![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the length base unit for SI? |
Meter |
|
|
Energy exists in which two states? |
Kinetic & potential |
|
|
What type of energy transfers between two bodies of differing temperatures such as the sun and the earth? |
Heat |
|
|
What factors determine how much power is needed to complete a task? |
Amount of energy & period of time |
|
|
What is the mechanical equivalent of heat? |
1 calorie equals 4.187 J |
|
|
How does temperature affect the rate of heat transfer? The ______ the _____ in temperature between 2 the bodies, the greater the transfer rate |
Greater; difference |
|
|
What mechanisms transfer heat from one body to another? |
Conduction, convection, and radiation |
|
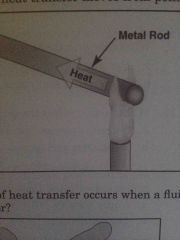
What type of heat transfer moves from point to point? |
Conduction |
|
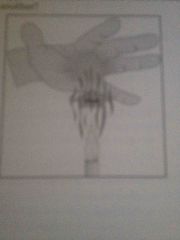
What type of heat transfer occurs when a fluid or gas flows from one place to another? |
Convection |
|
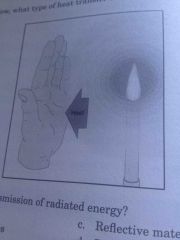
What type of heat transfer occurs without an intervening medium? |
Radiation |
|
|
What disrupts the transmission of radiated energy? |
Reflective material |
|
|
What factors effect the physical state of matter? |
Temperature and pressure |
|
|
The ratio of the mass of a given volume of liquid compared with the mass of an equal volume of water? |
Specific gravity |
|
|
What basic principle does the law of conservation of mass teach? |
Mass and energy are neither created nor destroyed |
|
|
What process transforms matter from one state to another or produces a new substance? |
Chemical reaction |
|
|
What reaction gives off energy as it occurs?
A. Endothermic B. Rusting C. Refraction D. Confection |
B. Rusting |
|
|
What reaction is produced when iron and oxygen combine? |
Oxidation |
|
|
Explosions are a result of what kind of reaction? A. A slow reaction of a fuel and an oxidizer B. A slow reaction of a fuel and heat C. A rapid reaction of a fuel and an oxidizer D. A rapid reaction of a fuel and heatwhat com |
C. A rapid reaction of a fuel and an oxidizer |
|
|
What components must come together for combustion to occur? |
Oxidizing agent, fuel, heat, and a self-sustained chemical reaction |
|
|
What affect does an oxygen-enriched atmosphere have on fire? A. Some petroleum-based materials autoignite B. Most materials exhibit the same burning characteristics. C. Many materials that burn at normal oxygen levels do not burn at elevated levels D. All of the above |
A. Some petroleum-based materials autoignite |
|
|
What two factors influence the combustion process? |
Physical state and distribution of the fuel |
|
|
Which of the following wood products has the highest surface-to-mass ratio? A. Logs B. Sawdust C. Boards D. Tree stumps hat happens |
B. Saw dust |
|
|
What happens to fuel as its surface area increases? A. Less material becomes exposed to the heat B. Materials generate less burnable gases due to pyrolysis C. Fuel particles become smaller, and ignitability increases D. Less fuel becomes available, and ignitability decreases |
C. Fuel particles become smaller, and ignitability increases |
|
|
How does positioning affect the way a solid fuel burns? |
Fire spreads more rapidly in vertically positioned solid fuels. |
|
|
What events must occur for spontaneous combustion to happen? A. The rate of heat production must raise the temperature to within 10 degrees of its ignition temperature B. The air supply to the material being heated must be undetectable C. The materials surrounding the fuel must prevent the heat from dissipating D. The ignitable vapors must come into contact with an ignition source |
C. The materials surrounding the fuel must prevent the heat from dissipating |
|
|
What fuel type exists in the natural state requires for ignition? A. Solid B. Liquid C. Gas D. Compressedgaseo |
C. Gas |
|
|
Gaseous fuels must mix with the proper ratio of oxidizer for combustion to occur. What is the ratio? A. Below LFL B. Above UFL C. Between LFL and UFL D. Below LFL or above LFL |
C. Between LFL an UFL |
|
|
In general, how does an increase in temperature affect the flammable range of a material? |
Broadens it |
|
|
What is the total amount (mass) of fuel in a compartment multiplied by the heat of the combustion of the materials? |
Fuel load |
|
|
Which of the following items would not be considered a fuel package? A. Mattress an box spring B. Foam padded upholstery chair C. Computer and office furniture D. Stack of bricks |
D. Stack of bricks |
|
|
How is combustion influenced when heat comes into contact with a fuel? |
Provides energy for ignition |
|
|
Which of the following materials is most likely to spontaneously heat? A. Linseed oil rags B. Fertilizer C. Hay D. Iron metal powders hat |
A. Linseed oil rags |
|
|
What type of heat energy is generated by friction and compression? |
Mechanical |
|
|
What characterizes slow oxidation reactions? A. They do not produce heat fast enough to reach ignition B. They never generate sufficient heat to become self-sustained C. They are exothermic reactions D. All of the above |
D. All of the above |
|
|
What factors control the growth and development of a compartment fire? A. Size and duration B. Duration and fuel C. Fuel and ventilation D. Ventilation and size |
C. Fuel and ventilation |
|
|
Which fuel packages entrain the least air and have the highest plume temperatures? A. Fuel packages in corners B. Fuel packages against walls C. Fuel packages in the middle of a room D. Fuel packages near windows |
A. Fuel packages in corners |
|
|
Which of the following scenarios best describes flashovers? A. The transition between the growth and full development of a fire B. A fully developed fire C. The ignition of a fuel package by radiant heat D. The decay stage of a compartment fire |
A. The transition between growth an full development of a fire |
|
|
What is the HRR?which of |
The amount of heat being released over time |
|
|
HRR |
Heat release rate |
|
|
LFL |
Lower flammable limit |
|
|
UFL |
Upper flammable limit |
|
|
CO |
Carbon monoxide |
|
|
HCN |
Hydrogen cyanide |
|
|
CO2 |
Carbon dioxide |
|
|
MSDS |
Material substance data sheet |
|
|
NAERG |
North American emergency response guide |
|
|
Which of the followings the highest HRR? A. Wastebasket full of milk cartons B. Cotton mattresses C. Wooden pallet D. Metal chairs with cotton padding |
C. Wooden pallets |
|
|
How man heat generated in a compartment fire transmit from the initial fuel package to other fuels? A. Refraction B. Reflection C. Confection D. Radiation |
D. Radiation |
|
|
How should firefighters deal with thermal layering? A. Apply water to the upper level of the layer B. Avoid disrupting the thermal balance C. Ventilate the structure horizontally D. Avoid working in the lower level of the layer |
B. Avoid disrupting the thermal layer |
|
|
What condition signals a possible backdraft? A. Billowing black smoke exiting large openings B. Large flames C. Smoke-stained windows D. Smoke leaving the building in a continuous motion |
C. Smoke-stained windows |
|
|
What common narcotic gases are found in smoke? A. CO, HCL, and N2O B. N2O, HCL, and CO2 C. CO2, CLN, and HCN D. HCN, CO, and CO2 |
D. HCN, CO, and CO2 |
|
|
What does flooding an area with inert gas do to a fire? A. Reduces the temperature B. Eliminates the available fuel C. Disrupts the combustion process D. Creates a fire-resistant barrier |
C. Disrupts the combustion process |
|
|
How does water combat fire? |
Reduces the temperature |
|
|
SI |
International system of units |
|
|
NIST |
National institute of standards and technology |
|
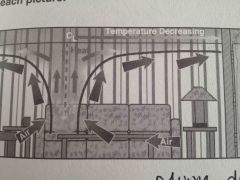
Which fire stage? |
Plume development |
|

