![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Blood Plasma
|
-55% of blood
-92% water -7% are plasma proteins that are created by liver Albumin - maintain blood osmotic pressure Globulins - antibodies fibronegin - clotthing -1% other |
|
|
What are the formed elements of blood?
|
Erythrocytes (RBC) - 99%
Leukocytes Thrombocytes |
|
|
Hematocrit
|
% of blood occupied by erythrocytes
Female - 38-46% Male - 40 -50% |
|
|
Anemia and Polycythemia
|
Not enough RBCs or not enough hemoglobin
too many RBC (over 65%), dehydraiton, tissue hypoxia, blood doping |
|
|
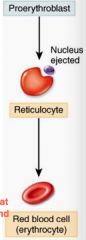
Erythrocytes
|
7.8 um
Prortyhroblasts give rise to immature reticulocytes Once in circulated become erythrocytes -Biconcave disk -, flexible, no cell division or mitochondria -120 days |
|
|
Sickle Cell
|
Point mutation where glutamic acid is replaced by Valine
Leads to deformed shape, decreasing capacity for O2 |
|
|
Leukocytes
|
WBC and are nucleated
Contain MHC Granular (specific granules) - eosionphils, basophils and neutrophils NO BIG IE Agranular Leukocyte - lymphocytes, and monocytes - not specific granules |
|
|
Rolling-Adhesion and migration
|
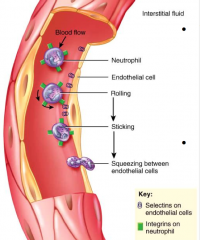
Chemotaxis (kinins) attracts WBC to disease or injury
1) WBC roll along endothelium and selections (on endothelial cells) help WBC stick 2) Integrins found on neutrophil wall assist movement through wall |
|
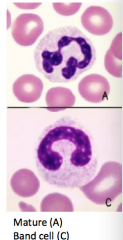
Neutrophil
|
Granulocyte
10-12 um 2-5 lobes - bacteria -have lysozymes (release hypchlorous acid) -young cells are called band cells - indicates not yet developed -60-70% of leukocytes -3-5 say life span -Have fc receptors, compliment and TL receptors |
|
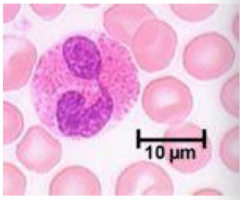
|
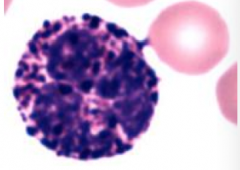
Granulocyte 10-12um
2-4% leukocytes Nucleus Bilobed -Fight Parasites -Contain MBP (major basic protein), ECP, EPO, EDN |
|
|
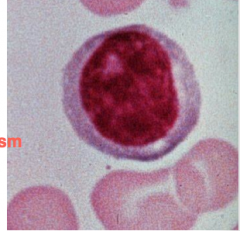
Granulocytes
less than 1% 8-10um -inflammatory and allergy Bilobed nuclei - large dark purple -Specific azurophilic granules Hepair - anticoagulant Histamine - vasoactive - vasodilation LK - constriction of smooth muscle -high sulfate give rise to granules |
|
|
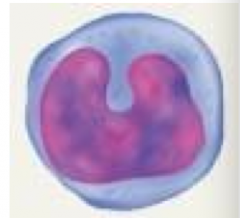
Angranylocyte 6-30 um
-Dark oval, nucleus occupies most of cytoplasm 20-25% of leukocytes T-cells -cell mediated amenity - attack viruses and fungi B cells -turn in plasma - produce antibodies NK cells |
|
|
Agranulocyte
3-8% 16-20um Nucleus is indented -Contain azurophilic granules (not specific) - like baso -leave capillaries and enter tissue Phagocytose bateria and other cells (viral) |
|

|
Stimulated by thrombopoetin.
