![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The circulatory system comprises of: |
A closed network of vessels (arteries, veins and capillaries) A pump (the heart) Bloody he |
|
|
The circulatory system: |
Transports food, oxygen and water to cells Removes waste products - CO2, lactic acid Is closely linked to the respiratory and digestive systems |
|
|
What shape is the heart? |
Coned |
|
|
Where does the heart lie |
Between the lungs in the thoracic cavity in the mediastinum |
|
|
The approximate size of the heart is? |
The size of the persons own clenched fist |
|
|
The heart is superior to? |
The diaphragm |
|
|
The heart is posterior to |
The sternum and slightly left of midline |
|
|
How many atria and ventricles does the heart have? |
2 of each |
|
|
Pulmonary circulation |
Right side of heart - sends de-oxygenated blood returning from the body to the lungs |
|
|
Systemic circulation |
Left side of heart - sends oxygenated blood returning from the lungs to the body |
|
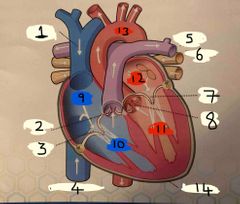
What is number 1 |
Superior vena cava |
|
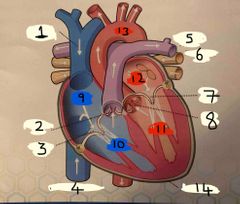
What is number 2 |
Pulmonary valve |
|
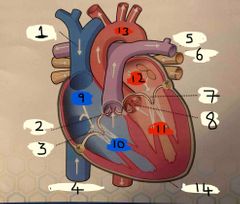
What is 3 |
Tricuspid valve |
|
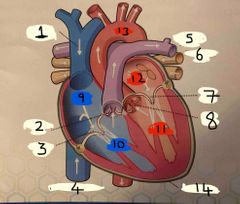
What is 4 |
Inferior vena cava |
|
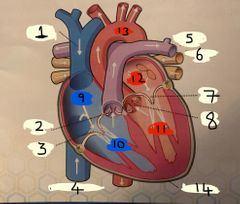
What is 5 |
Pulmonary Artery |
|
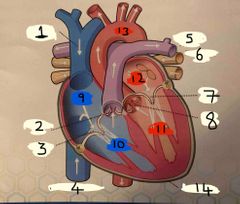
What is 6 |
Pulmonary vein |
|
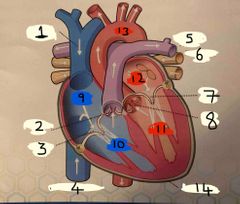
What is 7 |
Mitral valve |
|
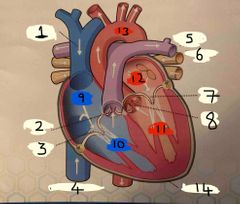
What is 8 |
Aortic valve |
|
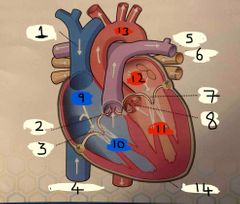
What is 9 |
Right Atrium |
|
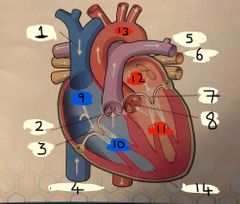
What is 10 |
Right ventricle |
|
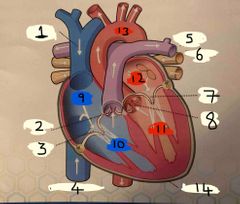
What is 11 |
Left ventricle |
|
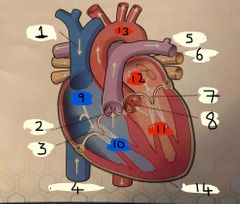
What is 12 |
Left atrium |
|
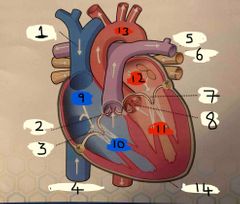
What is 13 |
Aorta |
|
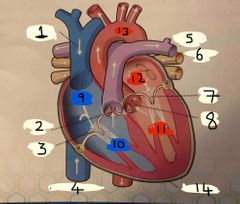
What is 14 |
Pericardium |
|
|
What do the valves in the veins in the lower limbs do? |
Prevent back flow |
|
|
What are capillaries |
The smallest and most numerous of blood vessels |
|
|
How thick are capillaries? |
One epithelial cell (endothelium) |
|
|
What do capillaries do? |
Semi-permeable - allowing for easy movement of gases, nutrients and waste products between blood and the cells of the tissues |
|
|
When checking for pulses what do you use? |
The pads of your fingers and not the thumb - it has its own pulse! |
|
|
Where are the main pulse sites? |
Carotid Brachial Radial Femoral Pedal |
|
|
What is the main function of the electrical conduction system? |
Create an electrical impulse and transmit it in an organised manner to the rest of the heart muscle (myocardium) |
|
|
Where is the electrical conduction system found? |
In the walls of the heart |
|
|
What is displayed on an ECG? |
The electrochemical process that creates electrical energy |

