![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Arteriosclerosis |
Arteri = artery Term means hardening of the artery |
|
|
Common root word meanings |
A word root (sometimes called a word stem) is the subject of a medical term and the foundation on which the term is built. The root is a word or word element that expresses the basic or general meaning of the term, and it is the base to which other word elements are attached to modify the meaning or form a new word. The meaning of a medical term is established by analyzing the other word elements (i.e., prefixes and suffixes) attached to the word root. |
|
|
Common suffixes |
A suffix is a word ending (suf means “beneath,” or, in this case, “behind”; fix means to “fasten”). It follows a word root and either changes or adds to the meaning of the word root. Generally, the best way to determine the meaning of a medical term is to first identify the meaning of the suffix. |
|
|
Common word elements |
The key to understanding medical terminology is knowing the meanings of the basic word elements that make up medical terms. Most medical terms are formed from two or more of these elements. If the meanings of the word elements are known, the general meaning of most medical terms can be established (though the actual definition may differ slightly). The three basic word elements, which are often derived from Greek and Latin words, are called word roots, prefixes, and suffixes |
|
|
ESR/sed |
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
|
|
Leukocyte |
White Blood cells. Leuk=white |
|
|
Myalgia |
My= muscle Algia = pain Muscle ache |
|
|
Nephritis |
Nephr = kidney Kidney inflammation |
|
|
Phalanx |
One finger |
|
|
Prefix |
A prefix modifies the meaning of the word root by adding information such as presence, absence, location, number, or size; this information makes the word more specific. |
|
|
Singular form of key words |
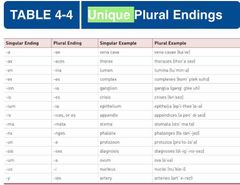
The plural forms (indicating more than one) of some medical terms follow English rules by adding “s” or “es” to the end of the singular term. Others have unique plural endings that follow the rules of the Greek or Latin from which they originated. It is important to evaluate medical terms individually to determine the correct plural form. Table 4-4 lists the unique plural forms of some typical singular medical term endings. |
|
|
PP |
Postprandial (after meal) |
|
|
UTI |
Urinary tract infection |
|
|
Suffix |
A suffix is a word ending (suf means “beneath,” or, in this case, “behind”; fix means to “fasten”). It follows a word root and either changes or adds to the meaning of the word root. Generally, the best way to determine the meaning of a medical term is to first identify the meaning of the suffix. |
|
|
Thrombosis |
Throm = clot Formation of a blood clot |
|
|
C sounds like S |
Cell, circulation, cytology |
|
|
G sounds like J |
Genetic, giardia, gyrate |

