![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
145 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Revenue recognition (ISTAR) |
Step 1: identify the contract with the customer Step 2: identify the separate performance obligations in the contract Step 3: determine the transaction price Step 4: allocate the transaction price to the separate performance obligations Step 5: recognize revenue when or as the entity satisfies each performance obligation |
|
|
Criteria for revenue recognition |
* all parties have approved the contract and have committed to perform their obligations *The rights of each party regarding contracted goods or services are identified *Payment terms can be identified *the contract has commercial substance meaning future cash flows are expected to change as a result of the contract *it is probable that the entity will collect substantially all of the consideration due under the contract |
|
|
Rule of conservatism |
Revenue when a job is done (earned) |
|
|
Cash basis to accrual revenue |
Cash basis revenue +Ending AR - beginning AR - ending unearned revenue + Beginning unearned revenue = Accrual basis revenue |
|
|
Cash paid for purchases to COGS |
+ Ending AP - Beginning AP - Ending inventory + Begining inventory = Cost of good sold |
|
|
Cash to accrual operating expenses |
Cash paid for operating expenses + Ending accrued liabilities - Beginning accrued liabilities - Ending prepaid expenses + Beginning prepaid expenses = Accruals basis operating expenses |
|
|
DuPont return on assets |
Profit margin x asset turnover |
|
|
Cash to accrual interest expense |
Cash basis interest expense + Decrease or - increase in prepaid int - decrease or + increase in int payable = Accrual basis interest expense |
|
|
Cash to accrual Revenue |
Add increases in current assets Subtract decreases in current assets Add decreases in current liabilities Subtract increases in current liabilities |
|
|
Total asset turnover |
Net sales/average total assets |
|
|
Without recourse |
Risk of loss with buyer |
|
|
Ending Uncollectible AR Expense |
Beginning balance + Uncollectible accounts provision - write offs + recovered previously written off balance + Begging AR - End balance |
|
|
Precious metals and farm product inventory |
Gold, silver, other precious metals, meat, and some agriculture are valued at net realizable value (net selling price - cost of disposal) |
|
|
Normal inventory valuation rules do not apply when |
- The subsequent sales price of an end product is not affected by it's market value; or - The company has a firm sales price contract |
|
|
Market ceiling |
Net realizable value (net selling price - cost to complete and dispose) |
|
|
Market floor |
Market ceiling (nrv) - normal profit margin |
|
|
Period inventory COGS |
Beginning inventory +Purchases - ending inventory *Based on physical count |
|
|
FIFO in periods of rising prices |
Results in the highest ending inventory, lowest COGS, and highest NI (current costs are not matched with current revenues) |
|
|
Moving average inventory valuation method |
Computes the weighed average cost after each purchase by dividing total cost of inventory available after each purchase (inventory + current purchase) by total units available after each purchase |
|
|
LIFO in rising price environment |
Results in the lowest ending inventory, highest COGS, and lowest NI. |
|
|
Dollar value LIFO |
CY ending inventory cost ÷ base yr inventory cost = annual cost index * annual increments (layers) (change from PY ending inventory cost and CY ending inventory cost) Plus - PY ending inventory cost ÷ base year inventory cost= annual cost index * annual increments |
|
|
Price index |
Current year cost (CY + Layer) ÷ Base year cost (Base cost + layer) |
|
|
LIFO layer |
Price index *base year layer |
|
|
Cash to accrual AR |
Beginning AR - cash collections + Unearned revenue - ending AR |
|
|
Allowance for Uncollectible accounts on the BS |
Beginning Uncollectible accounts - write offs + Provision for Uncollectible accounts = Allowance on the BS |
|
|
COGS - LIFO |
Most closely approximates the costs for COGS because inventory last in (most recently purchased) is first out (expensed currently) |
|
|
Ending inventory - FIFO |
Most closely approximates current cost for inventory because inventory first in (oldest purchases) is first out (expensed currently) and the most recent purchases are left in ending inventory. |
|
|
Capitalized interest |
Lesser of interest cost incurred or avoidable interest |
|
|
Avoidable interest |
Weighted average accumulated expenditures times interest on specific borrowing |
|
|
Composite life |
Total depreciable costs÷annual depreciation |
|
|
Impairment amount under GAAP |
