![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Is the cerebral cortex dependent of the thalamus? If yes, why?
|

|
|
|
What is the difference in the function between the primary motor, primary sensory areas as compared to the secondary supplementary motor, premotor, and secondary sensory areas?
|

|
|
|
What is the function of the Wernicke's area? What is the function of the angular gyrus?
|

|
|
|
What are the two main functions of the prefrontal association area?
|
The prefrontal area is involved with thinking and planning complex motor activities, as well as thinking in general, and possibly storing short term or "working" memory (thinking about ideas as they come into your head). Some studies indicate that the frontal lobe is the last to fully develop (as late as 25 years of age), and has been linked to the ability to connect actions to consequences
|
|
|
What is the main function of Broca's area?
|
Broca's area plans the motor output necessary to speak using words or phrases
|
|
|
What are the main functions of the limbic association area?
|
Behavior, motivation, emotions
|
|
|
Where is the face recognition portion of the brain?
|
Inferior surface of the brain: medial occipital and temporal lobes
|
|
|
Which hemisphere has the most developed Werkicke's area in most right-handed individuals? If the dominanat Wernicke's area were damaged, would the person still appear intelligent?
|
Left because it is a right-handed person's dominant side of the brain.
Damage leads to almost complete lack of intelligence (as our culture tends to define it); including ability to read, perform math, think logically |
|
|
What is the function of the corpus callosum?
|
Allow communication between the two hemispheres of the brain
|
|
|
Name some functions of the non-dominant Wernicke's area?
|
Interpreting music, visual patterns, spatial relationships, body language, voice intonation, body experiences from the limbs and hands
|
|
|
Name some functions lost in patients following a prefrontal lobotomy
|
Complex problem solving, sequential tasks, learning, staying focused, multi-tasking, ambition, appropriate sexual activity and excretion, maintaining mood
|
|
|
Describe the "holistic theory" of thoughts
|
Thoughts are patterns of stimulation of various areas of the brain including the cerebral cortex, thalamus, limbic system and brain stem.
|
|
|
Define short term memory, intermediate term memory and long term memory
|
Short: Ability to remember 7-10 discrete pieces of information for the durtion of time that you are thinking about it
Intermediate: Changes to the pre or postsynaptic neuron that helps the memory trace remain activated (minutes to weeks). Long term: structural changes in the pre or postsynaptic neuron help the memory trace to remain activated (years to life time) |
|
|
Where is the hippocampus and what effect does removal have on memory?
|
The hippocampus is on the medial portion of the temporal lobe, and the removal of both hippocampi make it impossible to create intermediate or long term memories (anterograde amnesia)
|
|
|
Why is the hypothalamus described as "one of the most important of the control pathways of the limbic system?"
|
Although very small, the hypothalamus sends and receives information from all portions of the limbic system. In addition, it sends information to the brain stem and beyond to the autonomic nervous system, it sends information to the thalaus and cortex, and it sends information to the pituitary gland (which in turn secretes hormones with systemic effects).
|
|
|
Premotor area
|
Where the "motor image" first forms and where the pattern is broken down into its individual parts. From here the signal for each pattern of motion, which includes activity of motion, which includes activity in the muscles of the shoulder, arm and hand, can directly stimulate the appropriate areas in the PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX (or the meeage could first be sent to the basal ganglia and thalamus, followed by the primary motor cortex).
i.e. reaching and grasping which is a pattern of movement this area is anterior to the primary motor cortex |
|
|
Supplementary motor area
|
An area that, when stimulated, provides "background" muscle activities such as body positioning, or head and eye positioning, that would assist my ability to reach out and grasp the apple
|
|
|
Pyramidal tract aka corticospinal tract
(meaning from the cortex to the spinal cord) |
Where the signal is sent down to the muscles. The impulses concerned with helping my arm to reach out, and my fingers to grasp the apple, will synapse with INTERNEURONS in the spinal cord, and some ALPHA MOTOR NEURONS directs (i.e. neurons that will lead to the deltoid muscle of the shoulder, extensor muscles of the hand, flexor muscles of the elbow, etc.)
|
|
|
Cerebellum
|
A place where sensory and motor information is compared, and adjustments are made. The cerebellum receives information about the desired motor pattern from the motor cortex, and then compares this to the sensory information it is receiving.
Helps to produce smooth coordinated movements. The cerebellum would be able to excite motor pathways to produce more muscle contraction in the muscles to extend the arm, so the reach pattern would be more accurate |
|
|
Basal ganglia
|

