![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
86 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
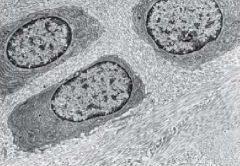
Cartilage Cell-
Chondrocytes |
|
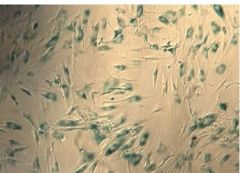
|
Cartilage-Mesenchymal Cells
|
|
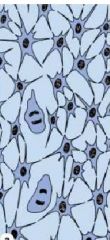
|
Cartilage-Mesenchymal Cells
|
|
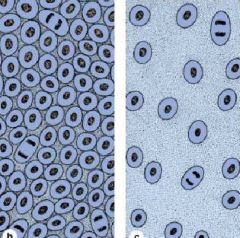
|
Cartilage -Chondroblasts Cells
|
|

|
Cartilage - Chondrocyte Cells
|
|
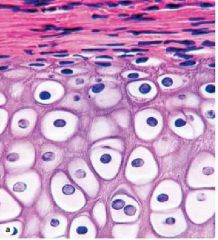
|
Cartilage Growth, specifically, Appositional Growth
|
|
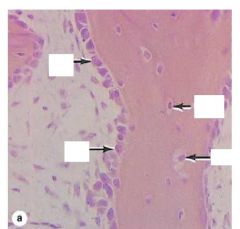
|
Bone
Along the edge are Osteoblasts In the center = Osteocytes |
|
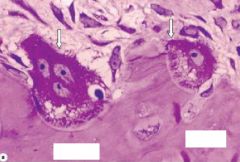
|
Bone Cells =
Osteoclasts |
|
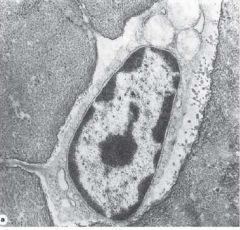
|
Bone Cell = Osteocytes
|
|
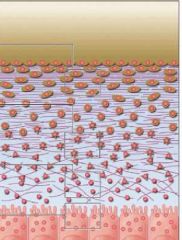
Name the Process
|
Mineralization:
a. Mineralized Bone b. Osteoid Layer c. Osteoblasts |
|
|
Bone Cells =
Osteoclasts |
|
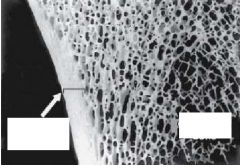
|
Compact Bone at the edge
Cancellous Bone in the middle |
|
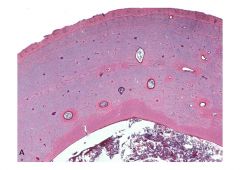
|
Cross section of Cortical Bone
|
|
|
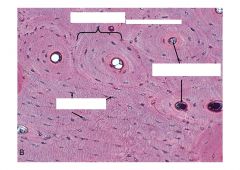
Bone:
Top: Haversian System Tiny dots: Osteocyte Lacunae Center of the rings = Haversian Canals that contain the neurovascular system |
|
|
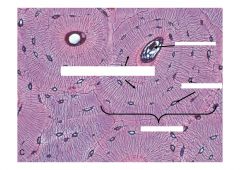
Haversian Canal
Canaliculi (tiny striations) Little dots = osteocyte lacuna One large ring = Haversian System |
|
|
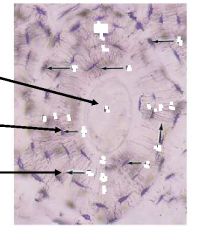
Lamella
Osteocytes Haversian Center Canaliculi |
|

|
Bone Formation =
Endochondral Ossification Zone 1 = resting cartilage Zone 2 =Proliferating cartilage Zone 3 = Hypertrophic cartilage Zone 4 = Calcified Cartilage Zone 5 = Ossification |
|
|
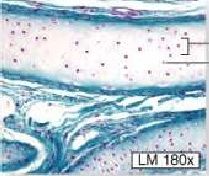
3 types of Cartilage =
Hyaline |
|
|
3 Types of Cartilage =
Fibrocartilage |
|

|
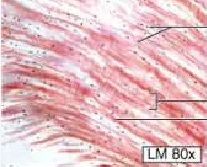
3 Types of Cartilage =
Elastic The white dots are lacunae with chondrocytes |
|
|
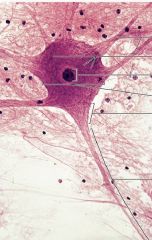
Dendrite
Nucleus Cell Body Axon Hillock Axon |
|
|
Neuron
|
|

