![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
◾◾ What is draughting? |
Draughting refers to the use of suction to move a liquid such as water from a vessel or body of water |
|
|
◾◾ What are the max lifts of draughting? |
Theoretical - 10 m Practical - 7.5 m |
|
|
◾◾ What is the rotary vane pump? |
It is a positive displacement pump (It pumps air)
It is driven by an electric motor and controlled by a priming valve. The shaft on which the rotator is mounted is off centre (Or eccentric) within the casing.
When the rotor is spinning it creates a partial vacuum. Air is then carried between the vanes and is forced out through the discharge. |
|
|
What is priming? |
Removing the air and filling the pump with liquid |
|
|
What is the purpose of flushing with clean water after draughting? |
To prevent damage to pump and appliance components. |
|
|
At what angle do you park when draughting? |
30 degrees to the waters edge |
|
|
◾◾ What route must you select when driving? |
The route you select must be safe, quick and reliable, to ensure you arrive in the scene, as soon as possible |
|
|
◾◾ at what distance do you place road cones from the sited appliance? |
Distance of road cone placement is directly proportional to the total stopping distance of an oncoming vehicle's road speed. They should be placed back a minimum of 1.5 times the speed limit to warn other road users of the hazard. E.g. if the road speed is 60kph, road cones should be placed 90m from the hazard |
|
|
◾◾ what are the 5 rules of breaking when driving an appliance? |
1. Brake in a straight line 2. Start stopping sooner 3. Vary brake pressure 4. Brake prior to bends 5. Select a lower gear prior to decents |
|
|
◾◾ list 4 responsibilities / accountability of drivers as per road traffic act 1961 |
4.1. Drivers are accountable for complying with the Road Traffic Act 1861 and other relative MFS official documents. I.e. policies, SAP's, operational procedures, service directives etc 4.2. Drivers are responsible to ensure the vehicle is road worthy at all times. 4.3. Appliance drivers are responsible for completing and recording the daily checks (M32 form) 4.4. The driver of the appliance shall comply with appropriate and reasonable instructions from the Officer In Charge |
|
|
As per SAP 26, what is a controlled area? |
Areas that have traffic lights, stop or give way signs, roundabouts, pedestrian crossings, one way streets, school signs, posted speed limit areas, etc |
|
|
As per SAP 26 what is a light fleet? |
Any vehicle less than 3.5 tonnes |
|
|
◾◾ what are the 3 components of finished foam? |
1. Foam compound (concentrate) 2. Water 3. Air |
|
|
◾◾ how does foam work to extinguish fires? |
Smothers: prevents air And flammable vapours from mixing Starves: creates a barrier between fuel and fire Cools: lowers fuel and surface temperatures Suppresses: prevents the release of flammable vapours |
|
|
◾◾ What are the safety considerations for using HEX foam? |
1. Lack of visibility 2. Lack of hearing 3. Suffocation risk 4. Feeling of isolation (can lead to panic) 5. Sense of direction may be affected 6. BA procedures are extremely important |
|
|
How can you prevent damage to the pump and appliance After draughting? |
Flush the pump, tank and waterways with clean water |
|
|
What type of fire do we use class B foam for? |
Class B fires: flammable and combustible liquids I.e. petrol, oil, paint, and gasoline/Alcohol blends less than 20% |
|
|
What is the "shear strength" of foam? |
A measurement of the foam's fire resistance |
|
|
What is the "induction rate" of foam? |
The percentage of foam compound mixed or induced into the water supply before making foam |
|
|
◾◾What is the aim of salvage? |
Minimise losses by indirect causes of fire and firefighting operations. Such as: ▪️smoke ▪️heat, steam, fumes and condensation to areas not involved in the fire ▪️water damage ▪️falling ceilings/roofs ________________________ ▪️weather conditions ▪️careless firefighter actions ▪️wear and tear of buildings and equipment ▪️careless direction and overuse of water |
|
|
◾◾ What are the stages of salvage? |
PREVENTION: when the fire is in progress - simultaneous with firefighting - minimal damage with fixed entry - using sufficient water only for fire extinguishment - ventilation PROTECTION: when the fire is under control - reduce water damage - protect goods: use salvage sheets - secondary ventilation RECOVERY: when fire is extinguished - making up hose outside - removal of excess water - secure premises - preserve fire scene - remove/cover roofing |
|
|
What are some salvage considerations? |
Do not cause unneccessary damage Do not undo salvage work that has already been carried out Attempt to keep fire and operations away from exposures Water is the most likely cause of damage |
|
|
List the uses of salvage sheets |
1. Build a dam 2. Removal of water/ build a channel 3. Keeping out the weather 4. Preventing damage to surrounding premises 5. Covering undamaged goods 6. Equipment staging points |
|
|
◾◾ What is the response to automatic for alarms? |
All responses to premises containing Automatic fire alarms shall be treated as a fore situation until such time as a thorough investigation determines otherwise |
|
|
◾◾ how do you respond when questioned about alarm systems? |
All queries should be referred yo the MFS monitored alarm section of the MFS website |
|
|
◾◾ what must be included in all sp135 entries? |
Officer's name in block letters and their signature |
