![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Body alignment
|
Relationship of one body part to another
|
|
|
Body balance
|
Achieved by low center of gravity; enhanced by posture
|
|
|
Friction
|
Effect of rubbing or resistance when a moving body meets a surface when turning
|
|
|
Name 4 things the Nervous system regulates
|
1. movement
2. posture 3. Proprioception 4. Balance |
|
|
Name 4 Pathological influenced conditions w/ example
|
1. Congenital defects e.g.scoliosis
2. Disorders of bones, joints, and muscles e.g. arthritis 3. CNS damage e.g. MS, 4. Musculoskeletal trauma e.g. sprains, and fractures |
|
|
Name 3 things you look for when assessing
body alignment |
(1) Standing: head erect and midline; body symmetrical; spine straight; abdomen tucked; knees slightly flexed in line of hips and ankles; feet flat
(2) Sitting: head erect; neck straight; weight on buttocks and thighs; feet on the floor; forearms supported (3) Recumbent: lateral position; vertebrae straight without curves |
|
|
Name 3 techniques for assessing
mobility |
(1) Range of joint motion - Used to determine limitation/injury to a joint
(2) Gait - Manner or style of walking, including rhythm, cadence, and speed (3) Exercise/activity tolerance Physical activity for conditioning body, improving health, maintaining fitness, therapy |
|
|
Name 6 Implementation Lifting Techniques
|
(1) Tighten stomach muscles and tuck pelvis.
(2) Bend at the knees. (3) Keep weight lifted close to the body. (4) Maintain trunk erect and knees bent. (5) Avoid twisting. (6) Maintain a center of gravity. |
|
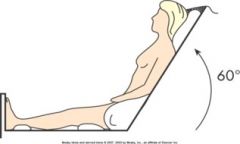
|
Fowler’s
HOB elevated 45 to 60 degrees, support and align hips and spine In high-Fowler's position, the head of the bed is 90 degrees. Patients with severe respiratory distress breathe more easily in high-Fowler's position. |
|
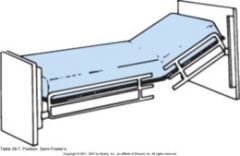
|
Semi Fowler’s
semi-Fowler's position the head of the bed is at a 30-degree angle; you will use this position for patients who will not tolerate a supine position, such as those with cardiac and respiratory problems. |
|
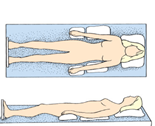
|
Supine
Back lying, support with pillows, trochanter rolls, splints |
|
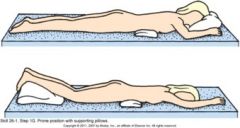
|
Prone
Face down |
|

|
Lateral
Side lying with proper spine alignment |
|
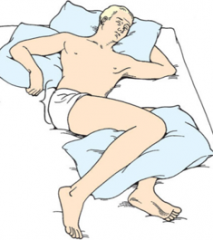
|
30 degree lateral
|
|
|
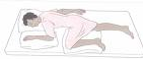
Sims
Semiprone on right or left side with weight placed on ilium, humerus, and clavicle |
|
|
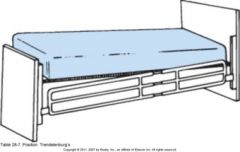
Trendelenburg
Head lowered |
|
|
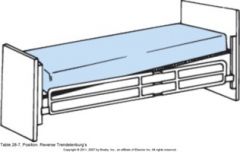
Reverse Trendelenburg
|
|
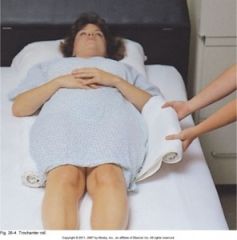
|
Trochanter roll- external rotation
|
|
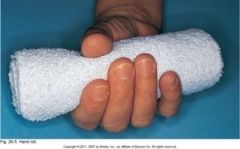
|
Hand roll- clenched fist
|
|

|
Abduction pillow - internal rotation (hip replacement)
|
|
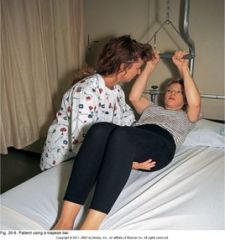
|
Trapeze bar - maintain upper body strength and to help nurse move pt in bed
|
|
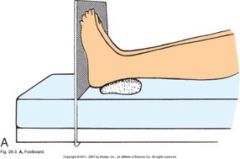
|
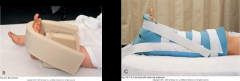
Foot board- prevent plantar flexion- footdrop
|
|
|
Footboots -prevent plantar flexion- footdrop
|
|

|
Footcradle
|
|
|
Name 3 Proper Transfer Techniques
|
Maintain patient safety
Protect nurse from injury Assist patient |
|
|
(def)
AROM |
Active: patient is able to move his or her joints
|
|
|
(def)
PROM |
Passive: nurse moves the patient’s joints
|
|
|
ROM (name type of joint )
Neck, cervical spine |
Pivotal
|
|
|
ROM (name type of joint )
Shoulder |
Ball and socket
|
|
|
ROM (name type of joint )
Elbow |
Hinge
|
|
|
ROM (name type of joint )
Forearm |
Pivotal
|
|
|
ROM (name type of joint )
Wrist |
Condyloid
|
|
|
ROM (name type of joint )
Fingers |
Condyloid hinge
|
|
|
ROM (name type of joint )
Thumb |
Saddle
|
|
|
ROM (name type of joint )
Hip |
Ball and socket
|
|
|
ROM (name type of joint )
Knee Hinge |
Hinge
|
|
|
ROM (name type of joint )
Ankle |
Hinge
|
|
|
ROM (name type of joint )
Foot |
Gliding
|
|
|
ROM (name type of joint )
Toes |
Condyloid
|
|
|
Discuss cane technique
|
cane on strong side
nurse on weak side |
|
|
Crutch "Four-point"
|
Alternating gait.
|
|
|
Crutch "Three-point gait " (Swing through)
|
Weight borne on unaffected leg.
|
|
|
Crutch "Two-point gait "
|
Weight borne partially on each foot and each crutch advancing with opposing leg.
|
|
|
Crutch Ascending (UP) stairs:
|
Strong leg leads (good goes up)
Cruches and trailing affected leg follow |
|
|
Crutch Descending stairs:
|
Crutches & extended affected (bad goes down) leg lead
Strong leg follows |
|