|
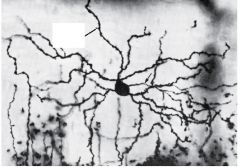
Unipolar Neuron
|
|
|
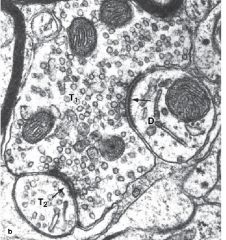
Presynaptic Neuron with all the synaptic vessels
Postsynaptic Membrane Postsynaptic Neuron with no vessels |
|
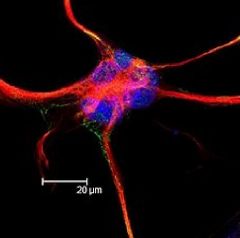
|
Astrocyte
|
|
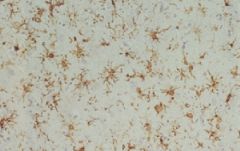
|
Microglial Cells
|
|
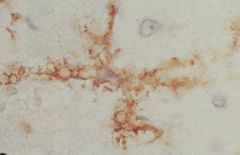
|
Microglial cells
|
|
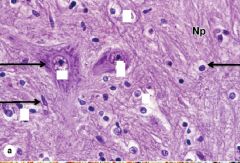
|
Neuron
Astrocyte Oligodendrocyte |
|
|
I think this is a microglial cell...please doublecheck!
|
|
|
White matter on the left
Gray matter on the right |
|
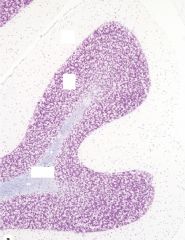
|
Cerebellum:
Granule Layer (dark purple) Molecular Layer (white layer) |
|
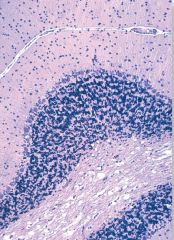
|
Cerebellum
Molecular Layer Granule Layer |
|

Very important Slide
|
Cerebellum
Molecular Layer Perkinje Cells Granule Layer |
|
|
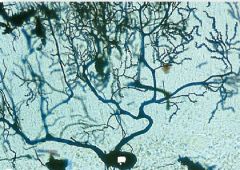
Cerebellum
You can only see the Perkinje Cell (the black dot) |
|
|
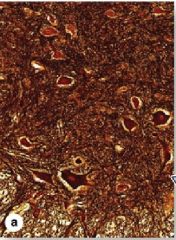
Spinal Cord
|
|

|
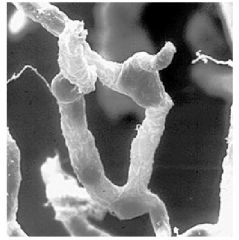
Spinal Cord
|
|
|
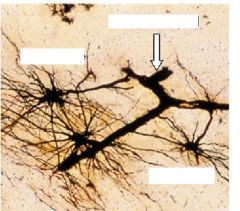
Blood vessel = blood brain barrier
|
|
|
Blood vessel = blood brain barrier
astrocytes |
|
|
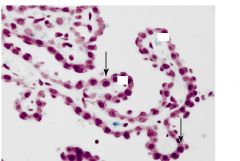
choroid plexus
|
|
|
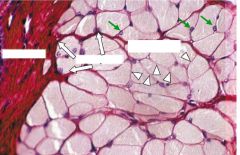
Outside to inside:
Skeletal Muscle Epimysium Perimysium Endomysium |
|
|
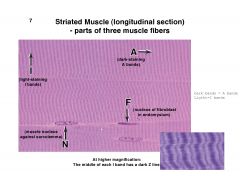
Striated Muscle - parts of 3 muscle fibers
A = Dark staining A bands I = Light staining I bands F= nucleus of bfibroblast in endomysium N = muscle nucleus against sarcolemma |
|
|
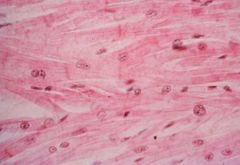
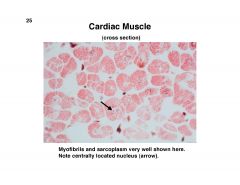
Cardiac Muscle
|
|
|
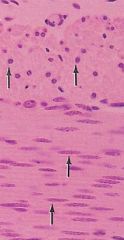
Cardiac Muscle
|
|
|
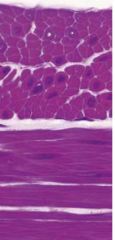
Smooth muscle
|
|
|
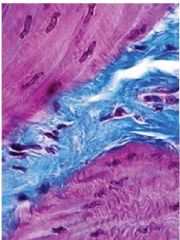
Smooth muscle
|
|

