![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is i? |
i is the square root of negative 1. |
|
|
What is the difference between a complex and imaginary number? |
An imaginary number can be written as bi where b is a real number. A complex number can be written as a+bi where a and b are real numbers. |
|
|
What is the conjugate pair of the complex number z= a+ bi? |
The conjugate z* = a - bi |
|
|
If the roots of a quadratic equation are non real complex numbers, what must their roots be? |
A conjugate pair. With roots æ and ß the equation is: (z-æ)(z-ß)=0 |
|
|
For a cubic equation with real coeeficients what two sets of roots can it have? |
Either all three real or one real and a conjugate pair of imaginary roots. |
|
|
For a quadratic equation with real coefficients what sets of roots can you have? |
All four real, two real and one conjugate pair or two sets of conjugate pairs. |
|
|
What do the X and y axis represent on an argand diagram? |
X axis is the real part, y axis is imaginary. The coordinate (X, y) can represent Z= X+iY |
|
|
What is the modulus and argument of a complex number? |

The modulus is the distance to that number from the origin on an argand diagram. The argument is the angle between the point and the origin. |
|
|
What is the modulus-argument form of a complex number with |z|= r and argz = ® |
Z=r(cos(®)+i sin(®)) |
|
|
What can |z1||z2| and |z1|÷|z2| be written as? |
|z1||z2|=|z1*z2| |Z1|÷|z2|=|z1÷z2| |
|
|
What can arg(z1z2) and arg(z1÷z2) be written as? |
Arg(z1z2)= arg(z1)+arg(z2) Arg(z1÷z2)= arg(z1)-arg(z2) |
|
|
How can sum of series be rearranged to simplify them? |
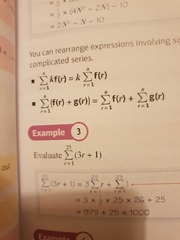
Constants can be put to the front and two functions added together can be summed up separately. |
|
|
For the quadratic equation ax²+bx+c with roots æ and ß, what does æ+ß and æß equal? |
æ+ß = -b÷a æß=c÷a |
|
|
What is the volume of revolution formed when y=f(X) is rotated through 2π radians between X=a and X=b? |

Volume = π × the integral of y² between b and a. |
|
|
If a 2×3 matrix is multiplied by a 3×3 matrix, what will the shape of the product matrix be? |
It will be a 2×3 matrix as the first number is row and second is collumn. |
|
|
How do you work out the determinant of a 2×2 matrix? |

The determinant is ad-bc. If the determinant is 0 the matrix is singular. |
|
|
How do you find the determinant of a 3×3 matrix? |

You reduce the determinant of the 3×3 matrix to 2×2 determinants using this formula. The straight line means determinant. |
|
|
How do you find the inverse of a 2×2 matrix? |
(d. -b) M^-1 = 1÷detM (-c. a) |
|
|
What are the 5 steps of inverting a 3×3 matrix (M)? |
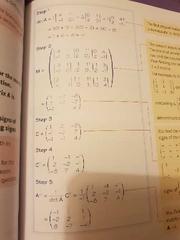
1. Find the determinant of M. 2. Form the matrix of minors from M. 3. Change the signs accordingly in the matrix of minors. 4. Transpose the matrix. To create CT. 5.M^-1 = 1÷detM × CT M^-1 = 1÷detM × CT |
|
|
What are the 4 steps for proof by induction? |
1. Basis. Show that the general statement is true for n=1. 2. Assumption. Assume that the general statement is true for n=k. 3. Inductive. Show that the general statement is true for n=k+1. 4. Conclusion. State that the general statement is therefore true for all values of n. |
|
|
How can you write the equation of a line in 3 dimensions? |
r=a+∆b. r is a general point on the line. a is the position vector of the origin to a point on the line. ∆ is a scalar. |
|
|
How can you rewrite r= a+ b∆ in Cartesian form? |
(x-a1)÷b1=(y-a2)÷b2=(z-a3)÷b3=∆ |
|
|
What is the equation of a plane? |
r=a+∆b+μc. r is a general point. a is a given vector from the origin. b and c are two non parallel vectors on the plane. ∆ and μ are scalars. |
|
|
What is the Cartesian equation of a plane r=a+∆b+μc? |
ax+by+cz=d where a, b, c and d are constants. The normal is the vector ai+bj+ck |
|
|
What is a.b equal to? |
a.b=|a||b|cos©. Where © is the angle between a and b. a.b is where you multiply each of the corresponding coordinates. |
|
|
What is the formula for sum of r? |
Sum of r= ½n(n+1) |
|
|
How can you find the roots of a cubic equation ax³+bx²+CX+d=0? |
αβγ=-b/a αβ+αγ+βγ=c/a αβγ=-d/a |
|
|
What is the equation for the angle between a line and a plane? |
a.b=|a||b|cos(©) |
|
|
what is the equation for angle between a line and a plane? |
b.n= |a||b|sin(©) where the line r=a+∆b and n is the normal to the plane. |
|
|
What is the equation for angle between two planes? |
n1.n2=|n1||n2|cos(©). where the ns are the two normals to the planes. |