The amount by which the carrying amount of an asset exceeds the fair vaule |
|
|
GAAP impairment test |
If the sum of the undiscounted expected future cash flows is less than the carrying amount of the asset then an impairment is recognized |
|
|
Classification of debt secutities |
1. Trading securities 2. Available for sale debt securities 3. Held to maturity debt securities |
|
|
Dividend income |
Number of shares x dividend per share |
|
|
Noncontrolling interest calculation |
Step 1: purchase price ÷ ownership % = FV of company aquired Step 2: FV of company aquired x noncontrolling interest % = beginning noncontrolling interest Step 3: Beginning noncontrolling interest + % noncontrolling interest income - % noncontrolling interest dividend = noncontrolling interest |
|
|
IFRS noncontrolling interest |
FV of subsidiaries net assets x NCI % |
|
|
IFRS partial Goodwill method |
Acquisition cost- (fair value of subsidiaries assets acquired x acquisition %) |
|
|
Unrealized profit intercompany elimination |
Intercompany profit on sale x (inventory on hand at year end÷total inventory purchased) |
|
|
IFRS recoverable amount |
Greater of 1. Assets fair value - cost to sell 2. Assets value in use |
|
|
IFRS Goodwill impairment loss |
Recoverable amount - carrying value |
|
|
Accretion expense |
Begging carrying value of asset x credit adjusted risk free interest rate |
|
|
Present value |
Future amount x present value factor |
|
|
Lesee Finance Lease Determination (OWNES) |
- Ownership of the underlying asset transfers from the lessor to the lessee by the end of the lease term. - Written option to purchase the underlying asset; the option is one that the lessee is "reasonably certain" to exercise. - Net present value (90%) of all lease payments and any guaranteed residual value is equal to or substantially exceeds the assets underlying fair value. - The term of the lease represents the major part of the Economic life (75%) remaining for the underlying asset. - The asset is Specialized such that it will not have an expected, alternative use to the lessor when the lease term ends. |
|
|
Amount of financing liability |
Sales price - fair value |
|
|
Gains in nonmonetary transactions |
Gains are recognized based on the difference between the fair value and carrying amount of the asset |
|
|
Debt securities include |
* Corporate bonds * Redeemable preferred stock (has a maturity date) * Government securities * Convertible debt * Commercial paper (notes/drafts) |
|
|
EJE for acquisition consolidation |
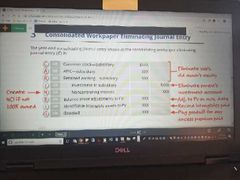
|
|
|
GAAP impairment |
Goodwill implied fair value - Goodwill book value |
|
|
Sales revenue |
Credit to sales revenue ÷ sales tax rate plus one |
|
|
Accretion expense |
Increase in the ARO liability due to passage of time |
|
|
ARO calculation |
Beginning ARO x credit risk adjusted interest rate |
|
|
Periodic interest rate |
GAAP interest expense÷carrying value at beginning of period |
|
|
Stated interest rate |
Interest/face value of bond |
|
|
Debenture bonds |
Unsecured bonds |
|
|
Interest payable on a bond |
Face value of the bond at the begining of the period * contractual interest rate |
|
|
Interest expense on a bond |
Carrying value of the bond at the beginning of the period * effective interest rate |
|
|
Carrying value of bonds at the balance sheet date |
Purchase price (including interest) - accrued interest = Carrying value before amortization - amortization of bond premium or + amortization of bond discount = Carrying value at the BS date |
|
|
Gain/loss on extinguishment of debt |
Equal to the difference between the reaquisition price and net carrying amount |
|
|
Net carrying value of a bond |
Face value - unamortized discount - unamortized bond issuance cost = Net carrying value |
|
|
Pro rata unamortized bond issuance costs |
Retired bond face value/original bond issuance face value * bond issuance costs |
|
|
Amortization of leasehold improvements |
Amortize over the lesser of the life of the leasehold improvements or the remaining life of the lease |
|
|
FC Translation/remeasurement on the BS |
Monetary items (AR & long term debt) convert using the current year end exchange rate Non-monetary items (inventory, fixed assets, common stock) converted using historical exchange rates from the date of purchase or issue |
|
|
Net periodic pension cost calculation |
Service costs + Interest costs (beg. PBO obligation *discount rate) - expected return on plan assets (beg. FV* expected rate) + Amortization of prior service costs (prior year unrecognized prior service costs ÷ average remaining service life) +/- amortization of gains and losses - amortization of transition asset (prior year unrecognized transition asset÷average remaining service life) = Net period pension cost |
