![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the collision theory? What are the requirments |
Molecular collisions-reactants mus collide with one another(ex. Air + steel collide a reaction occurs Activiation energy(Ea)-minimum kinetic energy that reactants must posses(ex. Energy from striking a match to start fire) Molecular orientation-molecules must have proper orientation to react(ex. Lock and key) |
|
|
Endothermic reactions do what? |
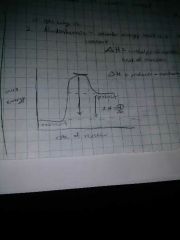
Absorb energy, heat is a reactant |
|
|
Exothermic reactions do what? |
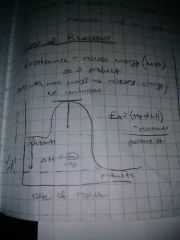
Release energy(heat) as a product- starts with more energy and releases energy(ex. Combustion) |
|
|
Activation energy(EA) equals? |
Product - reaction |
|
|
What influences reaction rates? |
Increase- The higher the concentration(M), the higher the reaction rate. As temp. Increases so does rate(double) Lowers (Ea)- the presence of a catalyst |
|
|
What is a catalysts? |
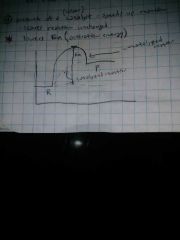
any substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction by changing the reaction pathway without being changed itself at the end of the reaction. A catalyst can't change the energy difference between reactants and products. It can reduce activation energy but can't change E. |
|
|
Equilibrium constant(Keq) equals? And excludes? |
Products ÷ Reactants Excludes solids(s) & liquids(l) |
|
|
Le Chateliers principle and how it relates to changes in concentration, pressure, and temperature |

Think old scale- shift towards side with less. Concentration- if you add to one side shift to other side. But if you remove from one side shift to same side Pressure-increase pressure means shift to side with fewest #moles(down volume) decrease pressure means shift to sode with more moles(up volume) TEMPERATURE- (Exo) add heat shift to reactant side. Remove heat shift to product. (Endo) add heat shift to product side. Remove heat shift to reactant side |
|
|
Bronsted-Lowry theory? |
Proton= H+ Acid is proton donor Base is proton acceptor |
|
|
Molarity =? And is used in? |
moles÷liters It is used in titration. Find mol first. Also remember mL ÷ 1000mL equals Liters |
|
|
How to work Titration problem? |
Find missing item.Write out equation. Balance equation. Get mol then then remember to use Molarity=mol÷Liters |
|
|
A buffer consists of? |
A mixture of either a weak acid, and it's conjugate base, or a weak acid and its conjugate acid. Resists a change in pH |
|
|
A conjugate acid is formed by? |
By adding H+ to base |
|
|
A conjugate base is formed by? |
Subtracting H+ from acid |
|
|
What are the strong acids? |
HCl-hydrochloric acid HBr-hydrobromic acid HI-hydroiodic acid HNO3-nitric acid H2SO4-sulfuric acid HClO3-chloric acid HClO4-perchloric acid |
|
|
The Henderson-Hasselbalck equation is? |
pH= pKa + log([conjugate base]/[weak acid]) |
|
|
pKa equals? |
-log(Ka) Ka is usually given |
|
|
Low pKa= ? High pKa= ? |
Low=strong acid High=weak acid |
|
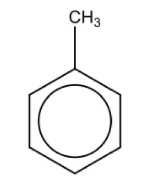
Name the structure: |
Toluene |
|
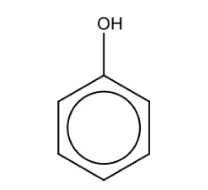
Name the structure: |
Phenol |
|
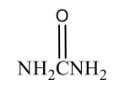
Name the structure: |
Urea |
|
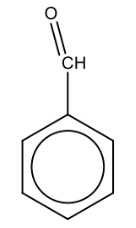
Name the structure: |
Benzaldehyde |
|
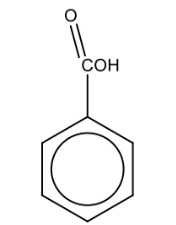
Name the structure: |
Benzoic acid |
|
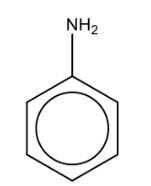
Name the structure: |
Aniline |

