![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Big Bang
|
- All mass and energy in a “Single Point” and explosion/expansion ~13.7 Ga
- Atoms and molecules coalesce in gaseous nebulae |
|
|
Expanding Universe
How do we know? |
- Light from galaxies was seen to be “red shifted"
- Hubble recognized the red shift as a Doppler Effect RED LIGHT (low frequency) away BLUE LIGHT (high frequency) towards |
|
|
Hypothesis
|
a reasonable idea that has the possibility of being correct, but has not been proven
|
|
|
Theory
|
scientific idea supported by an abundance of evidence that has passed many tests and failed none
|
|
|
Big Theories of Geology (2)
|
Plate Tectonics – theory that the outer layers of the Earth consists of separate plates that move w/ respect to one another
Geologic Time – span of time since the formation of the Earth |
|
|
Alfred Wegener
|
Continental Drift Hypothesis - Idea that continents are mobile; once a supercontinent Pangaea (Pangea)
|
|
|
Evidences for Continental Drift (5)
PGFR |
1. “Fit” of continents
2. Location of glaciers (GLACIATION) 3. Location/distribution of fossils 4. Rock types and structural similarities 5. Paleoclimates preserved in rocks |
|
|
(2) Glaciation
|
- Striations on rock cut by glacial movement indicate
direction of movement - Glacial tills present |
|
|
(3) Fossil Distribution
|
Identical fossils
Glossopteris- A subpolar plant with heavy seeds Plant evidenced in southern hemisphere of Pangea (Gondwanaland) |
|
|
(4) Rock types and structural similarities
|
Matching of Rock Types
- Geologic structures. - Rock types. - Rock ages - Mountain belts: The Appalachians & The Caledonides |
|
|
(5) Paleoclimates preserved in rocks
|
Minerals and rocks form in certain climates.
Reconstruction puts mineral in the right place for formation. EX: Russia has coal deposits |
|
|
Criticisms of Continental Drift
|
Why wasn’t the continental drift hypothesis accepted?
– There were no mechanisms for moving continents. – When Wegener died, the debate did too |
|
|
Continental Drift new evidence
|
This was provided by:
- Paleomagnetism - Age of the ocean floor - Volcano distribution - Earthquake distribution - Hot spots |
|
|
Sea-Floor Spreading
|
Process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge
Max ocean Age= 108 mya |
|
|
What are the dominant elements?
(1) Crust (2) Whole Earth |
(1) Crust: Oxygen – 46% Silicon – 28%
(2) Whole Earth: Iron - 35% Oxygen – 30% Early settling of core |
|
|
Compositional Differences
|
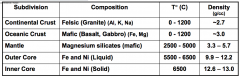
|
|
|
Heat of the Earth (3)
|
1. Particle collision
2. Gravity settling, 3. Radioactive decay* |
|
|
P-Wave Travel
|
P waves travel through all materials
|
|
|
S-Wave Travel
|
S waves can’t pass through liquids
|
|
|
Earth is dynamic, Mars is static. What other differences?
|
(1) core has been lost
(2) Remnants of magnetic field Mars biggest volcano is Olympus |
|
|
Layers:
(1) Crust (2) Lithosphere (3) Mantle (4) Outer Core (5) Inner Core |
(1) Crust: Continental and Oceanic
(2) Lithosphere: Includes crust and upper mantle (3) Mantle – solid to plastic (4) Outer Core - liquid (5) Inner Core - solid |
|
|
Earthquakes
|
Found to be concentrated at the areas of
- spreading (shallow) - convergent (deeper) - transform “plate” boundaries -some occur within plates (intraplate) |
|
|
Hot spots
|
- Not related to plate margins
- Source of magma is believed to be deep within the mantle at fixed locations |
|
|
Plate Tectonics
Mechanisms for driving plates |
Slab Pull
|