|
|
Expected return on plan assets |
Beginning FV of plan assets x expected rate of return |
|
|
Actual return on plan assets |
Beginning plan assets + Contributions - benefits paid - ending plan assets = Actual return on plan assets |
|
|
Projected benefit obligation |
Beginning balance + 10% interest costs + Current year service costs - pension benefits paid during the year = Projected benefit obligation |
|
|
U.S. GAAP amounts to be reported in AOCI |
+ Unrecognized prior service cost Unrecognized net (gains) or + losses + Unrecognized transition obligations or (assets) |
|
|
IFRS amounts to be reported in AOCI for pension plans |
Re-measurements of defined-benefit (asset) or liability, including re measurements from actuarial gains |
|
|
Book value per common share |
Common shareholders equity (total shareholders equity - preferred stockholders interest)÷common shares outstanding (issued-repo) |
|
|
Common stockholders equity formula |
Total shareholders equity (A-L) - preferred stock outstanding (@greater of call price or par value) - cumulative preferred dividends in arrears |
|
|
Components of AOCI (PUFER) |
Pension adjustments, unrealized gains and losses on available-for-sale securities, foreign currency translation adjustment, deferred gains and losses on the effective portion of cash flow Hedges, and re-evaluation surpluses (IFRS only) |
|
|
Cost of stock rights |
((FMV of rights ÷ (FMV of rights+FMV of stock ex rights))*cost of stock |
|
|
Basic EPS |
Income available to common stockholders (NI-PD)÷ weighted average number of common shares outstanding |
|
|
Weighted average number if shares outstanding |
Shares outstanding at beginning of the period + Shares sold during the period (on time weighed basis) -shares reacquired during the period (on time weighed basis) + Stock dividends and stick splits (retroactively adjusted) = Weighted average number of common shares outstanding |
|
|
Dilutive |
Only if the average price is greater than the strike (exercise) price "In the money" |
|
|
Diluted EPS |
Common stock + Convertible bonds = Total common shares outstanding Net income + Interest in bonds, less tax effects = Total net income Diluted EPS = total net income ÷ total common shares outstanding |
|
|
Additional shares outstanding |
Number of option shares - ((number of option shares * exercise price)/average market price)) |
|
|
Indirect CF from operations |
NI + Depr./Amort. + Losses -gains/Amort. Bond premium - equity earnings - (+/- change in operating assets) + (+/- change in operating liabilities) |
|
|
Governmental funds (GRaSPP) |
Fund types: General fund special Revenue funds and debt Service funds capital Projects funds Permanent fund
Modified accrual accounting (no FA or non-current liabilities; current assets only)
Current financial resources measurement Focus
Show up in the governmental activities column of a government wide financial statement along with the Internal Service Funds |
|
|
Proprietary funds (SE) |
internal Service funds Enterprise funds
Full accrual accounting Economic resources measurement Focus |
|
|
Fiduciary (trust) funds (CIP POE) |
Custodial funds Investment trust funds Private purpose trust funds Pension and Other Employee benefit trust funds
Full accrual accounting Economic resources measurement Focus |
|
|
Categories of Fund Balance (NU CAR) |
Non spendable fund balance Restricted fund balance Committed fund balance Assigned fund balance Unassigned fund balance |
|
|
Reconciliation of change in fund balance in governmental fund financial statements to the change in net position for governmental activities in the government wide financials (CPAS RIDES or SITS) |
Change in fund balance Capital items Accumulated depreciation Non-current liabilities + Capital outlay + Principal payments on debt - Book value of assets sold during the year - Sources (uses) financing + Revenue (accrual) - Interest expense (accrual) - DEpreciation + Service (internal) net income Eliminate interfund transactions |
|
|
Criteria for classification as an Enterprise fund |
1. The activity is financed with debt that is secured solely by a pledge of the net revenue from fees and charges 2. Laws and regulations require that the cost of providing services be recovered through fees 3. The pricing policies of the activity establish fees and charges designed to recover it's costs |
|
|
Primary government criteria (SELF) |
Separately Elected board Legally separated entity Financially independent |
|
|
Gain in nonmonetary transaction |
Cash received ÷ total consideration (FMV of asset given up) Above % x difference between FMV and carrying value of asset given up |
|
|
Nonmonetary exchange |
When an exchange has commercial substance the entire gain is recognized |
|
|
