![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
80 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a parameter? What is statics? |
Population is parameter ; sample is statists |
|
|
The height of a histogram bar represents: |
Absolute frequency |
|
|
What is MEAN ABSOLUTE DEVIATION? |
Sum of |Xi-avg X|/N |
|
|
How to calculate quintile and quartile in a set of samples? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is Chebysgevs inequality? |

|
|
|
Difference between coefficient of variation and standard deviation? |
Coefficient of variation is relative and scale free but standard deviation is absolute |
|
|
What is coefficient variation ?how to calculate it? |
Coefficient variation is every units of average value’s standard deviation; CV= Sd of x / avg of x |
|
|
What is 8% around the mean of Chebyshevs ? |
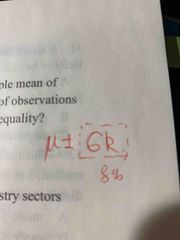
Back (Definition) |
|
|
For a positive skewed distribution is the mean bigger than the medium or smaller? For negative skewed Distribution is the mode smaller or bigger than mean? |
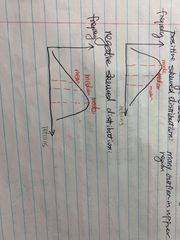
Back (Definition) |
|
|
A return distribution with frequent small gains and a few extreme losses is mostly likely to be called: |
Negatively skewed |
|
|
What is the sequence best represents the relative sizes of the mean median and mode for a positively screwed unimodel distribution |
Mean > median >mode |
|
|
What is the opposite of leptokurtic? What is normal distribution‘s kurtosis description? |
Negative kurtosis: plattkurtic Normal kurtosis: mesokurtic |
|
|
Went to use harmonic mean? |
Harmonic mean is appropriate for determining the average price per unit not evaluating a funds return history; Harmonic mean is applicable when ratios are repeatedly applied to a fix quantity to yield a variable numbers of units such as cost averaging |
|
|
What’s the order of arithmetic mean geometric mean and harmonic mean? |
A>= G>=H |
|
|
If the probability that Zola’s company sales exceed last years sales is 0.2, the odds for exceeding sales are closest to: |
1 to 4 |
|
|
What is exhaustive event? |
Events that include all potential outcomes |
|
|
What are permutation formula and combination formula? |
Permutation: chosen in specific order Combination: chosen and sequence doesn’t matter |
|
|
What is multinomial formula? |
Bionomial is part of the multi nominal. The experiment consists of k times repeated trial |
|
|
Pick r number of event from N number of events. If the sequence matter, what’s the formula for the number of groups? What if the sequence don’t matter? |
Sequence matter: n!/(n-r)! Sequence doesn’t matter: n!/(n-r)!*r! |
|
|
Over the last 10 years, a company’s annual earnings increases 7 times and decreased 3 times year over year, what is the probability that earnings will increase in exactly 5 of the next 10 years? |

|
|
|
What is the formula of binomial distribution formula? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
True or false? For a probability distribution for the number of days the air pollution is above a specific level PX =0 when x cannot occur, or PX >0 when it can |
True. Because it’s a discrete distribution |
|
|
For a probability distribution for the specific level of air pollution on a given day PX=0 even the X can occur |
True. Continuous distribution |
|
|
What’s the difference between Bernoulli random variables and binomial random variables? |
Bernoulli: only did once Binomial: did n times Both has two types of outcomes |
|
|
How many standard deviations of the mean will be within 95% percent of all outcome of a normal distribution? |
Z=1.96 so about 2 standard deviations |
|
|
Approximately 99percent of all outcomes of a normal random variables will be within how many standard deviations? |
3 standard deviations. Z=2.575 |
|
|
What is a multivariate distribution? |
The multivariate normal distribution is useful in analyzing the relationship between multiple normally distributed variables, and thus has heavy application to biology and economics where the relationship between approximately-normal variables is of great interest. Such as a portfolio of stocks rather than one stock |
|
|
How many parameters does multi variate normal distribution have? |
N means, n variances and n(n-1)/2 correlations. |
|
|
What’s covariance return formula on Ra and zen? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What are the probabilities for odds for and odds against? |
Odds for: p( happen)/p( not happening) Odds against: p( not happening)/p(happen) |
|
|
in a normal distribution, how much probability there is when k=1, k=1.65, k=1.96, k=2.58? |
k=1 P=68%, k=1.65 P=90%, k=1.96 P=95%, k=2.58 P=99% |
|
|
if a distribution's X~N(2,25), then P(3<=X<=4) is? |
step 1: normalize it by Z=[(3-2)/5] and Z=[(4-2)/5]; F (1/5<=Z<=2/5) step 2: calculation Z~N(0,1) F(2/5)-F(1/5) |
|
|
What are the features of lognormal distribution? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is using lognormal distribution to measure and what is using normal distribution to measure? |
Lognormal: only positive numbers such as stock prices; Normal distribution: numbers that can be both negative and positive, such as return |
|
|
Difference between Monte Carlo simulation vs historical simulation |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Difference between standard deviation and standard error? |
Standard deviation: from a set of sample Standard error: from n times of experiment each time there’s a mean; sigma X bar=sigma X/sqr of n |
|
|
What are the conditions for central limit Therom? |
N>=30 Know Mean and Sd |
|
|
What are the unbiased, efficiency and consistency about for the estimator? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Difference between normal distribution and t distribution? |
Normal distribution is a special example of t distribution. T distribution is more lower kurtosis and fatter tail |