|
Continuous passive motion (CPM)
|
|
|
(def)
Pathogens |
Microorganisms capable of producing disease.
|
|
|
(def)
Infection |
invasion of susceptible host by microorganisms resulting in disease.
|
|
|
(def)
Colonization |
microorganisms are present but not causing disease.
|
|
|
(def)
Symptomatic |
clinical signs and symptoms
|
|
|
(def)
Asymptomatic |
no signs or symptoms
|
|
|
Name the stages in Chain of Infection
|
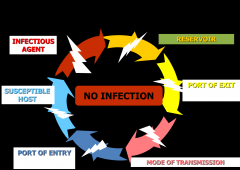
(1) Infectious agent
(2) Reservoir (3) Portal of exit (4) Mode of transmission (5) Portal of entry (6) Susceptible host |
|
|
(def)
Infectious agent |
The development of an infection depends on the number of microorganisms present; their virulence, or the ability to produce disease; their ability to enter and survive in the host; and the susceptibility of the host.
|
|
|
(def)
Reservoir |
A place where microorganisms survive, multiply, and wait to transfer to a susceptible host
e.g. Frequent reservoirs for health care–associated infections (HAIs) include health care workers (especially their hands), patients’ body excretions and secretions, equipment, and the health care environment. |
|
|
(def)
Portal of Exit |
After microorganisms find a site in which to grow and multiply, they must find a portal of exit
e.g.skin, mucous membranes, respiratory , gastrointestinal, urinary tract and reproductive tracts and in blood. |
|
|
(def)
Mode of Transmission |
How an infectious agent gets into a susceptible host.
Note: by practicing infection prevention and control techniques, such as hand hygiene, you interrupt the mode of transmission |
|
|
(def)
Portal of Entry |
Organisms are able to enter the body through the same routes they use for exiting. Common portals of entry include broken skin, mucous membranes, genitourinary (GU) tract, gastrointestinal (GI) tract, and respiratory tract. For example, obstruction to the flow of urine due to the presence of a blocked urinary catheter allows organisms to ascend the urethra.
|
|
|
(def)
Susceptible Host |
Susceptibility to an infection depends on the individual's degree of resistance to pathogens.
|
|
|
(def)
Direct transmission |
person-to-person or physical contact between source and susceptible host (e.g., touching patient feces and then touching own face or mouth or consuming contaminated food)
|
|
|
(def)
Indirect transmission |
Personal contact of susceptible host with contaminated inanimate object (e.g., needles or sharps, dressings)
|
|
|
(def)
Droplet transmission |
Droplet: Large particles that travel up to 3 feet and come in contact with susceptible host (e.g., from coughing, sneezing, talking)
Influenza Pertussis (whooping cough) Streptococcus (pharyngitis, pneumonia) Meningococcal meningitis |
|
|
(def)
Airborne transmission |
Droplet nuclei, residue or evaporated droplets suspended in air (e.g., from coughing, sneezing, talking)
TB Chickenpox (Varicella) Measles SARS |
|
|
Name 5 Vehicles of transmission
|
(1) Contaminated items
(2) Water (3) Drugs, solutions (4) Blood (5) Food (improperly handled, stored, cooked; fresh or thawed meats) |
|
|
Name two types of Vector's
|
(1) External mechanical transfer (flies)
(2) Internal transmission such as with parasitic conditions between vector and host, for example: Mosquito, Lice (louse), Tick, Flea |
|
|
(def)
Exogenous |
pathogens from other people or the environment
|
|
|
(def)
Endogenous |
the client’s own organisms
|
|
|
(def)
Health Care- Associated Infection |
Infection the patient didn’t have when they came into the system. (former term - nosocomial)
|
|
|
(def)
Medical asepsis |
“Clean” technique = Disinfection (low-level)
Hand hygiene, barrier technique, cleaning of environment and surfaces, non-sterile dressing changes, peripheral IV insertion. Goal: reduce/eliminate pathogens |
|
|
(def)
Surgical asepsis |
sterile technique =High level disinfection–kills everything
Sterilization-kills all organisms and spores Goal: eliminate all organisms, prevent introduction of any organisms --for sterile procedure (sterile dressing change, urinary catheter insertion): sterile gloves, equipment, drapes --for surgery: surgical hand washing, sterile gown, gloves, mask |
|
|
Donning PPE
|
(1) Gown
(2) Mask (3) Gloves (last thing on first thing off) |
|
|
Doffing PPE
|
(1) gloves
(2) Gown (3) mask |
|
|
(def)
Empiric precautions |
using the appropriate barrier for the suspected diagnosis as indicated by clinical symptoms
(form of standard precaution) |
|
|
(def)
Contact transmission |
Surface dwellers
Hand to mouth/nose/eyes, hand to contaminated equipment e.g. Intestinal pathogens (any pt with diarrhea) MRSA |
|
|
(def)
AIIR |
airborne infection isolation room (negative air-flow room)
|

