![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Producers capture energy from the ______ and make _________. |
Sun; Food |
|
|
Give a Bible Verse about producers (plants). |
Genesis 1. 29-30 |
|
|
Consumers gain _________ by eating _____________ or other __________. |
Energy; Producers; Consumers |
|
|
The passing of energy from one organism to another is called a ____________. |
Food Chain |
|
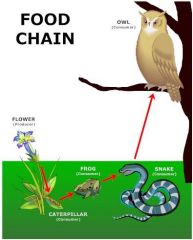
Write this using words and hyphens (instead of arrows). |
Plant-Caterpillar-Frog-Owl-Decomposer |
|
|
The arrows we use when writing a food chain mean___________. |
"Goes Into" |
|
|
Food chains always begin with a ______________ and end with a _____________. |
Producer; Decomposer |
|
|
All of the interrelated food chains in an ecosystem from a ______________. |
Food Web |
|
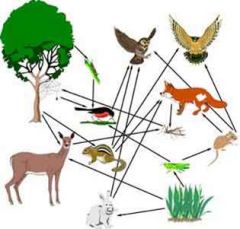
This is a _____________. |
Food Web |
|
|
Something that eats dead things is called a _____________. |
Decomposer |
|
|
What are the 4 ecological relationships between organisms? |
Predator- Prey; Parasite- Host; Mutualism; Commensalism. |
|
|
Define Predator- Prey Relationships. |
One animal (predator) kills and eats another animal (prey) |
|
|
Define Parasite- Host Relationships. |
One organism (parasite) lives in or on another organism (host) and feeds off of the host. |
|
|
Define Mutualism. |
An association between two organisms of different populations that benefits both organisms. |
|
|
Define Commensalism. |
One organism benefits from another organism which is unaffected. |
|
|
Give an example of a predator- prey relationship. |
Lion eats a zebra |
|
|
Give an example of a parasite- host relationship. |
Tick feeds on a dog |
|
|
Give an example of mutualism. |
Lichens (algae & fungus) |
|
|
Give an example of commensalism. |
Barnacles on whales. |
|
|
Define Ecology |
The study of the interrelationships of organisms and their environment |
|
|
Define Ecosystem |
A limited area in which living and non living things interact Ex. A meadow |
|
|
Define Habitat |
Something that provides the right living conditions for an organism |
|
|
Define Abiotic Environment |
The physical environment; all the non living factors in an ecosystem |
|
|
Define Biotic Community |
All the living organisms in an ecosystem |
|
|
Define Population |
All the individuals from the same species in an ecosystem |
|
|
Define Producer Organisms |
Manufacture their own food |
|
|
Define Consumer Organisms |
Cannot manufacture food; they must obtain their energy from other sources |
|
|
Define Decomposer Organisms |
Usually bacteria or fungi that break down the remains of dead organisms and return this material to the soil |