|
|
What’s the formula for confidence interval for central therom estimation? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What are the characters of t distribution? |
1. Symmetrical 2. 决定t分布变量只有一个, degree of freedom n-1 3. Less peaked than normal distribution 4. T distribution converges to normal distribution as degree of freedom goes to infinity 5. Same significance level, t’s confidence interval is wider |
|
|
T distribution VS normal distribution? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is data mining bias? |
把偶然当必然 |
|
|
Is the hypothesis testing on population or sample? |
Population |
|
|
What are the characteristics for null hypothesis? |
Mu 0: Has an smaller than and equal sign |
|
|
What is Bernoulli trail example ? |
The flip of a coin; one of the twins; only two options available |
|
|
What is Bernoulli trail example ? |
The flip of a coin; one of the twins; only two options available |
|
|
How to calculate the compounded return? |
In (V1/v0) |
|
|
What’s the probability of generating the value of exactly 0.3 in a continuous uniform distribution? |
0 |
|
|
Monte Carlo simulation can be used to |
Test the sensitivity of a model to changes in assumptions |
|
|
Does Monte Carlo simulation require historical record? |
No |
|
|
What’s the Rf for safety first? |
Withdrawal/ total portfolio =rf Ri-rf/ sigma |
|
|
What’s the Rf for safety first? |
Withdrawal/ total portfolio =rf Ri-rf/ sigma |
|
|
Why lognormal distribution is more accurate for stock prices? |
Unbounded; always positive |
|
|
If we are using a set of table of data to calculate standard deviation, should we use sample standard deviation or population standard deviation? |
Sample deviation |
|
|
What aspect of the data makes us uncomfortable about using t tables to construct confidence intervals for the population mean forecast? |
When the sample is small and the distribution appears to be bimodal we cannot compute a confidence interval for the population mean because we have to probably sample it from a distribution that is not normal |
|
|
Explain the differences between constructing a confidence interval when sampling from a normal population with a no population barriers and sampling from a normal population with an unknown variance |
I know variance: 1. Use sample standard deviation 2. Use t distribution |
|
|
What’s the difference between Ho and H alternative? |
Ho: reject, has equal sign H alpha: accept , no equal sign |
|
|
What is P value? |
P is the the area of rejection, p>=0 |
|
|
What is the formula for correlation testing? |
1. Ho:P=0,Ha: p doesn’t equal to zero 2. t=r/ [(1-r^2)/(n-2)]^0.5=r*(n-2)^0.5/(1-r^2)^0.5 |
|
|
What are the distribution to test variances? |
One variance: chi Two variances: F |
|
|
What are type I and type II errors? |
Type I error: 冤枉 Type II error:纵容 |
|
|
What are type I and type II errors? |
Type I error: 冤枉 Type II error:纵容 |
|
|
What is power of test? |
When the hypothesis is wrong and reject P=1-P(II) |
|
|
What the correlation between Type I error and Type II error? How to reduce it? |
Negatively correlated; increase n population |
|
|
What are the difference between parametric tests and non parametric test? |
Parametric test is based on specific distribution of assumptions for the population; Even if the underlying distribution is unknown, parametric tests can be used on numerical data if the sample is large. A non-parametric test is when data do not meet distribution of assumptions when data are given in ranks or signsor groups, and they are used when numerical parameters are not known or do not meet assumptions about distributions |
|
|
When to use paired comparisons t test? |
When there null hypothesis saying Population mean one minus population mean 2 =0 versus HA population mean 1 minus population mean 2 doesn’t equal to zero; Where those samples are drawn from normally distributed populations with unknown variance the observations and the two samples are correlated |
|
|
Difference of calculating confidence interval and doing test to reject or not reject? |
Confidence interval: x= mu +/- Z* SD/sq root of n Test: (x-mu)/[sd/ sq root of n] to reject or not reject |
|
|
Null hypothesis is considered to be true unless the sample provides evidence showing it is false |
True |
|
|
If the data is normal distributed, variance is unknown, sample size is big, can we use Z distribution? If data is non normal distribution, sample is big, can we use Z? |
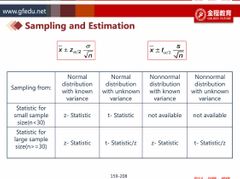
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What does statistically significant mean? |
The test got rejected. |
|
|
what is the ahlpha for a one tail test and two tail test for z distribtuion? |
alpha include all the rejectiona area no matter one tail or two tails |
|
|
Difference between exclusive and mutually exclusive |
Exclusive cover all the probability; Mutual exclusive: independent but doesn’t cover all probability |
|
|
How to calculate mean absolute deviation? |
|X-avg X|/N |
|
|
When a P-value is less or more than or equal to the significance level, do you reject the null hypothesis? |
less |
|
|
what happens if p-value is more than a significance level? |
fail to reject the null hypotheis |
|
|
what is a F test formula? |
F= S1^2/S2^2 |
|
|
when to use a pool estimator? |
pooled estimator is used when the two population variances are assumed to be equal |
|
|
when to use paired comparison? |
paired comparison test is used to test mean differences when the samples are assumed to be dependent. |
|
|
how to calculate economic profit? |
Economic profit = Accounting profit – Total implicit opportunity costs; Accounting profit = Total revenue – Total variable costs – Total fixed costs; Total opportunity costs = opportunity cost of capital + opportunity cost of labor |

