![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Global Mindset |
Combines an openness to and an awareness of diversity across markets and cultures with a propensity and ability to synthesize across this diversity. |
|
|
Leadership |
The behaviors and processes involved with organizing a group of people in order to achieve a common purpose or goal. |
|
|
Global Leadership Roles |
Monitoring: scanning environment, seeking info Spokesperson: represent company, communicating info Liaison: networking, coordinating Leader: motivating and coaching Negotiator: making deals, manage conflict Innovator: new ideas, promote company Decision Maker: troubleshoot, make decisions Change Agent: take action, change plans for company |
|
|
Global Leadership Skills |
-Adaptability across cultures -Capability to develop individuals from and across diverse cultures -Global strategic thinking -Ability to establish business in new markets -Capability for building global teams -Competency in interacting with local political interests |
|
|
Global Leadership Triad |
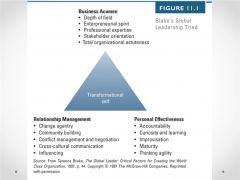
|
|
|
Pyramid Model of Global Leadership |

|
|
|
Global Leadership Expertise Development (GLED) Model |
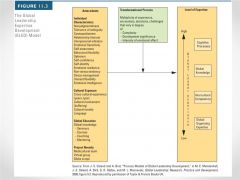
|
|
|
Global Team |
A team characterized by a high level of diversity, geographic dispersion, and virtual rather than face to face interaction |
|
|
Team norms |
Legitimate, shared standards against which the appropriateness of behavior can be evaluated |
|
|
Social loafing |
Tendency of some people to put forth less effort when they are members of a group |
|
|
Change Model: Kurt Lewin |
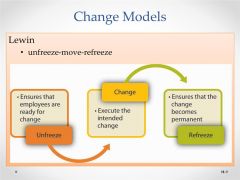
|
|
|
Change Model: John Kotter |

|
|
|
Leading Global Teams |

|
|
|
Differences between Traditional and Global Teams |
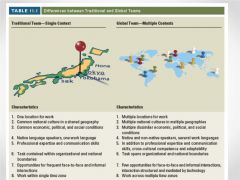
|
|
|
Critical issues for performance management in global teams |

|
|
|
When choosing rewards |
1. What is the nature of the task? Greater the task independence, the higher the portion of team-based rewards should be 2. How stable is team membership? If team boundaries are fluid or if membership changes are frequent, appropriate team rewards will be difficult to determine 3. What are the national cultures of the team members? With high levels of cultural diversity, the team should be involved in the development of the reward system 4. What are the labor laws that affect employee compensation? Salary levels are set by local or national laws or by labor unions 5. What are the available reward options? Recognition is a valued reward. These rewards are most successful when they incorporate national cultural values of team memebers |