Which fire stage? |
Flashover |
|

Which fire stage? |
Rollover |
|

Which method of fire extinguishment? |
Exclusion of oxygen |
|
|
Which fire stage? |
Backdraft |
|
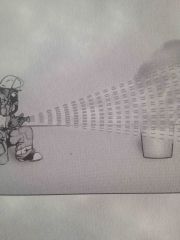
Which method of fire extinguishment? |
Reduction of temperature |
|
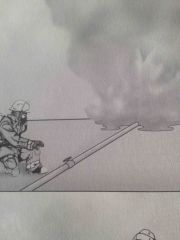
Which method of fire extinguishment? |
Removal of fuel |
|

Which method of fire extinguishment? |
Inhibition of chain reaction |
|

Which fuel class? |
Class D |
|
|
Congrats your done with chp2 |
Yay |
|
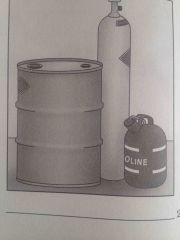
Which fuel class? |
Class B |
|
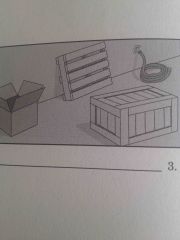
Which fuel class? |
Class A |
|
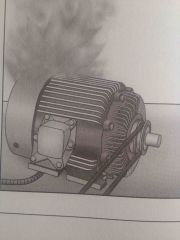
Which fuel class? |
Class C |

