![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Chain of Infection: |
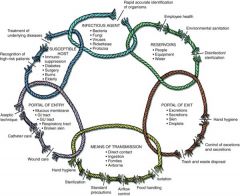
|
|
|
How do nurses contribute to the prevention of and spread of infection? |
|
|
|
A host |
a person who provides living conditions to support a microorganism |
|
|
A carrier |
a person who carries an organism without apparent signs and symptoms and is able to transmit an infection to others |
|
|
Colonization |
describes microorganisms present without host inference or interaction |
|
|
Infection |
indicates host interaction with the organism |
|
|
Disease |
the infected host displays a decline in wellness caused by the infection |
|
|
Information Resources |
- World Health Organization (WHO) - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) - Occupational safety and health administration (OSHA) - Local agencies - Hospital and facility infection control specialists and facility policies |
|
|
CDC |
is a federal agency responsible for monitoring endemic and epidemic disease, recommending strategies to decrease incidence, and developing guidelines to reduce risk to patients and health care workers |
|
|
Isolation Precautions |
- Guidelines to prevent the transmission of microorganisms in hospitals - Standard precautions used for all patients - The primary strategy for preventing HAIs - Transmission-based precautions are for patients with known infectious diseases spread by airborne, droplet, or contact routes |
|
|
Elements of Standard Precautions |
- Hand hygiene - Use of gloves and other barriers - Needle sticks - Proper handling of patient care equipment and linen - Environmental control - Prevention of injury from sharps and needles - Patient placement |
|
|
Organisms of HAI Infection Potential |
- C. diff
- MRSA - VRE - Multidrug-resistant gram-negative organisms How are these treated? Risks that can lead to C. diff, MRSA, VRE and multidrug-resistance gram-negative organisms? Need to know what type of precautions are used for each of these organisms. |
|
|
Airborne precautions |
Hospitalized patient should be in negative pressure room with the door closed; health care providers should wear an N-95 respirator (mask) at all times when in the room |
|
|
Droplet precautions |
Wear a face mask but door may remain open; transmission is limited to close contact |
|
|
Contact precautions |
Use of barriers to prevent transmission; emphasize cautious technique because organisms are easily transmitted by contact between the health care worker and the patient Know 3 vectors transmitted by each means |
|
|
Prevention of Infection |
- HAI bloodstream infections - Community-acquired infections - Vaccination programs - Planning for a pandemic Need to know. When thinking about vaccines, you must look at the big picture...Need to know and understand why nurses are required to get vaccines, particularly the flu vaccine. |
|
|
Emerging Infectious Diseases |
- West Nile virus - Legionnaires disease - Pertussis - Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome - Viral hemorrhagic fevers - Other resistant bacteria Nice to know. |
|
|
Reduction of risk to patients (Home-Based Care of Infectious Disease) |
- Care of equipment - Patient education |
|
|
Reduction of risk to household members (Home-Based Care of Infectious Disease) |
- Prevention of transmission - Education - Fever and comfort |
|
|
Health care workers (Home-Based Care Measures to Reduce the Risk of Infection) |
Health care workers should follow standard precautions in the home setting |
|
|
Patient and family education (Home-Based Care Measures to Reduce the Risk of Infection) |
- Establish an environment that facilitates hand hygiene and aseptic technique - Family caregivers should receive annual influenza vaccine - Equipment care - "Common-sense cleanliness" - Food preparation and personal hygiene - Establishment of reasonable barriers to protect family members |
|
|
Nursing Process: The Care of the Patient with an Infectious Disease - Assessment |
Health history: investigate the likelihood and probable source of infection, associated pathology and symptoms See questions listed in text (chart 71-5) Physical exam |
|
|
Nursing Process: The Care of the Patient with an Infectious Disease - Diagnoses |
- Risk for infection transmission - Deficient knowledge - Risk for ineffective thermoregulation |
|
|
Collaborative Problems and Potential Complications |
- septicemia, bacteremia, or sepsis - septic shock - dehydration - abscess formation - endocarditis - infectious disease - related cancers - infertility - congenital abnormalities |
|
|
Nursing Process: The Care of the Patient with an Infectious Disease - Planning |
Major goals may include prevention of spread of infection, increased knowledge about the infection and its treatment, control of fever and related discomforts, and absence of complications. |
|
|
Interventions |
1. Preventing the spread of infection - handwashing - standard precautions (standard: minimal for every patient) - recognition of mode of transmission and establishment of transmission-based precautions as indicated 2. Education about infectious process and the prevention of the spread of infections 3. Assessment and treatment of fever |
|
|
Diarrheal Diseases |
1. transmission 2. causes - bacterial - viral - parasitic |
|
|
Nursing Process: The Care of the Patient with an Infectious Disease - Assessment |
History: recent travel, use of antibiotics, food intake Hydration status: thirst, dry mucous membranes, weak pulse, loss of skin turgor, sunken eyes, I&O |
|
|
Nursing Process: The Care of the Patient with an Infectious Disease - Diagnosis |
- Deficient fluid volume - Deficient knowledge |
|
|
Collaborative Problems and Potential Complications |
- Bacteremia - Hypovolemic shock If the problems are collaborative, what would be included in any treatments? |
|
|
Nursing Process: The Care of the Patient with an Infectious Disease - Planning |
- Maintenance of fluid and electrolyte balance - Increase knowledge about disease and risk for transmission This is the plan, what is the goal? How would you measure if the goal were met? |
|
|
Correction of Dehydration |
- oral versus intravenous - mild, moderate, severe dehydration - oral-goal/ is goal met? - dehydration-goal/ is goal met? |
|
|
Vaccinations |
- goal of vaccination program - table 71-2 impact of vaccines on diseases (need to know) - nursing education of common vaccine (need to know) - review and know how varicella vaccine has affected the incidence of chicken pox - who, at what age and when is a person most susceptible to shingles |
|
|
Immunizations |
- How have immunizations impacted the United States and infectious disease? - If you had a parent who refused to immunize their child what would you do? |

