![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
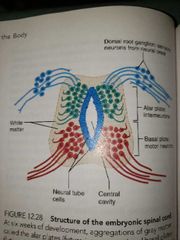
Dorsal Alar plate Ventral basal plate
Asar plate neuroblasts become interneurons
Basal plate neuroblasts become motor neurons and sprout axons that grow out to the effector organs |
Embryonic development of spinal cord |
|
|
Spinal dura meter |
Outermost tough fibrous layer Not attached to the bony walls of the vertebral column |
|
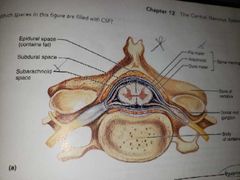
Epidural space |
Found between the bony vertebrae and the dorsal sheath Is a soft padding of fat and network of veins Injection site |
|
|
Subarachnoid space |
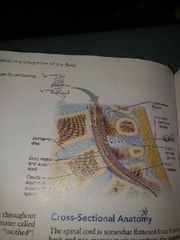
Between the arachnid and pia mater meninges Filled with CSF fluid Site for lumbar tap |
|
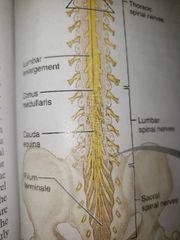
Conus medullaris Filum terminale |
Fibrous extensions of the conus medullaris covered by pia mater leads inferiorly to the coccyx, where it anchors the spinal cord, not jostled by body movements |
|
|
Dentculate ligaments |
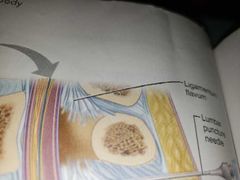
These help secure the spinal cord to the tough dura mater to the pia mater |
|
|
Inflammation of the meninges due to bacterial or viral infection |
Meningitis |
|
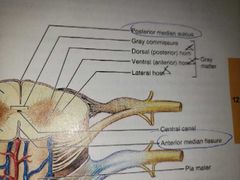
Posterior median sulcus--shallow Anterior median fissure--deep |
Partially divide the spinal cord into right and left halves |
|
|
Gray commissure |
Gray matter of the cord looks like a butterfly Posterior parts are the DORSAL HORNS anterior parts are the VENTRAL HORNS |
|
|
All neurons occupying the gray matter of the cord are multipolar. Name the neurons found |
DORSAL HORNS----HOUSE INTERNEURONS VENTRAL HORNS----HOUSE SOMATIC MOTOR NEURONS |
|
|
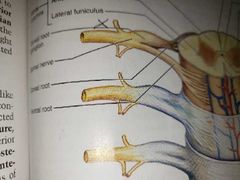
Lateral horn neurons |
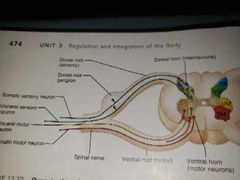
Are autonomic motor neurons that serve visceral organs They leave via the ventral root |
|
|
Ventral horns send their axons out via the ventral roots of the spinal cord to? |
Skeletal muscles [ effector organs] |
|
|
Afferent fibers carrying impulses from peripheral sensory receptors |
Dorsal roots To the spinal cord |
|
|
White matter of spinal cord |
Composed of myleinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers that allow communication between different parts of the spinal cord and between the cord and brain Run in 3 directions,: ASCENDING--up to higher centera DESCENDING---down to the cord from the brain or within the cord to lower levels TRSNSVERSELY----across from one side of the cord to the other |
|
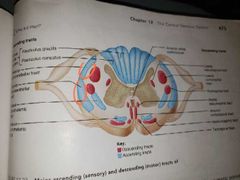
Ascending pathways to the brain |
Spinocerebellar tract [ anterior and posterior] Dorsal white column |
|
|
Afferent fibers |
Carry sensory signals from receptors to the CNS |
|
|
Efferent fibers |
Carry motor signals from CNS to its effectors |
|
|
Somatic fibers |
Innervate skin, skeletal muscles, bones, joints |
|
|
Visceral fibers |
Innervate blood vessels, glands, and viscera |
|
|
Dense outer network of collagen fibers |
EPINEURIUM |
|
|
Perineurium |
Middle layer that separates nerve into fascicles |
|
|
Endoneurium |
INNERMOST layer that surrounds individual neurons |
|
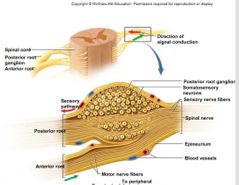
Direction of signal conduction into and out of the spinal cord |
Sensory info comes in through the POSTERIOR ROOT cell bodies of the ANTERIOR ROOT carry motor information to effectors |
|
|
Nonspecific ascending pathways |
Receive inputs from many different types of sensory receptors and make multiple synapses in the brain stem. |
|
|
Nonspecific ascending pathways |
Receive inputs from many different types of sensory receptors and make multiple synapses in the brain stem. |
|
|
Anterolateral pathways |
Located in the anterior and lateral white columns of the spinal cord Crossover of fibers occurs in the spinal cord Transmit pain, temperature,and course touch impulses sensations |

