![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How do you convert g —> mol ? |
Divide by molar mass. |
|
|
How do you convert from mol —> g ? |
Multiply by molar mass. |
|
|
How do you convert from mol —> particles ? |
Multiply by Avagadro’s number. |
|
|
How do you convert from particles —> mol ? |
Divide by Avagadro’s number. |
|
|
What is Avagadro’s number? |
6.022 x 10^23 |
|
|
________ is the number of entities composing one mole. |
Avogadro’s number. |
|
|
__________ is the amount of substance containing the same number of discrete entities as the number of atoms in a sample of pure 12C weighing exactly 12 g. |
The mole. |
|
|
Avogadro’s number is a(n) ______ number. |
Exact. |
|
|
What is meant by Avogadro’s number being an exact number? |
It does not have a set number of significant figures. It is an infinite number. |
|
|
___________ is the mass of one mol of anything. |
Molar Mass. |
|
|
g/mol is the unit for ___________. |
Molar mass. |
|
|
The empirical formula of a compound can be derived from...? |
The masses of all elements in the sample. |
|
|
_______ formulas give the lowest whole number ratio of atoms in a molecule. |
Empirical formula‘s. |
|
|
_______ formulas give the total number of atoms in a molecule. |
Molecular formulas. |
|
|
_______ formulas give the total number of atoms in a molecule. |
Molecular formulas. |
|
|
_______ compounds are always written as the empirical formula. |
Ionic compounds. |
|
|
________ : the relative number of particles in a given volume of solution. |
Concentration. |
|
|
________ : the relative number of particles in a given volume of solution. |
Concentration. |
|
|
________ : the component of a solution in the greatest quantity. |
Solvent. |
|
|
_______: the component of a solution which is dispersed in the solvent. |
Solute. |
|
|
Solutions where water is the solvent are called... |
Aqueous solutions. |
|
|
What is the formula for molarity? |

M = moles solute / liters of solution |
|
|
Chemical reactions take place on a _________, the most common unit of concentration for solutions is _______. |
Molar basis ; molarity. |
|
|
_______ is the process of making a solution less concentrated by adding more solvent. |
Dilution. |
|
|
Dilution is the process of making a _____ less concentrated by adding more ______. |
Solution ; Solvent. |
|
|
What is the formula to determine the concentration of a diluted solution? |

(C1)(V1) = (C2)(V2) |
|
|
____________ is the ratio of a solute’s mass to the mass of the solution, expressed as a percentage. |
Mass percentage. |
|
|
___________ is the ratio of a solute’s volume to the volume of the solution, expressed as a percentage. |
Volume percentage. |
|
|
What is the mass percentage formula? |
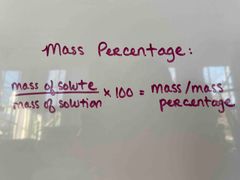
(Mass of solute/mass of solution) x 100 = mass/mass percentage. |
|
|
What is the formula for volume percentage? |
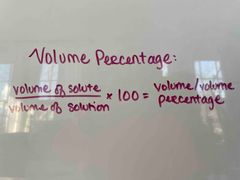
(Volume of solute/volume of solution) x 100 = volume/volume percentage |
|
|
___________ is the ratio of a solute’s mass to the solution’s volume, expressed as a percentage. |
Mass/volume percentage. |
|
|
What is the mass/volume percentage formula? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Mixed percent units (“mass/volume percentage”) are usually seen in... |
Healthcare. |
|
|
PPM stands for ______ and can be identified by 10^___. |
Parts per MILLION. ; 10^6. |
|
|
PPB stands for _______ and can be identified by 10^___. |
Parts per BILLION. ; 10^9. |
|
|
T/F: Parts per million (ppm) and parts per billion (ppb) are units calculated in a manner close to percentage (part per hundred). |
True. |
|

Front (Term) |

Back (Definition) |
|

Front (Term) |

Back (Definition) |
|

Front (Term) |

Back (Definition) |
|

Front (Term) |

Back (Definition) |
|

Front (Term) |

Back (Definition) |
|

Front (Term) |

Back (Definition) |
|

Front (Term) |

Back (Definition) |
|

Front (Term) |
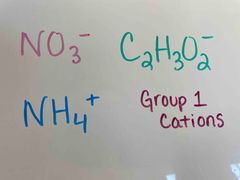
Back (Definition) |
|
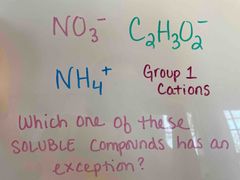
Front (Term) |

Back (Definition) |
|
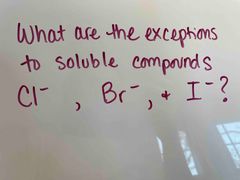
Front (Term) |
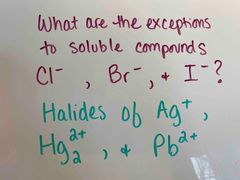
Back (Definition) |
|

Front (Term) |

Back (Definition) |
|

Front (Term) |

Back (Definition) |
|
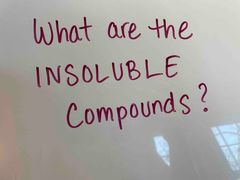
Front (Term) |
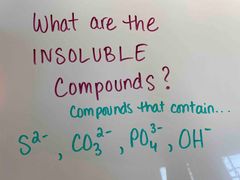
Back (Definition) |
|

Front (Term) |
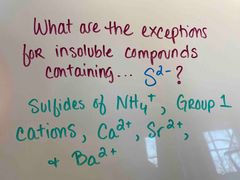
Back (Definition) |
|

Front (Term) |
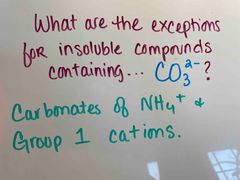
Back (Definition) |
|

Front (Term) |
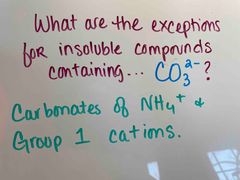
Back (Definition) |
|
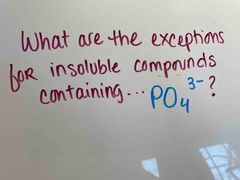
Front (Term) |
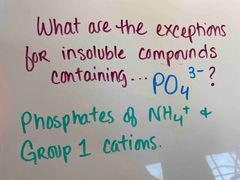
Back (Definition) |
|

Front (Term) |
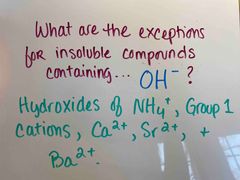
Back (Definition) |