2-4um 5-9 days Have alpha and dense granules Alpha: clotthing factors Dense: ADP, ATP, Ca2+ = produce thromboxane Hemostatis- blood clotting |
|
|
CLotthing cascade
|
Prothrombinase is formed from either intrinisc or extrinsic - final common pathway produces fibrinogen
During clot, fibrin threads cause clot retration from factor 8 released by platlets |
|
|
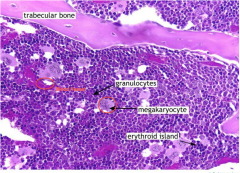
Hematopoiesis phase
|
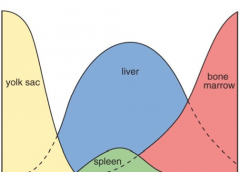
Yolk phase - 3rd week of gestation
Hepatic - major blood forming 2nd trimester Bone Marrow phase - begin during second After birth, takes palce only in bone marrow |
|
|
Myeloid lineage
|
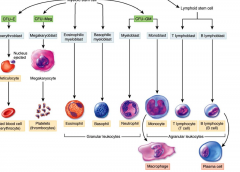
Common myeloid progenitor cells (CMP)
RBS Platelets Granulocytes (N, B, E) And Neutrophils |
|
|
Lymphoid Lineage
|
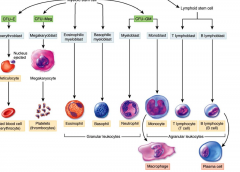
Common lympoid progenitor cells (CLP_
Give rise to Lymphocytes (b and t cells) |
|
|
Stem Cell Niche
|
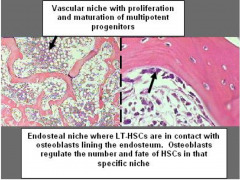
Found in epiphyseal areas (spongy or cancellous bone)
Niche contains Stroma, maintains self-renewal and inhibition of differentiation. Cytokines - signals HSC migrate to vascular niche in center of bone and establish hematopoeisis. |
|
|
Red Marrow and Yellow Marrow
|
Red marrow is site of active hematopoesis and yellow marrow is fat capillaries, reticular cells.
|
|
|
EPO (erythropoetin)
|
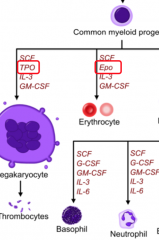
Produced by kidneys and increases erythrocyte precursors.
|
|
|
TPO ) thrombopoetin
|
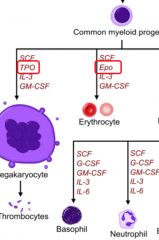
Hormone from liver, stimulates thrombocyte formation
|
|
|
Cytokines and colony stimulating factor (CSF)
|
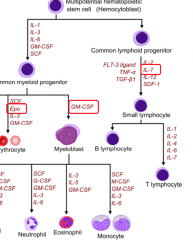
Produced by stem cell niche stroma to induce differentiation
|
|
|
Erythropoeiesis
|
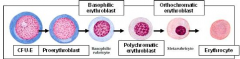
Stimulated by HYPOXIA
EPO produced by kidney Proerythroblast (no heme) turns to erythroblast (some heme) turns into reticulocyte (more heme, nucleus ejected) ---> erthrocytes -recycled by liver or spleen (split to iron Fe3+) |
|
|
Fate of Heme
|
Iron Fe3+
-transported to blood and attach to transferrin protein, stored in liver Biliveredin (green) -converted to bilirubin and secreted by liver into bile |
|
|
Granulocytopoeisis
|
1) Takes 11 days, controlled by cytokines
Myleoblasts precurosor --> myelocyte - specific granules develop |
|
|
Monocytopoesis
|
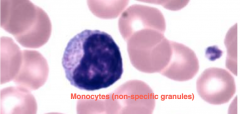
Starts with monoblasts and ends with monocytes
When in tissue, is called macrophages. |
|
|
Thrombopoesis
|
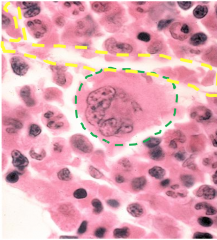
TPO induced from liver
Starts with megaryoblasts then to megakaryocytic (40-100um) in bone marrow. Platelets pinch off from. |
|
|
|