|
smooth muscle
|
|
|
smooth muscle = during contraction
|
|
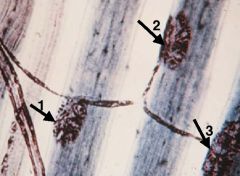
|
One axon giving rise to 3 motor end plates
|
|
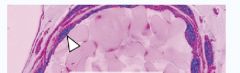
|
Epithelial Cells =
Squamous Identifier:Flat (Blood Vessel) |
|
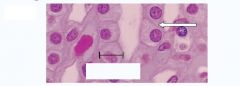
|
Epithelial Cells
Simple Cuboidal |
|
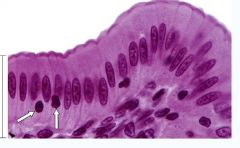
|
Epithelial Cells
Columnar |
|
|
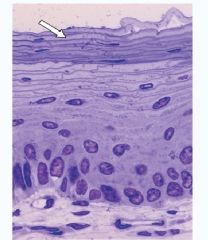
Epithelia
Stratified Layer |
|
|
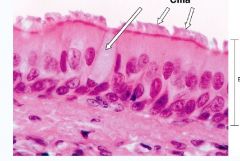
Epithelia
Psuedostratified |
|
|
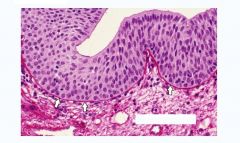
Epithelia
Transitional |
|
|
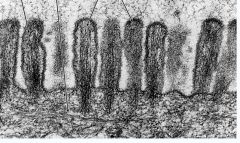
Epithelia
Microvilli Made of Microfilaments Fcn: Increase surface area covered by protein coat, Glycocalyx Do not move |
|

|
Epithelia
Microvilli - Microfilaments is in the middle and the round circles are the microvilli |
|
|
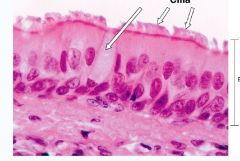
epithelia
cilia |
|
|
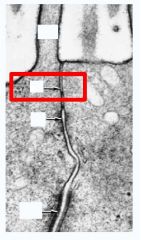
Epithelia
Top: Zonula Occulens = Tight Junction = forms a continuous band around cell to fuse neighboring cells to prevent flow of material between cells Middle : Zonula Adherens = Provides adhesion to neighboring cells Bottom: Macula Adherens (desmosomes) = Strong cell-to-cell adhesion Note: a. Tight Junctions seal epithelium b. Desmosomes and ZA provides structural support c. Gap Junctions allow ion exchange between neighboring epithelia |
|
|
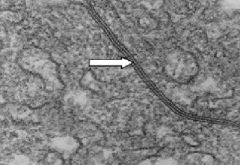
Epithelia
Gap Junctions |
|
|
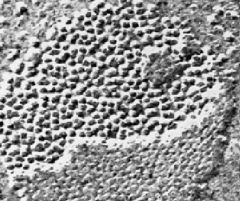
Epithelia
Gap Junctions |
|
|
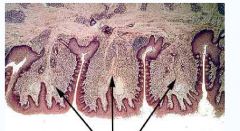
Epithelia
Infoldings of the Basal membrane = increase surface area Found in tissues that is subjective to stress...tongue or skin Foliate Papillae of the tongue |
|