IFRS exchange of dissimilar assets |
Regarded as exchanges that generate revenue and all gains and losses are recognized. |
|
|
Goodwill calculation attributible to acquisition |
Investment less: NBV x % owned Total excess Allocated to identifiable assets: FV - NBV Total x % owned (a) Total excess - a = goodwill |
|
|
Stockholders equity |
Parent company's equity + non controlling interest |
|
|
Beginning non controlling interest |
Acquisition cost * (1-owned %) |
|
|
Ending non controlling interest |
Beginning noncontrolling interest (acquisition cost *noncontrolling interest) +NCI share of NI (beginning RE - dividends - ending RE = NI * noncontrolling interest) - NCI share of dividends = Ending noncontrolling interest |
|
|
Consolidated current assets |
Parent company CA + Subsidiary CA + Current FA valuation adjustment |
|
|
Plant assets |
Parent company book value plant assets + Subsidiary fair value plant assets |
|
|
Goodwill impairment US GAAP |
FV - Book value |
|
|
Present value |
Future value * present value |
|
|
Intercompany sales |
Parent's revenues + Subsidiary revenues - consolidated revenues |
|
|
Unrealized intercompany profit |
Parent's gross profit + Subsidiary gross profit - consolidated gross profit |
|
|
Unrealized profit to be eliminated from inventory on intercompany consolidation |
Intercompany profit * (ending inventory/total purchases) |
|
|
Non-controlling interest |
Non-controlling interest is only adjusted if the bonds were originally issued by the subsidiary and, as a result, a portion of the gain must be allocated to the non-controlling interest. |
|
|
Consolidated COGS |
Parent company's COGS + Subsidiary's COGS - intercompany sales |
|
|
Cost of inventory sold to subsidiary |
Cost * (1+ mark up %) = total intercompany sales Cost - original purchase price = intercompany profit |
|
|
Inventory reported on a combined BS |
Inventory aquired from outside parties + Intercompany inventory still on hand at year end - unrealized gross profit ((total inventory purchased - inventory shipped/ inventory purchased)*inventory on hand at year end |
|
|
Amount received when note is discounted at bank |
Note maturity value (face value + interest) Minus bank discount (face value * bank percent * time remaining on note ) |
|
|
Deferred tax expense |
Current period temporary differences * the enacted tax rate |
|
|
Gains on exchanges lacking commercial substance |
Gains are recognized in exchanges lacking commercial substance only when cash is received. When cash is received a gain is recognized based on total consideration (cash received÷fair value of asset given up) Gain is calculated as: fair value of property given up - book value of property given up)* consideration % calculated above.
If the cash is at least 25% of total consideration then the whole gain (FV- Book value) is recognized. |
|
|
Cash basis to accrual |
Add increases in current assets Subtract decreases in current assets Add decreases in current liabilities Subtract increases in current liabilities
|
|
|
Operating cash flow ratio |
Operating cash flow ÷ ending current liabilities |
|
|
COGS |
Beginning inventory + Purchases - ending inventory |
|
|
Net periodic pension cost calculation (SIR AGE) |
S - Service cost I - Plus interest cost (beginning PBO*discount rate) R - Minus expected return on plan assets (Beginning FV*expected return on plan assets) A - plus Amortization of prior service cost (unrecognized prior service cost÷average remaining service life) G - Amortization of (gains)/losses E - Minus amortization of transition assets (prior year unrecognized prior service cost/average remaining service life) |
|
|
Minimum recognized amount to be reported for unrecognized gain for a pension plan |
Unrecognized gain/loss (10% of the greater of the PBO or FMV of plan assets at the beginning of the year=excess Excess/average remaining service life |
|
|
Actual return on plan assets |
Beginning FV of plan assets +Contributions - Benefits paid + Actual return on plan assets (squeeze) - Ending FV of plan assets |
|
|
Net loss amortization |
Unrecognized net loss - 10% of the greater of the beginning PBO or Plan Assets = Excess ÷ average remaining service life = net loss amortization |
|
|
Projected benefit obligation |
Beginning balance + Interest cost (assumed discount rate* beginning PBO) + Current year service cost - pension benefits paid during the year = Ending balance |
|
|
Unrecognized prior service cost amortization |
Unrecognized prior service cost ÷ (service hours this year÷expected service hours in the future) Or Unrecognized prior service cost Beginning of the year - amortization of prior service cost (unrecognized prior service cost ÷ avg. remaining service life) |
|
|
Unrecognized prior service cost to be reported in OCI |
