![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the FBE clues of of hereditary spherocytosis?
|
Spherocytes
Polychromasia N or + MCHC (spherocytes) + MCV (reticulocytosis) |
|
|
What tests should be ordered for hereditary spherocytosis?
|
DAT
Unconjugated bilirubin Flow cytometry Osmotic fragility test Family history Molecular studies Acidified glycerol lysis time Cryohaemolysis Spectrin radioimmunoassay |
|
|
What results should we see for hereditary spherocytosis?
|

|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of hereditary spherocytosis>
|

|
|
|
identify cells
|
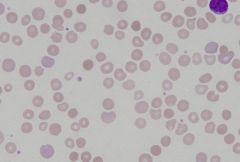
polychromasia
spherocytes |
|
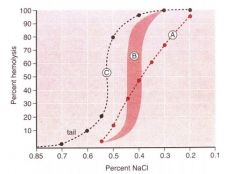
Interpret C - identify test and result
|
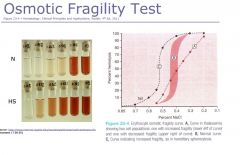
Osmotic Fragility Test
A. thalassemia B. normal C. spherocytes present or fragility --> proceed to Flow Cytometry and Sprectrin immunoassay |
|
|
What do we see in hyposplenism
|
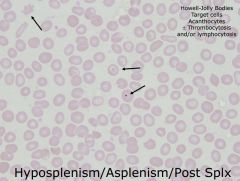
HAT
TL |
|
|
What are Howell Jolly bodies? when are they seen?
|
-RBC intracellular inclusion
- Post splenectomy/hyposplensim, asplenism - reticuloendothelial overlaod |
|
|
Presentation of Hereditaory elliptocytosis
|
areas where malaria is epidemic
elliptocytes 30-100% transient HA in infectionm pregnancy and vitamin deficiences mild haemolysis |
|
|
causes of HE?
|
MUTATIONS
alpha spectrin 80% beta spectrin 5% Band 4.1 15% INTERACTION Spectrin + 4.1 Spectrin + glycophorin |
|
Identify and order appropriate tests
|
HE
osmotic fragility molecular tests |
|
|
Describe HP
|
autosomal recessive
spectrin mutation heat 45-46 causes HP RBC to fragment instead of 49C clinically:: - severe HA - bizarre morph - poikilocytosis, budding RBC, elliptocytes and fragments - gall stones - facial bone abnormalities |
|
ID and order tests
|
HP
- retic count - low MCV - anisocytosis - microspherocytosis |
|
|
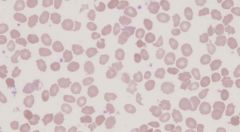
Describe South East Asian Ovalocytosis
|
Autosomal dominant
SLC4A1 deletion abnormal binding of band 3 to ankyrin RBC have increased stability and rigidity so will not burst in osmotic fragility testing confers resistance to P. falciparum |
|
|
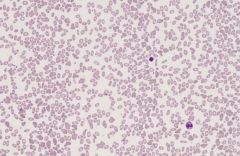
Describe SEAO film morphology
|
|
|
|
What is seen in a G6PD film
|
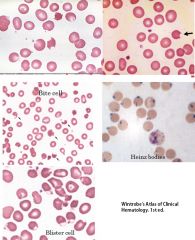
Polychromasia
+/- basophilic stippling +/- Heinz bodies (!! can’t see with Romanowsky stain) |
|
|
What tests can we order to confirm crisis in G6PD
|

