![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an alkane |
Carbon atoms that are linked to four other atoms by single bonds |
|
|
Characteristics of alkanes |
Fairly unreactive Burn well |
|
|
What is the general formula for alkanes |
Cx H(2x+2) |
|
|
How is crude oil made ? |
Formed over millions of years from fossilised remains of dead animals Found in porous rock in earths crust |
|
|
Is crude oil finite ? |
Yes crude oil is finite (non renewable) |
|
|
What is crude oil made up of ? |
Crude oil is made up of hydrocarbons that are all different lengths |
|
|
Properties of larger hydrocarbons |
Don’t flow as easy Higher boiling points Less volatile Less easy it ignites |
|
|
How does a fractional distillation work |
First crude oil is heated until it evaporates The vapour moves up the fractionating column The top is a lot colder than the bottom Shorter hydrocarbons can reach the top before they condense and collected Longer hydrocarbon molecules condense at higher temperatures and are therefore collected closer to the bottom |
|
|
What length of alkanes are more wanted for fuels ? |
Smaller due to shorter alkanes releasing energy more quickly making them burn better |
|
|
What is the process of combustion |
The burning of a substance |
|
|
What are formulations |
Mixtures that have been carefully designed to have specific properties e.g fuels ,paint |
|
|
Why is paper chromatography |
During chromatography mixtures are separated into their constituent components The solvent dissolved the samples and carries them up the paper Each component moves a different distance up the paper depending on its attraction for the paper and for the solvent Chromatography is used to identify artificial colours by comparing them to the results obtained from know substances |
|
|
What happens when hydrocarbon fuels combust |
Both carbon and hydrogen are oxidised Energy is released Waste products are releases into atmosphere |
|
|
What happens if combustion with hydrocarbon fuels isn’t properly completed ? |
Carbon monoxide is released |
|
|
Properties of carbon monoxide |
Colourless Odourless And toxic |
|
|
What is cracking hydrocarbons |
Process of breaking longer chained hydrocarbons into smaller more useful hydrocarbons |
|
|
What is Catalytic cracking |
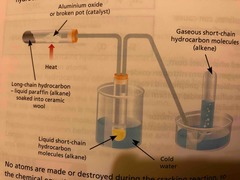
Hydrocarbons are heated until vaporised Vapour is passed over aluminium oxide catalyst A thermal decomposition reaction then takes place |
|
|
What is more reactive alkanes or alkenes |

Alkenes They react when shaken with bromine water turning it from orange to colourless This is used to differentiate the two |
|
|
What is Catalytic cracking |
Hydrocarbons are heated until vaporised Vapour is passed over aluminium oxide catalyst A thermal decomposition reaction then takes place |
|
|
What is more reactive alkanes or alkenes |
Alkenes They react when shaken with bromine water turning it from orange to colourless This is used to differentiate the two |
|
|
What is a pure substance |
A pure substance is a substance that only contains one type of element or one type of compound |
|
|
How do you test for hydrogen ? |
Thumb over test tube during reaction Move thumb and put Lit match over test tube If hydrogen is present it will make a squeaky pop |
|
|
How do you test for chlorine ? |
Put damp paper in it solution Chlorine will turn the paper white |
|
|
How do you test for oxygen ? |
Put thumb over test tube whilst reaction is happening Put glowing splint over test tube If oxygen is present the splint will relight |
|
|
How do you test for carbon dioxide ? |
Bubble the gas through limewater If limewater goes cloudy then carbon dioxide is present |
|
|
What made up the Start of earths atmosphere |
Intense volcanic activity led to most of the atmosphere being carbon dioxide with small pets being methan and ammonia |
|
|
What was the structure of earths atmosphere in the middle |
Less volcanic action Carbon dioxide is reduced as plants take it in and release oxygen Carbon from carbon dioxide gets locked up in sedimentary rocks formed from dead animals Other gases react with oxygen to realise nitrogen Nitrogen is also produced by bacteria
|
|
|
What is the atmosphere structure now ? |
There is about 20% oxygen and about 79% nitrogen with carbon dioxide and noble gasses making up about 1% |
|
|
Why is copper a useful metal ? |
Good conductor Easily bent but hard enough to make water pipes and tanks Doesn’t react with water so lasts a long time |
|
|
What is phytomining ? |
A method that uses plants to absorb copper which is then stored as the plants grow Plants are then burned to leave behind copper rich ashes |
|
|
What is phytomining ? |
A method that uses plants to absorb copper which is then stored as the plants grow Plants are then burned to leave behind copper rich ashes |
|
|
What is bioleaching ? |
Uses bacteria to extract metals from low grade ores A solution contains bacteria is mixed with a low grade ore The bacteria convert the copper into a solution (leachate solution ) where copper can be easily extracted |
|
|
What is potable water ? |
Water that is good enough quality to drink |
|
|
What are the steps taken to purify water ? |
1)Fresh water is collected from a suitable source 2)it’s passed through a filter bed to remove any solid particles 3) chlorine gas is added to kill any harmful microorganisms (ozone and ultraviolet can also be used ) 4)fluoride is added to drinking water to reduce teeth decay |
|
|
What are the steps taken to purify water ? |
1)Fresh water is collected from a suitable source 2)it’s passed through a filter bed to remove any solid particles 3) chlorine gas is added to kill any harmful microorganisms (ozone and ultraviolet can also be used ) 4)fluoride is added to drinking water to reduce teeth decay |
|
|
What is it called when sea water is made pure and what does it involve ? |
Desalination Where sea water can be distilled or reverse osmosis In distillation water is boiled to produce steam - steam condenses to produce pure liquid water |
|
|
What happens in sewage treatment? |
1)screening and grit removal 2) sedimentation to produce sludge and effluent 3)anaerobic digestion of Sewage sludge 4) aerobic biological treatment of effluent |

