![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
224 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sacrum |
5 fused vertebrae forming one bone towards base of spine |
|
|
Coccyx |
The last 4 vertebrae, fused together, to make the tailbone |
|
|
Thorax |
The Chest, containing the heart, lungs, esophagus and great vessels |
|
|
Spinal column Diagram |
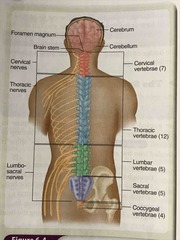
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Thorax Diagram |
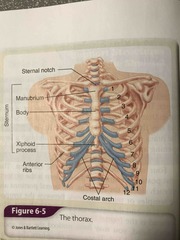
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Joint Capsule |
A fibrous sack that holds together bone ends of a joint |
|
|
Metacarpals |
bone in the hand between the carpals and phalanges |
|
|
Pelvis Diagram |
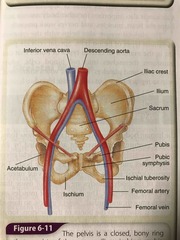
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Lumbar spine |
5 Vertebrae under the thoracic spine |
|
|
Thoracic spine |
12 vertebrae under the cervical spine |
|
|
Cervical spine |
First seven vertebrae in the neck |
|
|
Occipital bone |
Posterior portion of cranium |
|
|
Orbit |
I socket made up of the maxilla and zygoma bones |
|
|
Mandible |
Lower movable portion of the jaw |
|
|
Zygomas |
Cheekbones |
|
|
Maxillae |
Upper non-movable jaw bones |
|
|
Ventral |
The anterior surface of the body |
|
|
Supine |
Lying face up |
|
|
Superior |
Above a body part or nearer to the head |
|
|
Superficial |
Closer to or on the skin |
|
|
Quadrants |
Describe sections of the abdomen cavity that have been divided into four equal imaginary areas |
|
|
Proximal |
Closer to the trunk |
|
|
Prefix |
Part of a term that is before a root word |
|
|
Posterior |
Back surface of the body |
|
|
Plantar |
Bottom surface of the foot |
|
|
Palmar |
Forward facing part of the hand in the anatomical position |
|
|
Medial |
Parts of the body that are closer to the midline |
|
|
Lateral |
Parts of the body that are farther from the midline |
|
|
Inferior |
The lower body part or nearer to the feet |
|
|
Fowler position |
On incline position in which the head of bed is raised |
|
|
Flexion |
Bending of a joint |
|
|
Extension |
Straightening of a joint |
|
|
Dorsal |
The posterior surface of the body including back of the hand (back side of body) |
|
|
Distal |
Further from the trunk or nearer to the free end of an extremity |
|
|
Bilateral |
A body part or condition that appears on both sides of the body |
|
|
Anterior |
Front surface of the body |
|
|
Adduction |
Motion of limb toward the midline |
|
|
Abduction |
Motion of a limb away from midline |
|
|
Temporel bones Frontal bone Parietal bone |
The four major bones that make up the cranium |
|
|
Foramen magnum |
Large opening at the base of the skull |
|
|
Thorax |
Encloses the heart longs esophagus and great vessels |
|
|
The two main portions of the skeletal system |
Axial and appendicular skeleton |
|
|
Appendicular skeleton |
The arms and legs, their connective points, and the pelvis |
|
|
Axial skeleton |
Forms the foundation to which the arms and legs are attached, a skeletal system |
|
|
Cartilage |
Smooth tissue that covers the ends of bones at mobile joints |
|
|
Tendons |
Connects muscle to bone |
|
|
Ligaments |
Connects bone to bone |
|
|
Midsagittal plane (Midline) |
Divides body into right and left equal sides |
|
|
Sagittal plane (Lateral) |
Divides body into right and left sides |
|
|
Transverse plane (Axial) |
Divides body and to top and bottom belly button |
|
|
Frontal plane (coronal) |
Divides body into front and back |
|
|
Three types of muscle |
Skeletal (voluntary) Smooth (intestines) Cardiac (involuntary) |
|
|
Homeostasis |
A balance of all the systems in the body |
|
|
Respiratory system |
All the structures of the body that contribute to respiration, or breathing |
|
|
The upper airway includes? |
Nose Mouth Tongue Jaw Pharynx Larynx |
|
|
Larynx |
Voice box |
|
|
Oropharnyx (pharynx) |
Throat |
|
|
Respiratory Diagram |
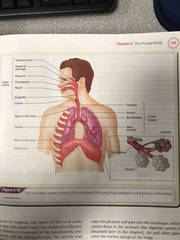
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Muscle Diagram |
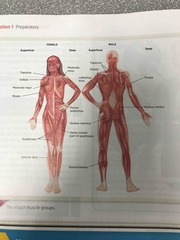
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Thyroid cartilage is also known as? |
The Adams apple |
|
|
Lower airway diagram |
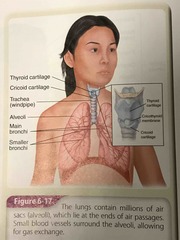
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Trachea |
Windpipe Found below the Adam’s apple and holds up the lungs with the help of arteries and veins |
|
|
Lung lobe diagram |
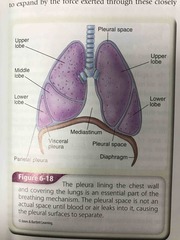