More complex unconsciously controlled motor actions of the body would also require input from the basal ganglia. The simple action of reaching for the apple may not, but writing the alphabet, throwing a football, hammering nails, etc., would include connections between the motor cortex and the basal ganglia (as well as connections with the thalamus)***
|
|
|
Fusiform gyrus
|
recognizes people's faces
|
|
|
Amygdala
|
determines emotional significance of stimuli
|
|
|
Learned paralysis
|
repeated bouts in which the CNS commands the arm to move with no response, due to severed peripheral nerve
|
|
|
How is a mirror box used to relive the pain of a "paralyzed" phantom arm?
|

|
|
|
Synaesthesia
|

|
|
|
Why do most people assign the same shapes to the names Buba and Kiki?
|

|
|
|
What is meant by "sympathetic and parasympathetic tone" and how it benefits the function of the autonomic nervous system
|

|
|
|
Spinal Cord
|

|
|
|
Lower Brain or Subcortical level
|

|
|
|
Higher Brain or Cortical level
|

|
|
|
Muscle stretch reflex
|

|
|
|
Sensory receptor
|

|
|
|
Vision: Step 1
|
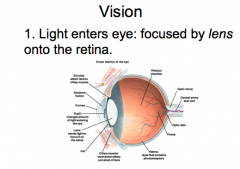
|
|
|
Vision: Step 2
|
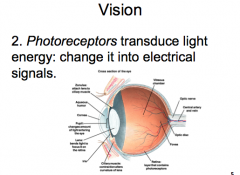
|
|
|
Vision: Step 3
|
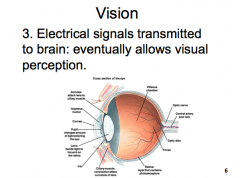
|
|
|
How does light travel through the eye?
|
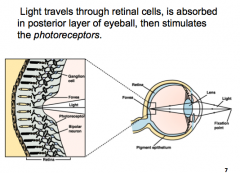
|
|
|
What absorbs light and prevents reflection within the eye?
|
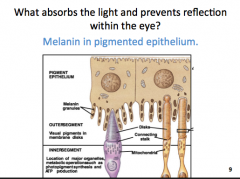
Melanin in pigmented epithelium
|
|
|
What is the first step in the process of transducing light energy into neuronal electric signals in a rod?
|

|
|
|
What happens to rhodopsin when it absorbs light?
|
Changes shape and activates G-protein Transducin
|
|
|
What are the results (direct or indirect) of "activated" rhodopsin?
|
results in decreased intracellular cGMP and activates phosphodiesterase enzyme
|
|
|
How does cGMP affect cation (Na+, Ca2+) channels or ion flow?
|
When cGMP is bound, the ion channels open and a decrease in cGMP in the cell causes sodium to stop slowing into the cell
|
|
|
Sequence of events when light enters the eye
|
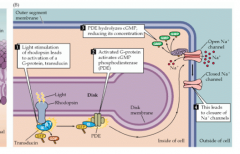
|
|
|
How does hyperpolarization affect glutamate release?
|
Decreases glutamate release
There is tonic release of glutamate in the absence of light, due to open sodium and calcium channels depolarizing the cell |
|
|
What is true about the synaptic connections in the retina?
|
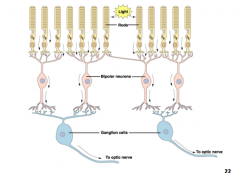
Ganglia cells are the only retinal cells with an action potential
Bipolar cells synapse with ganglia cells |
|
|
Which of the following are true regarding the path of the neuronal activity to the brain?
|
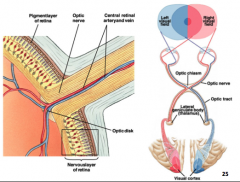
Ganglion cell axons make up the optic nerve
The optic nerve fibers terminate in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus |
|
|
Unable to identify the same objects when felt with the left hand, but touch pathway is intact
|
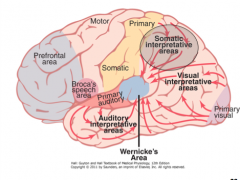
Right somatosensory area
|
|
|
Slow muscle fibers
|
Lots of mitochondria
Lots of myoglobin Innervated by smallest motor neurons |
|
|
What ultimately determines speed of cross bridge cycling?
|

