![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List 4 basic cell types
|
1. muscle
2. nerve 3. epithelium 4. connective tissue |
|
|
6 characteristics of Epithelium
|
1. avascular
2. lines the internal and covers the ext surface of the body 3. specialize in different function 4. polarized cells 5. can be one or more layers 6. cell close to each other w/ little intercellular space |
|
|
3 cell types of epithelia
|
1. squamous
2. cuboidal 3. columnar |
|
|
3 characteristics of simple squamous epithelium
|
1. single layer of flatten cell
2. line blood vessels, pleural, and peritoneal and other serous cavity 3. parietal layer of Bowman's capsule & thin loop Henle |
|
|
2 characteristics of simple cuboidal epithelium
|
1. single layer of polyhedral cells
2. lines distal tubules (kidney), follicles in thyroid, surface of ovary |
|
|
3 characteristics of simple columnar epithelium
|
1. polyhedral shape appearing columnar
2. single layer 3. lines stomach, intestine, and excretory ducts of many glands |
|
|
3 characteristics of stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium
|
1. several layers
2. outermost cell is flattened 3. line moist surfaces like mouth, vagina, and esophagus |
|
|
3 characteristics of stratified squamous keratinized epithelium
|
1. several layers
2. outermost layer have lost their nuclei filled with keratin 3. epidermis |
|
|
2 characteristics of stratified cuboidal epithelium
|
1. two or more layers
2. lines duct of sweat glands (uncommon) |
|
|
2 characteristics of stratified columnar epithelium
|
1. two or more layers
2. rare but can be found in large excretory ducts |
|
|
2 characteristics of pseudostratified epithelium
|
1. falsely stratified, every cell touch the basal lamina not all reach lumen
2. lines trachea, primary bronchi, excretory ducts in parotid gland |
|
|
3 characteristics of transitional epithelium
|
1. stratified epith whose superficial cells in relaxed state are dome shaped
2. stretch to a thin layer 3. lines the excretory passages in urinary system |
|
|
Lateral Surfaces
|
contains Junctional Complexes
corresponds to the “terminal bar” |
|
|
3 components of Junctional complexes
|
1. zonula occludens
2. zonula adherens 3. macula adherens |
|
|
Zonula Occludens (tight junction)
|
1. membrane fuse around entire apical perimeter
2. complexity of # strands determine "leakiness" 3. prevent entrance/exit to intercellular space |
|
|
Fasciae Occludentes
|
analogous (ribbon-like) structures present in capillaries but
do not extend around the entire cell. |
|
|
3 main components of connective tissues
|
cells
fibers ground substances |
|
|
general purposes of connective tissues
|
structural support for tissues and organs
mechanical support maintain form of body |
|
|
extracellular matrix is composed of these:
|
* protein fibers (collagen fibers, reticular fibers, elastic fibers)
* amorphous ground substance * tissue fluid |
|
|
If fluid is collected in connective tissue, what is this condition called?
|
Edema
|
|
|
How does connective tissue give structural support?
|
* capsules surrounding organs
* fill the spaces between organs * specialized orderly forms like tendons and elastic ligaments * skeletal tissues (cartilage and bone) |
|
|
How does the connective tissues serve a nutritive role?
|
Aid the diffusion of nutrient from blood to tissues and reverse with waste
adipose cell serve as fat (energy) storage and insulation |
|
|
What are Hematopoietic tissues? Where are they found?
|
specialized form of connective tissue
myeloid tissue (bone marrow) and the lymphoid (lymphatic) tissue |
|
|
Why are macrophages important?
|
they repair and defend against bacterial infection
|
|
|
What do fibroblasts do in response to injury?
|
proliferate and migrate to the injured site and deposit new collagen fibers, which forms fibrous scar tissues
|
|
|
List some functions of adipocytes
|
metabolic
energy storage thermal insulation |
|
|
What are Mesenchyme cells?
|
all CT derives from these cells
found in embryos in mesoderm layer only found in embryos |
|
|
What is the most common connective tissue?
|
fibroblast
|
|
|
Fibroblasts vs. fibrocytes
|
more active (lots of active Golgi bodies) vs. less active
|
|
|
What are some cells fibroblasts synthesize?
|
collagen, reticular and elastic fibers and the amorphous extracellular
substance (including the glycosaminoglycans and glycoproteins). |
|
|
What does MPS stand for? What it for?