|
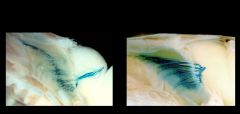
Epithelia
Basal Lamina Functions: physical support negative charge barrier differentiation of overlaying cells |
|
|
Olfactory Neurons projecting to the brain
|
|
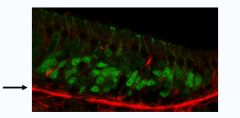
|
Basal Lamina at the olfactory epithelium
|
|
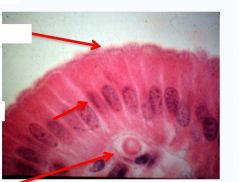
|
epithelial cells
Apical pole lumen/free surface lateral surface basal lamina Basal Pole |
|
|
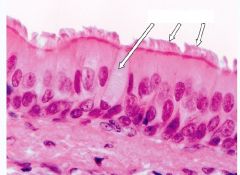
Modifications of the Apical Surface of the Epithelium
Cilia |
|
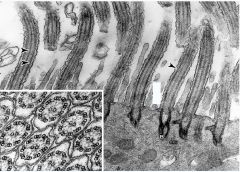
|
Cilia
Pseudostratified Columnar Back and forth motion to create flow of fluid in one direction Use ATP as the energy source for movement |
|
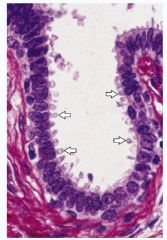
What is the function that this slide is depicting?
|
Epithelium
Secretion The picture is of the Apocrine Secretion |
|
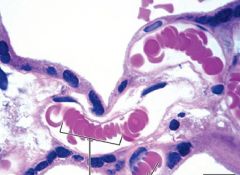
|
Erythrocytes
Function: Carry O2 and CO2 NO nucleus or organelles Large surface to volume ratio makes for efficient gas exchange |
|
|
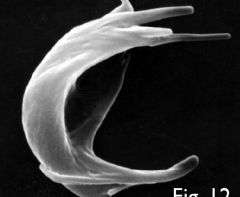
Sickel cell anemia
mutation of one nucletide in DNA (glutamic acid to valine) |
|
|
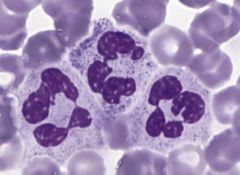
Neutrophils
Nucleus: multilobulated Phagocytosis of bacteria hours to days |
|
|
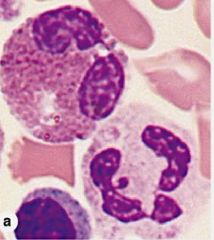
Eosinophils
Nucleus: Bilobed Phagocytosis; defense against parasites 8-12 days |
|
|
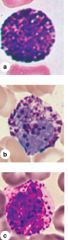
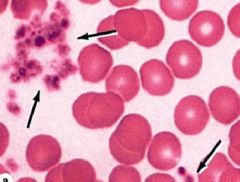
Basophils
Nucleus: Irregular Shape Basophilic granules contain heparin and histamine Fcn: associated with Allergies |
|
|
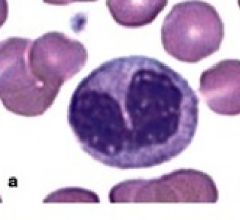
Monocytes
Nucleus is indented/folded Source of Macrophage, ingulf and digest bacteria, dead or dying cells |
|
|
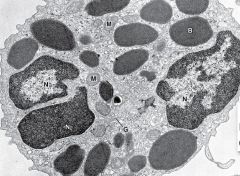
Platelets
Numerous cytoplasmic organelles Functions: release clotting factors at injury sites and release serotonin to slow or stop blood flow; vasoconstrict |
|
|
Basophil
|
|
|
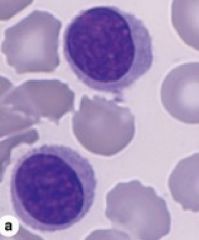
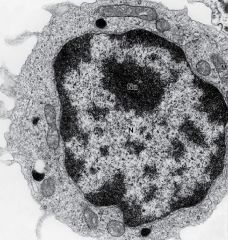
Lymphocytes
|
|
|
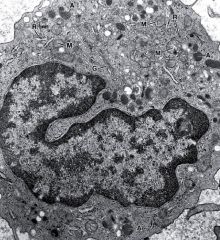
Lymphocytes
|
|
|
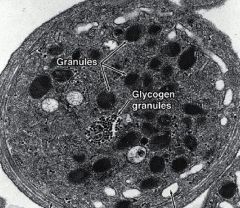
Monocytes
|
|
|
Platelets
|
|

|
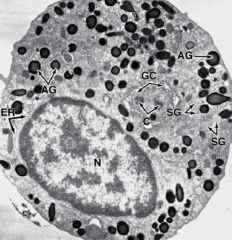
Platelets
Fibrin Platelets Erythrocytes |
|
|
Neutrophilic Myelocyte
|
|
|
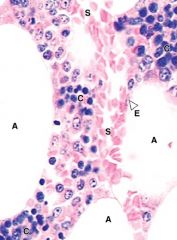
Hemopoiesis
Red Bone Marrow Sinusoid capillaries Adipocytes Cords of Hemopoietic Cells |
|
|
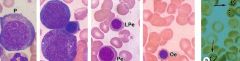
Erythropoiesis
Decrease in ribosomes, basophilia, nuclear volume Increase in chromatin condensation, hemoglobin |
|

|
Erythropoiesis - RBC
Granulopoiesis - Neutrophil, Eosinophil, and Basophil |
|
|
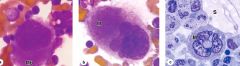
Megakaryoblast
Megakaryocyte Sinusoids |