Heinz body preparation (methyl violet)
inc. plasma haemoglobin inc. unconjugated bilirubin dec. haptoglobin G6PD spot test G6PD enzyme detection PCR mutation and variants |
|
|
Testing for PK Deficiency
|
direct assaying enzymes levels
|
|
|
Treatment for PK Deficiency
|
transfusion
removing spleen |
|
|
PK FBE results
|
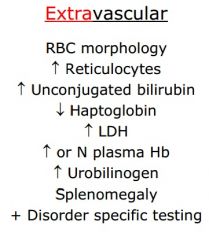
|
|
|
PK blood films
|
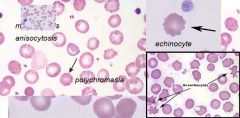
- NO SPHEROCYTOSIS
- Anisocytosis - Macrocytosis - Polychromasia - Echinocytes and acanthocytes |
|
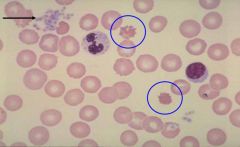
ID disorder and order tests, cause and treatment
|
PK deficiency
unconjugated bilirubin and LDH (increased) haptoglobins (decreased) (if intravascular haemolysis occurs) Enzyme activity assay (PKR, PKM2) PCR for mutation analysis autosomal recessive and rare disorder effects Embden-Meyerhof pathway, Shift to right of oxygen dissociation curve treatment :: Removing the spleen can help in this disorder however transfusion therapy is usually used |
|
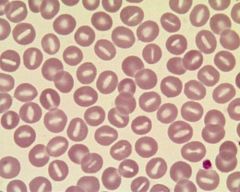
Describe the above
|
macrocytic anaemia
mean cell volume (MCV) is characteristically elevated correspondingly low mean corpuscular haemoglobin concentration (MCHC) Splenectomy has proven to be the most beneficial treatment in reducing the degree of haemolysis. |
|
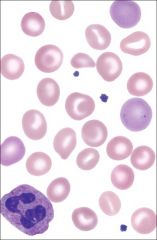
Describe the above
|
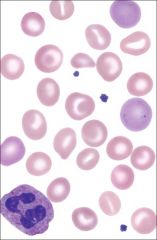
Hereditary xerocytosis
- eccentrocytes (cells with eccentric hemoglobin puddling), stomatocytes, and reticulocytes |
|
|
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Haemoglobinuria (PNH)
|
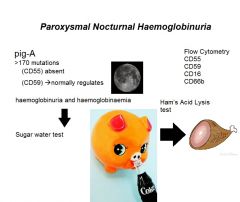
Sugar water test
Isotonic sucrose solution + fresh complement >5% lysis suggestive of PNH Ham’s Acid Lysis test |
|
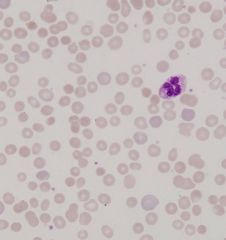
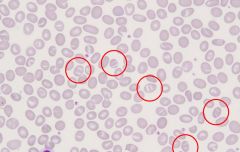
what cell is found here? what could it mean?
|
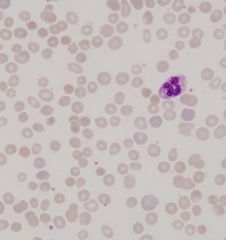
spherocytes
- H. spherocytosis - H. spherocytosis - hemolytic an. |
|
what cell is found here? what could it mean?
|
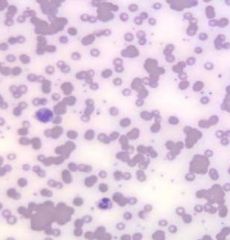
Spherocytes
Polychromasia Howell Jolly Bodies agglutination on film --> cold auto immune mediated HA |
|
|
What do we see in burn films?
|
microspherocytes
|
|
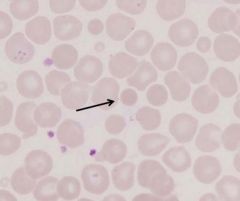
ID
|
microspherocyte
- burns - AIHA |
|
|
causes of Alloimmune/Isoimmune HA
|
Blood transfusion reactions
Haemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN) Post BM or organ trnsplant |
|
|
What are the two types of drug induced HA?
|
immune mediated or metabolic
|
|
|
What are three examples of immune mediated dug induced HA?
|
Penicillin
complement fixing antibody Ab to hapten (quinidine) aAb to Rh (alpha methyldopa) AgAb complex Stibophen |
|
|
What are three examples of metabolic (oxidative) dug induced HA?
|

|
|
|
DIHA diagnostic tests
|
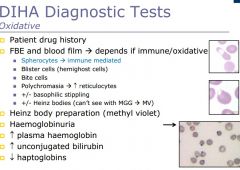
|
|
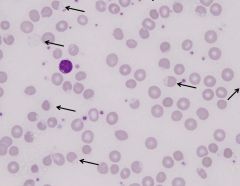
ID cells
|

|
|
|
metabolic oxidative diagnostic tests
|

|
|
|
morphology of Paroxysmal Cold Haemoglobinuria (PCH)
|
chronic -->no specific morphology
acute --> spherocytes +_ agglutination (Leucopenia may be present) |
|
|
Test for Paroxysmal Cold Haemoglobinuria (PCH)
|
Donath-Landsteiner test
|
|
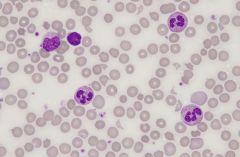
Identify problem on slide
|
fragmentation
|
|
|
What are the Microangiopathic Haemolytic
Anaemia (MAHA) RBC Fragmentation Disorders |
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome (HUS) Heart valve replacement |
|
|
What is seen on Microangiopathic Haemolytic
Anaemia (MAHA) - tests ordered? |
RBC fragments, spherocytes, RBC damage and polychromasia, WBC changes,
LFT, UEC, coagulation assays (PT, APTT, FIB, D-Dimer and TCT), blood cultures, culture and sensitivity + others |
|
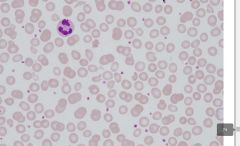
find problem
|
fragmentation due to heart valve
|
|
|
DIC tests?
|

|
|
|
DIC morphology
|
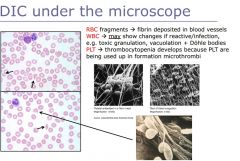
|
|
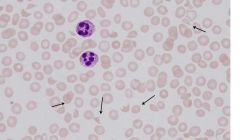
ID problems
|
fragments - different sizes
schistocytes toxic granulation thrombocytopenia |
|
|
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)
|
inhibition of enzyme ADAMTS13
vWF release which adheres platelets platelet plugs --? multiorgan system failure Normal PT, APTT, FIB and - - -PLT Fever, change in mental state, renal insufficiency and MAHA |
|
|
Haemolytic uraemic syndrome (HUS)
|
children
bacterial infection - shigella, E. coli renal insufficiency marked thrombocytopenia Abnormal UEC |
|
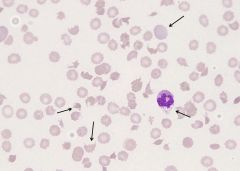
what could this be indicative of?
|
fragmented erythrocytes of different sizes with pointed extremeties (schistocytes)
Reticulocytes vaccuolation TESTS Creatinine BUN, LDH, Haptoglobin RBC transfusions, dialysis no Antibiotics |