|
Mononuclear Phagocyte System
common system to categorize macrophages |
|
|
Main function of macrophages
|
* ingestion by phagocytosis of microorganisms
* also participate in the breakdown of aged cells including erythrocytes |
|
|
List 4 general functions of connective tissues:
|
1. Structural support
2. Metabolic functions 3. Blood component 4. Defensive functions |
|
|
Function of mast cells
|
contains histamine and heparin, which are released in inflammatory response
|
|
|
List 5 connective tissues cells:
|
1. Fibroblasts
2. Macrophages 3. Plasma cells 4. Mast cells 5. Leukocytes |
|
|
What are the 3 main connective tissue fibers?
|
1. collagen fibers (most abundant protein in the body)
2. elastic fibers 3. reticular fibers |
|
|
Type I collagen type:
Main sites and special features |
Main sites: Bones, tendons, organ
capsules, dentin Special features: Most abundant, Typical collagen fibers |
|
|
Type II collagen type:
Main sites and special features |
Main sites: Hyaline cartilage
Elastic cartilage Special features: Very thin fibrils |
|
|
Type III collagen type:
Main sites and special features |
Main sites: Reticular fibers
Special features: Often associated with Type I |
|
|
Type IV collagen type:
Main sites and special features |
Main sites: Basal lamina associated with epithelial and endothelial cells
Special features: Amorphous (non-fibrous) |
|
|
Type V collagen type:
Main sites and special features |
Main sites: Basal lamina associated with muscle
Special features: Amorphous (non-fibrous) |
|
|
What are the 3 main amino acids of collagen?
|
(a) glycine (33.5%)
(b) proline (12%) (c) hydroxyproline (10%) |
|
|
What are Tropocollagen molecules
|
(280 nm long, 1.5 nm wide) form the basic unit, which polymerize to form collagen fibrils
|
|
|
argyrophilia
|
affinity for silver
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reticular fibers contain lots of glycoproteins which can be stain with this method:
|
PAS reaction
|
|
|
Where are reticular fibers found?
|
lymphatic organs (lymph nodes, spleen), smooth muscle (in the sheath
surrounding each myocyte), in endoneurium (connective tissue surrounding peripheral nerve fibers), and supporting epithelial cells of several glands (liver, endocrine glands) |
|
|
Elastic fibers are made from this type of protein:
What two unique AA are in this protein? |
formed from the protein elastin
similar to collagen, is rich in glycine and proline, but in addition has two unusual amino acids, desmosine and isodesmosine. |
|
|
In high concentration, what color are elastic fibers?
|
Yellow
|
|
|
Amorphous Ground Substance
|
transparent material composed mainly of glycoproteins and proteoglycans, with a fairly high water content
|
|
|
What makes up amorphous grand substance?
|
The main proteoglycans consist of a core protein associated with sulfated glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
|
|
|
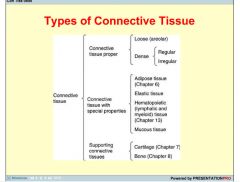
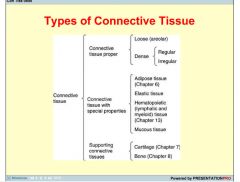
What are the two main categories of CT?
|
Loose Connective Tissue
Dense Connective Tissue |
|
|
List some characteristics of Loose Connective Tissue
|
(areolar tissue) is the more common type.
Flexible, rich in blood supply, not resistant to stress fewer cells more fiber |
|
|
What are the 2 sub-categories of dense connective tissue?
|
dense irregular connective tissue
dense regular connective tissue |
|
|
Dense regular connective tissue
|
specific orientation of collagen fibers
tendons / ligaments |
|
|
Dense irregular connective tissue
|
bundles of collagen fibers that appear to be fairly randomly orientated (as in the dermis)
|
|
|
connective tissue condition:
Ehlers Danlos syndrome |
abnormal collagen
hyper ext. of skin hyper ext of joints |
|
|
connective tissue condition:
Scurvy |
decrease collagen due to the lack of Vitamin C
|
|
|
connective tissue condition:
Marfan's Syndrome |
decreased elastic fiber
|
|
|
Anaphylactic Shock
|
increase mast cell release of histamine
|
|
|
Fibrosis
|
increase collagen due to burns or surgery
|
|
|
Mucous tissue
found where? What is it composed of? |
found in the umbilical cord (Wharton's jelly)
loose connective tissue composed of fibroblasts |
|
|
Ligaments
What type of CT? |
special type of dense regular connective tissue
abundance of elastic fibers in the tissue (not yellow) |
|
|
List some characteristics of tendons:
|
most common type of dense regular connective tissue
dominance of the collagen fibers, the tendons have a white color primary bundle has orderly-arranged rows of fibrocytes |