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Alveoli |
Small air sacs at the end of bronchi in the lungs that are responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide |
|
|
Pulmonary capillaries |
Network of tiny blood vessels on the walls of alveoli |
|
|
Pleura |
Smooth, glistening tissue covering the lungs that allow the lungs to move and glide for breathing |
|
|
Pleural space |
A potential space between the lungs and chest cavity that in normal conditions does not exist |
|
|
Diaphragm |
The primary muscle used to make the long is expand and contract for breeding |
|
|
Medical director |
The physician who authorizes or delegates to the EMT |
|
|
Acute stress reactions |
Occurred during a stressful situation |
|
|
Delayed a stress reactions |
Manifest after the stressful event |
|
|
Cumulative stress reactions |
Occurs when you were exposed to prolonged or excessive stress |
|
|
Hepatitis |
Inflammation of the liver usually caused by a viral infection that causes fever loss of appetite, jaundice, fatigue, and altered liver function |
|
|
Host |
The organism more individual that is attacked by the infecting agent |
|
|
HIV |
Damages the cells of the body’s immune system so that the body is unable to fight infection or certain cancers |
|
|
Infection |
The abnormal invasion of a host or host tissues by organisms such as bacteria, viruses, or parasites, with or without signs or symptoms of disease |
|
|
Infectious disease |
A medical condition caused by the growth and spread of small, harmful organisms within the body |
|
|
Pathogen |
A micro organism that is capable of causing disease in a susceptible host |
|
|
Transmission |
The way in which an infectious disease is spread. Contact, airborne, by vehicles, or by vectors |
|
|
Vector-borne transmission |
The use of an animal to spread an organism for one person or place to another |
|
|
Abandonment |
Unilateral Termination of care by the EMT without the patient’s consent and without making provisions for transferring care to another medical professional |
|
|
Advance directive |
Written documentation that Specifies medical treatment for a competent patient should the patient be unable to make decisions |
|
|
Applied ethics |
The manner in which principles of ethics are incorporated into professional conduct |
|
|
Assault |
Unlawfully placing a patient in fear of bodily harm |
|
|
Battery |
Unlawfully touching a patient or providing emergency care without consent |
|
|
Bioethics |
The study of ethics related to issues that arise in healthcare |
|
|
Breach of confidentiality |
Disclosure of information without proper authorization |
|
|
Contributory negligence |
A legal defense that may be raised when the defendant feels that the conduct of the plaintive somehow contributed to any injuries or damages that were sustained by the plaintiff |
|
|
Credentialing |
And established process to determine the qualifications necessary to be allowed to practice a particular profession |
|
|
Defamation |
The communication of false information about a person that is damaging to that person’s reputation |
|
|
Dependent lividity |
Blood settling to the lowest point of the body causing discoloration of the skin |
|
|
Depositions |
Oral questions asked of parties and witnesses under oath |
|
|
DNR |
Written documentation by physician giving permission to medical personnel not to attempt resuscitation in the event of cardiac arrest |
|
|
Ethics |
The philosophy of right and wrong, of moral duties, and of ideal professional behaviors |
|
|
Expressed consent |
A type of consent in which the patient gives verbal or nonverbal authorization for provision of care or transport |
|
|
False imprisonment |
The confinement of a person without legal authority or the person’s consent |
|
|
Forcible restraint |
The active physically preventing an individual from initiating any physical action |
|
|
Gross negligence |
Conduct that constitutes a willful or reckless disregard for a duty or standard of care |
|
|
Health care directive |
A written document that specifies medical treatment for a competent patient should hear she become unable to make decisions. Also known as an advance directive |
|
|
Health care proxies |
A type of advance directive executed by a competent adult that a point to another individual to make medical treatment decisions on his or her behalf |
|
|
Implied consent |