The specific type of myosin ATPase on the myosin head, and the speed at which it converts ATP to ADP+Pi
|
|
|
Fast twitch Fibers
|
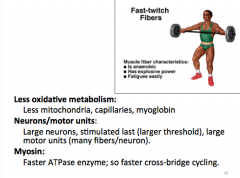
|
|
|
What is the advantage of asynchronous contraction?
|
Decrease fatigue (myofibers take turns)
Smooth contraction |
|
|
Frequency Summation and Tetanization
|
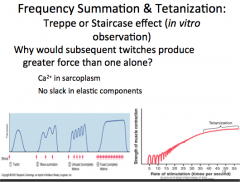
|
|
|
What are 3 ways to regulate force?
|
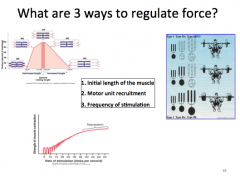
|
|
|
Which of the following best desribes the current thinking regarding how muscles increase in size following training?
|
More actin and myosin are produced
Myofibers increase in size New muscle cells are NOT produced |
|
|
Protein Kinase A
|
Can phosphorylate (activate) a protein
Example: PKA activates the Ca2+ ATPase pump on the SR in a cardiac myocyte (which pumps calcium back into the SR) Therefore binding of neurotransmitter to "stimulatory" G-protein, causes an increase in cAMP, leading to acivation of PKA and the Ca2+ ATPase pump in cardiac myocytes |
|
|
Adenylate Cyclase
|
Converts ATP to cAMP
cAMP activates Protein Kinase A PKA |
|
|
A bands
|
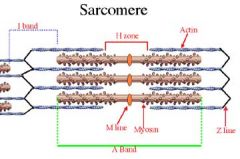
DARK BANDS
whole length of myosin filament overlapped by part of actin filament |
|
|
I bands
|
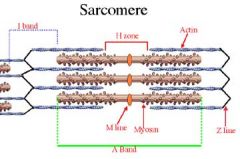
Light bands produced by ACTIN FILAMENTS ONLY
|
|
|
H band
|
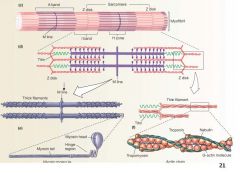
Portion of myosin filaments at center
NO OVERLAP with actin |
|
|
M line
|
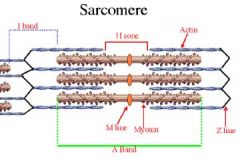
Bisects H band with fine strands that connect adjacent myosin filaments
|
|
|
Z Disc
|
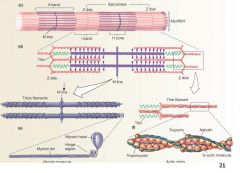
Delineates the sarcomere
serves as point of attachment for the actin and myosin (via titin) |
|
|
Myofibrils
|
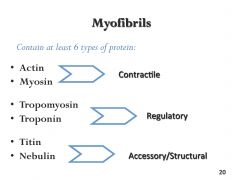
|
|
|
2 types of actin
|
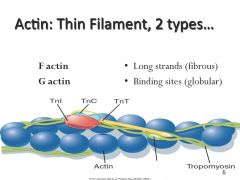
|
|
|
Tropomyosin and Troponin
|

|
|
|
What happens to the bands/zones in the sarcomere during contraction of a skeletal muscle cell?
|
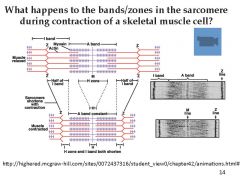
-Z-lines move closer together and sarcomeres shorten
- I bands shorten - A bands stay the same length, but H zones shorten |
|
|
What is necessary for sequential power strokes (muscle contraction) to occur?
|
- action potential from motor neuron
- calcium release from SR - available ATP |
|
|
What occurs when ATP is broken down into ADP + Pi at the myosin head?
|
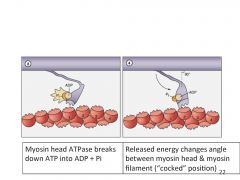
|
|
|
The Molecular basis of contraction
|
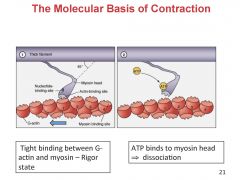
Power stroke: ADP + Pi are released
|
|
|
What happens to rhodopsin when it absorbs light?
|
Changes shape and activates G protein Transducin
|
|
|
Afferent vs efferent
|
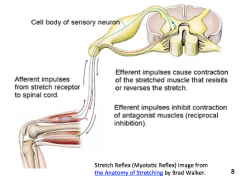
|
|
|
Describe the stretch reflex pathway
|
Muscle spindles send action potentials along afferent neurons to synapse at the spinal cord with Aalpha motor neurons to the agonist muscle
|
|
|
A(alpha) fibers
|
Ia muscle spindles and Ib golgi tendon organs
|
|
|
A(beta) and A(gamma) fibers
|
II tactile receptors (high discrimination)
|
|
|
A(delta) fibers
|
III temperature, deep pressure/touch, sharp pain
|
|
|
C fibers
|
IV temperature, crude touch, dull pain, itch
|

