![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Population |
Group of individuals of a single species living in the same general area. Fundamental characteristics are; density, dispersion, and demographics |
The fundamental characteristics (3D) |
|
|
Density |
Number of individuals per unit area or volume |
|
|
|
Dispersion |
The pattern of spacing among individuals within the boundaries of the population |
|
|
|
What do each of these variables stand for- x/n=m/N |
x=number of marked animals recaptured in second sampling n=total number captured in second sampling m=number marked animals in first sampling N=estimated population size |
|
|
|
What equation is this- N=mn/x |
Equation for population size |
|
|
|
First trapped 80, all marked. Second trapped 75 mice, 48 were already marked. What is N |
80×75/48=125 |
N=mn/x |
|
|
Immigration |
Movement into a population |
|
|
|
Emigration |
Exiting of individuals from a population |
|
|
|
Territoriality |
Needing physical space and being defensive and aggressive |
|
|
|
Demography |
Study of vital statistics of populations and how they change over time |
|
|
|
Life tables |
Age specific summaries of the survival pattern of a population |
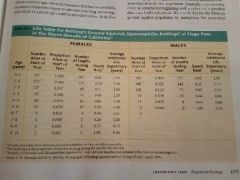
|
|
|
Cohort |
Group of individuals of same age from birth until death |
|
|
|
Survivorship curve |
Plot of the proportion or numbers in a cohort still alive at each age |
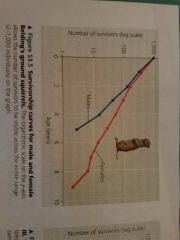
|
|
|
Reproductive table |
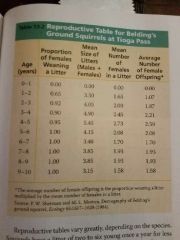
Age specific summary of the reproductive rates in a population |
Also known as fertility schedule |
|
|
Life history |
Traits that affect an organisms schedule of reproduction and survival Three main ones: Where reproduction begins How often the organism reproduces How many offspring produced through each reproduction episode |
Three traits |
|
|
Semelparity |
One-shot Produces a lot in one shot Ex: salmon produce thousands of eggs in a single reproductive opportunity before they die |
Also known as big-bang reproduction |
|
|
Iteroparity |
Reproduce multiple times through life Ex:some lizards lay eggs every year until death |
Also known as repeated reproduction |
|
|
Per capita birth rate |
Number of offspring produced per unit time by an average member of the population |
|
|
|
Per capita death rate |
Expected number of deaths per unit time in a population of any size |
|
|
|
Zero population growth (ZPG) |
It occurs when the per capita birth and death rates equal |
(r=0) |
|
|
What does r,d and b stand for? |
Per capita birth rate Per capita death rate Per capita rate of increase |
Per capita |
|
|
Exponential population growth |
-access to abundant food -free to reproduce at their physiological capacity Population increase under these conditions |
Also known as geometric population growth |
|
|
Logistic population growth |
Per capita of increase approaches zero as the carrying capacity is reached |
|
|
|
What does ◇N/◇t=rN used for |
A discrete, or fixed, time interval (often one year) and does not include immigration or emigration |
◇ is the triangle meaning change |
|
|
dN/dt=r'inst,N |
r'inst is simply the instantaneous per capita rate of increase Calculus equation used to express population growth instantaneously, as growth rate at a particular instant in time |
When is it used What does r'inst mean |
|
|
dN/dt=r'max,N |
Equation for exponential growth r'max stands for maximum rate for the species of the per capita rate of increase |
What is this equation What does r'max stand for |
|
|
What does N and t stand for in all equations in this chapter |
Population size -N Time- t |
|
|
|
Carrying Capacity |
Maximum population size that a particular environment can sustain |
Represented by K |
|
|
Sigmoid |
S-shaped growth curve. Happens when birth rate decreases, death rate increases or both |
|
|
|
Population dynamics |
Complex interactions between biotic and abiotic factors that cause variation in the size of populations |
Biotic & abiotic |
|
|
Metapopulation |
When multiple local populations are linked due to immigration and emigration |
Ex: immigration and emigration link ground squirrels population to other populations |
|
|
Metapopulation |
When multiple local populations are linked due to immigration and emigration |
Ex: immigration and emigration link ground squirrels population to other populations |
|
|
What are two possible configurations for a stable population |
Zero population growth= high birth rate- high death rate Zero population growth = low birth rate - low death rate |
|
|
|
Demographic transition |
Measures the change in both birth and death rates that affect a populations size |
|
|
|
Age structure |
Relative number of individuals of each age in the population |
|
|
|
Ecological footprint |
Concept that summarizes the aggregate land and water area required by each person, city, or nation to produce all the resources it consumes and to absorb all the waste it generates |
|