Type of consent in which a patient who is unable to give consent is given treatment under the legal assumption that he or she would want treatment |
|
|
In loco parentis |
Refers to the legal responsibility of a person or organization to take on some of the functions and responsibilities of a parent |
|
|
Libel |
False and damaging information about a person that is communicated in writing |
|
|
Negligence |
Failure to provide the same care that a person with similar training would provide |
|
|
Patient autonomy |
The right of the patient to make informed choices regarding his or her health care |
|
|
Putrefaction |
Decomposition of body tissues. A definitive sign of death |
|
|
Rigor mortis |
Stiffening of the body muscles |
|
|
Slander |
False and damaging information about a person that is communicated by the spoken word |
|
|
A repeater |
A special base station radio that receives messages and signals on one frequency and then automatically transmit them on a second frequency |
|
|
Telemetry |
Electronica signals are converted into coded, audible signal’s |
|
|
Standing orders |
Written documents that have been signed by the EMS system medical director |
|
|
Root word diagram |
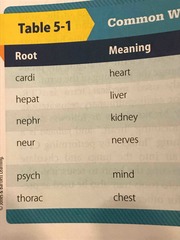
Root word diagram
|
|
|
Prefix diagram |

Back (Definition) |
|
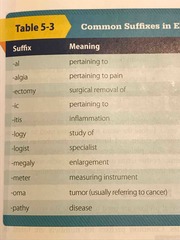
Suffixes Diagram |
Diagram |
|
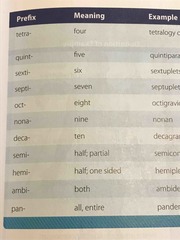
Number prefixes |

Number prefixes |
|
|
Root words color diagram |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Prefixes that describe position diagram |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Leg bone skeletal diagram |
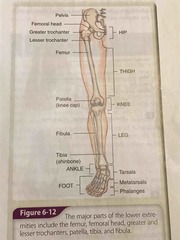
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Foot bone diagram |
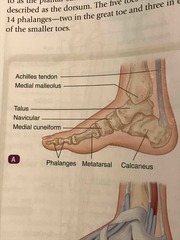
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Circulatory system diagram |
Circulatory system diagram |
|
|
Atrium |
Upper chamber of the heart |
|
|
Ventricle |
Lower chamber of the heart |
|
|
Myocardium |
Cardiac muscle, or heart muscle |
|
|
Septum |
A wall that divides the right and left sides of the heart |
|
|
Foot bone diagram |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Diffusion |
A passive process in which molecules move from an area with a higher concentration of molecules, the air, to an area of lower concentration, the bloodstream. |
|
|
Ventilation |
The simple movement of air between the lungs and the environment |
|
|
Respiration |
The process of gas exchange. Oxygen and carbon dioxide |
|
|
Circulatory system diagram |
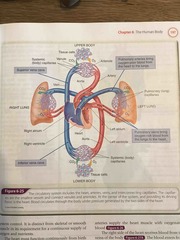
Circulatory system diagram |
|
|
Tidal volume |
The amount of air that is moved into or out of the lungs during a single breath |
|
|
Inspiratory reserve volume |
The deepest breath you can take after a normal breath |
|
|
Expiratory reserve volume |
The maximum amount of air that you can forcibly breathe out after a normal breath |
|
|
Residual volume |
The gas that remains in the lungs after exhalation simply to keep the lungs open |
|
|
Circulatory system |
A complex arrangement of connected tubes, including the arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins |
|
|
Systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation |
The systemic circulation is in the body and pulmonary in the lungs. The two circuits together form the circulatory system |
|
|
Heart |
A hollow muscular organ approximately the size of a clenched fist |
|
|
Pulmonary veins |
Provide oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart |
|
|
Anterior and posterior view of the heart |
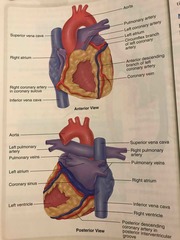
Anterior and posterior view of the heart |
|
|
Heart pumping diagram |
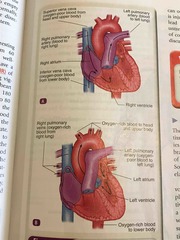
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Aorta |
The main artery leaving the back left side of the heart. It carries freshly oxygenated blood to the body |
|
|
The main arteries and veins diagram |
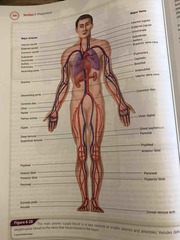
The main arteries diagram |
|
|
Pulmonary artery |
Begins at the right side of the heart and carries oxygen depleted, or de-oxygenated, blood to the lungs |
|
|
Arterioles |
The smallest branches of an artery leading to the vast network of capillaries |
|
|
Capillary vessels |
Fragile divisions of the arterial system that allowed contact between the blood and the cells of the tissues |
|
|
Pulse locations table |
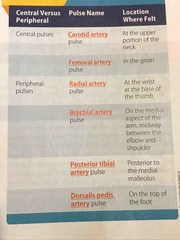
