![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Adaptive Management |
A plan that provides flexibility so that managers can modify it as changes occur |
|
|
Alpha Diversity |
The diversity within a particular area or ecosystem. Expressed by species richness or Simpson's Diversity |
|
|
Beta Diversity |
The change in species diversity between these ecosystems. Expressed by Whittaker
|
|
|
Buffer Zone |
Areas with less stringent controls on land use, but that can still meet the requirements of many species |
|
|
Communnity |
All of the populations of organisms within a given area |
|
|
HIPCO |
Habitat loss, Invasive species, Pollution, Climate change, Over harvesting |
|
|
Core Habitat |
The core is untouchable by people in a biosphere reserve. Meant to keep habitat in pristine condition |
|
|
Demographic Transition |
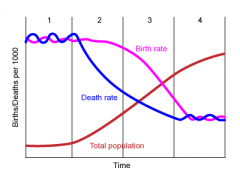
The transition from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates as a country develops.
|
|
|
Ecosystem Management |
Conserves major ecological services and restore natural resources while meeting the socioeconomic and cultural needs of future generations |
|
|
Edge Effect |
The changes in population or community that occur at the boundary of two habitats. |
|
|
Habitat Corridors |
Linear patches that connect blocks of habitat . Can reduce the effects of fragmentation by preventing isolation of population.
|
|
|
Habitat Fragmentation |
Creates isolated patches of landscape that can have harmful effects on biodiversity. Occurs because of human activities like new roads, housing developments. |
|
|
Habitat Matrix |
|
|
|
Metapopulation |
A group of spatially distinct populations that are connected by occasional movements of individuals between them
|
|
|
Permeability |
The ability of a substance to allow another substance to pass through it (concrete is not permeable) |
|
|
Rescue Effect |
A species arriving on an island may already be represented there and so may have the effect of reducing the chance of the extinction of that species from the island. |
|
|
Species-area Curve |
The relationship between the area of habitat and the number of species found within the area. Calculated with species richness over area |
|
|
Species Evenness |
The relative proportion of different species in a given area
|
|
|
Species Richness |
The number of species in a given area
|
|
|
Survivorship Curve |
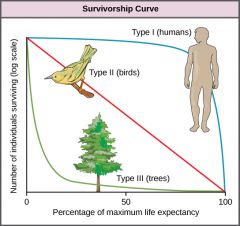
A graph that represents the distinct patterns of species survival as a function of age
|
|
|
Stakeholder |
A person or organization with an interest in a particular place or issue |
|
|
Stepping Stone |
Smaller, unconnected areas of preserved or restored habitat. Initially used to promote bird or insect movement |
|
|
Simpson's Diversity |
The probability that two randomly selected individuals belong to different species
|
|
|
Shannon's Diversity |
The relative uncertainty of the species-identity of an individual chosen at random.
|
|
|
Whittaker's Formula for Beta Diversity |
Species turnover along a gradient |
|
|
Nitrogen Cycle Step One |
Nitrogen is a limiting factor 1) Nitrogen Fixation- organisms convert N2 into ammonia |
|
|
Nitrogen Cycle Step Two |
2) Producers obtain fixed nitrogen, they take it in. Producers and consumers die, and then decompose |
|
|
Nitrogen Cycle Step Three |
3) Ammonification: fungal and bacterial decomposers use nitrogen waste as food source and excrete ammonium |
|
|
Nitrogen Cycle Step Four |
4) Nitrification: Converted into nitrate |
|
|
Nitrogen Cycle Step Five |
5) Dentrifiying bactera in oxygen-poor soil convert nitrate into nitrous oxide, and eventually nitrogen gas. |

