![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe a process to make pure,dry crystals of salt from a metal oxide and dilute acid |
-Add acid to beaker -Warm acid -Add metal oxide -Stir -Continue adding untill metal oxide is in excess
-Filter, using filter paper and funnel -To remove excess metal oxide
-Heat solution in evaporating basin to crystallisation point -Leave to crystallise -Pat with filter paper |
|
|
Why do alkene batteries eventually stop working |
The reactant/electrolyte is used up |
|
|
Why are alkene batteries not rechargeable |
Reaction is not reversable |
|
|
Why cannot electrolysis happen with a solid electrolyte |
-Electrolyte is solid -So ions cannot move |
|
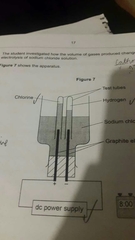
How should the apparatus be changed, with reason |
-Use a measuring cylinder -To measure volume of gas |
|

Describe trend |
-Hydrogen increased at a constant rate -Chlorine did not increase at a constant rate -Collection rate of chlorine accelerated |
|
|
Why would titanium chloride not be expected to be liquid at room tempreture |
-Metal chlorides are ionic -So high melting point -Because strong forces between ions |
|
|
Why can an acid be both strong and dilute |
-Strong = Completely ionised in aqueous solution -Dilute = Small amounts of acid per unit volume |