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Superior vena cava |
Carries blood returning to the heart from the head, neck, shoulders, and upper extremities. |
|
|
Inferior vena cava |
Carries blood returning from the abdomen, pelvis, and lower extremities back to the heart. The superior and inferior vena cava join at the right atrium of the heart |
|
|
Spleen |
A solid organ located under the rib cage of the left upper part of the abdomen. It is part of the lymphatic system. Blood passes through the spleen where it is filtered. It also assist with the body’s immune response |
|
|
Plasma |
Hey sticky, yellow fluid that carries the blood cells and nutrients |
|
|
Red blood cells |
Contain hemoglobin, which gives blood is red color. Hemoglobin carries oxygen throughout the body |
|
|
White blood cells |
Play a role in the body’s immune defense mechanisms against infection |
|
|
Platelets |
Tiny, disc shaped elements that are much smaller than the cells. They are essential in the initial formation of a blood clot, the mechanism that stops bleeding |
|
|
Sistole blood pressure |
The muscular contraction phase of blood pumping from the ventricle into the aorta. The pressure of the blood pumping |
|
|
Diastolic blood pressure |
When the muscle of the ventricle relaxers, the ventricle fills with blood. Diastolic is the pressure on the walls of the ventricles |
|
|
Perfusion |
The circulation of blood in an organ or tissue |
|
|
Shock |
The state of in adequate circulation, when it involves the entire body |
|
|
Hydrostatic pressure |
Occurs as fluid pushes against the vessel walls to force fluid out of the capillary |
|
|
Oncotic pressure |
An opposing force, caused by proteins in the blood plasma, that pull water into the capillary by diffusion. |
|
|
Epinephrine and Norepinephrine |
Epinephrine is a known as adrenaline, and norepinephrine is known as noradrenaline. Both are hormones in the body. The hormones are used to stimulate the heart and blood vessels |
|
|
Epidermis |
The most superficial layer of the skin and berries and thickness in different areas of the body |
|
|
Dermis |
Is below the surface of the skin, epidermis. |
|
|
What are the two layers of the epidermis? |
The germinal later, which is at the base of the epidermis, and the stratum corneal layer, which is the dead layer of skin. |
|
|
Sebaceous gland |
Lie next to hair follicles and secrete sebum along the hair follicle to the skin surface. |
|
|
Hair follicles |
Small organs that produce hair |
|
|
Skin layers diagram |
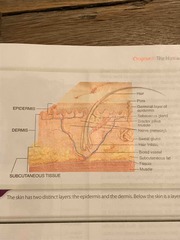
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Mucous membranes |
They provide a protective barrier against bacterial invasion by secreting mucus |
|
|
Mucus |
A watery substance that lubricates the openings |
|
|
Major organs of the retroperitoneal space that lies behind the abdominal cavity |
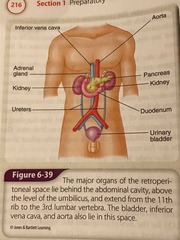
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Oropharynx |
A tubular structure that extends vertically from the back of the mouth to the esophagus and trachea |
|
|
Esophagus |
A collapsible tube about 10 inches long that extends from the end of the pharynx to the stomach. Muscle contractions propel food and liquids through it to the stomach |
|
|
Pancreas |
A flat, solid organ, that lies below and behind the liver and stomach. It is a major source of digestive enzymes and produces the hormone insulin |
|
|
The liver |
A large, solid organ that takes up most of the area immediately beneath the diaphragm in the right upper quadrant. It produces bile, stores glucose for immediate use by the body, and produces many substances that help regulate immune responses |
|
|
Lymph |
I thin, straw-colored fluid that carries oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to the cells and carries waste products of metabolism away from the cells and back into the capillaries so that they may be excreted |
|
|
Lymph nodes |
Tiny, oval shaped structures located in various places along the lymph vessels that filter lymph |
|
|
Midbrain |
The part of the brain that is responsible for helping to regulate the level of consciousness |
|
|
Gallbladder |
A sac on the undersurface of the liver that collects bile from the liver and discharges it into the duodenum through the common bile duct |
|
|
Small intestine |
The major hollow organ of the abdomen. What is the portion of the digestive to between the stomach and seek him. |
|
|
