used for lesions that cannot be operated |
|
|
Basal cell carcinoma |
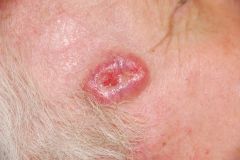
65-80% of all skin cancers seen in sun exposed areas, particularily face shiny or "pearly" appearance dx with shave or punch bx rx with surgical removal (Mohs microsurgery has greatest cure rate with instant frozens done to determine when enough tissue is removed) |
|
|
Psoriasis |
silvery scales develop on extensory surfaces can be local or extensive nail pitting is common rx with salicyclic acid to remove heaped up collections of scaly material --> if localized, topical steroids if severe --> coal tar or anthralin derivatives to avoid long term use of steroids, can use topical vit D (calcipotriene) or topical vit A (tazarotene) |