Beginning unrecognized prior service cost - amortization of prior service cost (unrecognized prior service cost ÷ avg. remaining service life) = Unrecognized prior service cost |
|
|
Amount to report in AOCI for a pension plan |
Unrecognized service cost - unrecognized gain + Unrecognized transition obligation |
|
|
Amount to report in AOCI under IFRS |
Remeasurement of defined benefit pension liability (asset), including remeasurement from actuarial gains. |
|
|
Fiduciary funds (CIPPOE) |
Custodial Investment Private purpose Pension and other employee benefit |
|
|
Ingredients of faithful representatation |
Completeness Neautrality Freedom of error |
|
|
Ingredients of relevance |
Predictive value Confirming value Material |
|
|
Appropriate measurement basis for assets at year end when will be disposed of within 3 months |
Net realizable value |
|
|
Interim financial statements emphasize the qualitative characteristic of |
Timelines |
|
|
Other Comprehensive Income includes |
*Pension gain/loss *Foreign currency translation loss *Revaluation surplus *Unrealized gain/loss on available for sale debt security and debt securities transferred from held to maturity to available for sale *Instrument specific credit risk *The effective portion of a cash flow hedge |
|
|
Financing activities statement of cash flows |
Payment to retire bonds - outflow Payment of dividends - outflow Proceeds from treasury stock - inflow Proceeds from the issuance of long-term debt - inflow Payments on long-term debt - outflow
Financing activities cover transactions involving long-term liabilities and equity |
|
|
Cash paid to suppliers |
COGS Minus: decrease in inventory Plus: decrease in AP |
|
|
Cash flows from investing activities |
- aquisition of buildings - purchase of bonds payable - outflow - cash proceeds from sale of investment - inflow - cash paid to purchase common stock - outflow
Include CF from available for sale and held to maturity security transactions |
|
|
Cash flows from operating activities |
Subtract increase in AR Add increase in allowance for AR Add decrease in prepaid Add increase in AP Add depreciation expense Add Goodwill impairment Subtract increase in inventory Add decrease in trading securities Subtract decrease in taxes payable Cash flows from operating activities are generated by current assets and current liabilities |
|
|
Cash collected from customers |
Beginning AR + Sales on account and cash - AR written off - Ending AR |
|
|
Operating Cash Flow Ratio |
Operating Cash flow÷ending current liabilities |
|
|
Working Capital Turnover |
Sales ÷ average working capital |
|
|
Composite life |
Total depreciable cost ÷ total annual depreciation |
|
|
IFRS Non-controlling interest partial goodwill method |
Fair value of assets * Non-controlling interest |
|
|
Pension plan - other comprehensive income |
Changes in the funded status due to (gains)/losses, prior service cost, and net transition assets/obligations |
|
|
Reconciliation of fund balance in governmental fund FS to net position for government wide FS |
Start with the change in the fund balance
+Capital outlay + Principal payments of debt - Asset disposal -/+ Sources (uses) financing + Revenue (accrual) - Interest expense (accrual) -DEpreciation expense Service internal net income |
|
|
Cash to accrual expense |
Subtract increases in current assets Add decreases in current assetsSubtract decreases in current liabilitiesAdd increases in current liabilities |
|
|
Operating Cash Flow Ratio |
Operating Cash Flow/ending current liabilities |
|
|
COGS |
Beginning inventory + Purchases - ending inventory = COGS |
|
|
Avoidable interest |
Average accumulated expenditures x interest rate in specific borrowing |
|
|
Composite depreciable life |
Depreciable cost (cost-salvage value) ÷ annual depreciation |
|
|
Bond issue price |
Sum of the present values of maturity value and the interest payment annuity (based on the yield rate) |
|
|
Accretion expense |
Beginning asset retirement obligation x risk-adjusted rate |
|
|
Reconciliation of measurement focus differences between fund FS and government wide statements |
+ Capital assets net of - Accumulated depreciation - Non-current liabilities + increase in Capital outlay + Principal payment expense - Asset disposal adjustment (NBV of disposed asset) - Sources (other financing) debt sources + Increase in accrued Revenue or - decrease in accrued Revenue - Interest accrual and DEpreciation expense + Service (internal service fund) net position or - negative financial position - Interfund Transfers |
|
|
IFRS partial goodwill method |
Goodwill= acquisition cost - fair value of assets acquired (fair value times acquired %) |
|
|
Dollar value LIFO price index |
Cost/base |