Large intestine |
The portion of the digestive tube that in encircles the abdomen around the small bowel, consisting of the cecum the colon and the rectum. It helps regulate water balance and aluminate solid waste. |
|
|
Digestive organs and functions table |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
The urinary system |
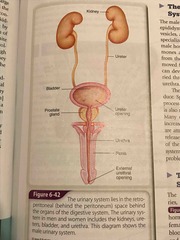
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Neonate |
Birth to one month old |
|
|
Adolescent |
A young person age 12 to 18 years |
|
|
Early adult age |
19 to 40 years |
|
|
Conventional reasoning |
A type of reasoning in which a child looks for approval from peers in society |
|
|
Fontanelles |
Areas where the Neo Nate‘s or infants goal has not fused together. Usually disappears at approximately 18 months of age |
|
|
Infant |
Age one month for one year |
|
|
Age of middle adult |
41 to 60 years |
|
|
Moro reflects |
An infant reflex in which when an infant is caught off guard the event opens his or her arms wide, spreads the fingers, and seems to grab at things |
|
|
Adolescent |
A young person age 12 to 18 years |
|
|
Post conventional reasoning |
What type of reasoning in which a child based his decisions on his or her conscience |
|
|
Early adult age |
19 to 40 years |
|
|
Conventional reasoning |
A type of reasoning in which a child looks for approval from peers in society |
|
|
Fontanelles |
Areas where the Neo Nate‘s or infants goal has not fused together. Usually disappears at approximately 18 months of age |
|
|
Infant |
Age one month for one year |
|
|
Age of middle adult |
41 to 60 years |
|
|
Moro reflects |
An infant reflex in which when an infant is caught off guard the event opens his or her arms wide, spreads the fingers, and seems to grab at things |
|
|
Nephrons |
The basic filtering units in the kidneys |
|
|
Older adult age |
61 years and older |
|
|
Palmar grasp |
An infant reflex that occurs when something is placed in the infants palm, the infant grasps the object |
|
|
Adolescent |
A young person age 12 to 18 years |
|
|
Post conventional reasoning |
What type of reasoning in which a child based his decisions on his or her conscience |
|
|
Preschooler |
Age 3 to 6 years |
|
|
Rooting reflex |
An infant reflex that occurs when something touches in infants cheek, and the infant instinctively turns his or her head toward the touch |
|
|
School-age |
A person who is 6 to 12 years of age |
|
|
Sucking reflex |
An infant reflex in which the infant start sucking when his or her lips are stroked |
|
|
Toddler |
Age 1 to 3 years |
|
|
Trust and miss trust with a child |
Refers to a stage of development from birth to approximately 18 months of age during which infants gain trust of their parents |
|
|
Early adult age |
19 to 40 years |
|
|
Conventional reasoning |
A type of reasoning in which a child looks for approval from peers in society |
|
|
Fontanelles |
Areas where the Neo Nate‘s or infants goal has not fused together. Usually disappears at approximately 18 months of age |
|
|
Infant |
Age one month for one year |
|
|
Age of middle adult |
41 to 60 years |
|
|
Moro reflects |
An infant reflex in which when an infant is caught off guard the event opens his or her arms wide, spreads the fingers, and seems to grab at things |
|
|
Nephrons |
The basic filtering units in the kidneys |
|
|
Older adult age |
61 years and older |
|
|
Palmar grasp |
An infant reflex that occurs when something is placed in the infants palm, the infant grasps the object |
|
|
Intravenous therapy |
IV therapy |
|
|
Clarification of information with a patient is called? |
Reflection |
|
|
Therapeutic communication |
Uses various communication techniques and strategies, both verbal and nonverbal, to encourage patient to express how they are feeling and to achieve a positive relationship with the patient. |
|
|
Ethnocentrism |
When you consider your own cultural values as more important when you are interacting with people of a different culture |
|
|
Cultural imposition |
Consciously or subconsciously forcing your cultural values on to the patient because of the belief that your values are better. |
|
|
Noise |
Anything that dampens or obscures the true meaning of the message |
|
|
Cardiac output (CO) |
The amount of blood to move in one minute throughout the body. This number can be calculated by multiplying the heart rate times the stroke volume |
|
|
Stroke volume |
The amount of blood moved in one beat |