|
|
◾◾ is it recommended to isolate alarms? |
The MFS does not support the isolation of Fire Detection Systems while the building is being occupied |
|
|
◾◾ how does an ionisation detector work? |
It has a small amount of radioactive matter inside the body of the detector that ionises the atmosphere within the sensing chamber. These ionised particles create a small electrical current flow which is registered within the detector. |
|
|
◾◾ what happens to trigger an ionisation detector? |
When smoke particles enter the chamber it slows the normal ion movement, causing a reduction in the electrical current which triggers an alarm. |
|
|
◾◾ how does a photo-electric detector operate? (Also known as photo-optical) |
It consists of a light source which the intensity is constantly monitored within the detector. |
|
|
◾◾ what causes a photo electric detector to trigger? |
When smoke enters the sensing chamber, the light source is partially obscured from the sensor which triggers the alarm |
|
|
What is the best type of detection system and why? |
Photo electric as it provides the best level of detection across a range of fires and are less prone to nuisance alarms than ionisation detectors. |
|
|
How are fire detectors usually activated? |
Heat Smoke Combustion gases Flames |
|
|
What is passive fire detection? |
Detects fire only |
|
|
What is a dynamic fire detector |
Automatic fire detection accompanied by a fire suppression system to help contain/extinguish the fire |
|
|
◾◾what are smoke sampling systems? |
Multi-aspirated smoke detection systems continually sample the atmosphere from within a fire zone by means of a series of sampling points which are linked via PVC pipework to a vacuum pump. The system operated when light beamed from a light source to a photo-optic (photo-electric) sensor is obscured by smoke particles. Most common is VESDA = very early smoke detection apparatus |
|
|
◾◾what are the 4 primary functions of a fire suppression sprinkler system? |
1. Detects the presence of Fire 2. Deliver and maintain fire-controlling and extinguishing water to a fire within the area that the fire sprinkler system protects 3. Provide building occupants with an effective early warning of a fire condition 4. Notify the fire service |
|
|
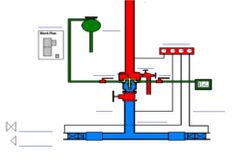
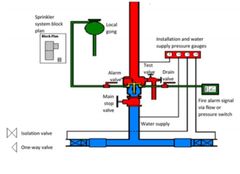
◾◾ what items of information are on a block plan? |
Location of hydrants & booster cabinets Contractor details & year of installation Tank capacity Building and street layout Maintenance provider |
|
|
What are the 2 types of hydrants systems? |
Feed and attack |
|
|
◾◾ what are feed hydrants? |
- mains pressure - supply appliance and requires on board pump (hose line directly off appliance) - faster and better than fire plugs - external hydrants locations within 20 m of appliance hardstand area |
|
|
◾◾ what are attack hydrants? |
- served by a booster system - usually close to structure - permits a hose line directly off the hydrant itself - external and internal hydrants |
|
|
◾◾ what are the booster system types? |
1. Attack hydrants 2. Sprinkler systems 3. Hose reels 4. Combination of all |
|
|
◾◾ what are the crew responsibilities when boosting? |
1. Ensure all outlets and inlets are connected 2. Ensure relief valve is OFF 3. monitor gauges to avoid cavitation 4. Familiarise yourself with block plans and info provided in cabinet 5. Communicate with crews to ensure adequate pressure |
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
What is a vortex and when does it occur? |
If the water is not deep enough, a vortex (small whirlpool) may introduce air into the suction hose and when drawn into the pump may cause loss of prime |
|
|
◾◾ What is foam? |
Firefighting foam is a stable mass of small, air filled bubbles with a lower density than oil, petrol or water. |
|
|
What concentrations are for hydrocarbon and polar solvents? |
Hydrocarbons (petrol, oil, paint) is 6% Polar solvents (alcohol) is 3% |
|
|
What are the application methods of foam? |
Roll on Rain down Bank down |
|
|
What are the categories for forcible entry? |
LOW URGENCY: - Minimal entry damage - public assistance - investigate private alarm HIGH URGENCY: - saving life - saving property - entry damage is acceptable |
|
|
What is involved in an external door assessment? |
- construction (solid/hollow) - materials it's made of - way the door swings - types of locks - how many locks |
|
|
Minimum required tools for forced entry? |
Hooligan/halligan Shove knife Sledge hammer |
|
|
3 types of tools for forced entry? |
LEVERING: - hooligan, halligan, crow bar, claw bar, shove knife STRIKING: - sledge hammer, axe, craw hammer CUTTING: - disc cutter, bolt cutter, hacksaw, eclipse saw, RIV |
|
|
Method for forcing door? |
1. Check to see if unlocked 2. Shock door 3. Set tool 4. Force door |
|
|
Considerations for working on a roof? |
- FF should not work on any roof if there are concerns for their safety or questions of integrity of the roof - work upwind so that the rising smoke and fire gases will be carried away from you, if this is not possible BA should be worn |
|
|
Precautions for asbestos roofing? |
Always wear BA is you suspect asbestos! |
|
|
What is thr fuel mix for 2 stroke fuel? |
50:1 |
|
|
When do you apply the chain brake when using a chainsaw? |
Before starting Finished a cut Moving around |
|
|
What is a safety consideration for both chainsaw and disc cutter? |
Do not over reach or cut above shoulder height |

