![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
151 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What happens to period and wavelength when frequency increases |
Both decrease (think more signals equals less space) |

|
|
|
Murmur w MR and TR |
Holosystolic murmur |
|
|
|
Murmur w MVP |
Mid systolic click |
|
|
|
Murmur w AS and PS |
Systolic ejection Crescendo-decrescendo |
|
|
|
Murmur w AI |
Diastolic murmur |
|
|
|
What is the Austin Flint murmur |
Indicates AMVL flutter from AI |
|
|
|
Murmur w PI |
Diastolic murmur |
|
|
|
Murmur w PDA |
Continuous and machine-like (machinery) |
|
|
|
Murmur w pericarditis |
Pericardial rub |
|
|
|
Heart located in __________ |
Mediastinum |
|
|
|
Pulmonary circuit starts at ___ and ends on ________ |
Starts at PA and ends on pulm veins |
|
|
|
Systemic circuit starts on ______ and ends on ______ |
Starts in AO and ends on SVC & IVC |
|
|
|
Coronaries fill mainly in _______. Flow goes ______ to _______ |
Diastole Epic to endo |
|
|
|
RA receives deoxygenated blood from 3 places: |
SVC, IVC, coronary sinus |
|
|
|
Lowest O2 concentration located in _______ |
Coronary sinus |
|
|
|
LA receives oxygenated blood from: |
The lungs via the 4 pulm veins |
|
|
|
RV ejects blood to the _____ through what? |
To the PA through the infundibulum (RVOT) |
|
|
|
LV ejects blood to the____ through what? |
To the AO through the LVOT |
|
|
|
First 2 branches/vessels of the AO are the coronary arteries. What 2 arteries? |
Sinuses of valsalva: LCA & RCA |
|
|
|
First branch out of the AO Arch |
Brachiocephalic or Innominate |
|
|
|
Another name for innominate artery? |
Brachiocephalic |
|
|
|
Second branch off of AO Arch |
Left common carotid |
|
|
|
3rd branch off of AO Arch |
Left subclavian |
|
|
|
Two branches of brachiocephalic artery |
Right subclavian Right common carotid |
|
|
|
Left coronary bifurcates into _____ and ______ |
LAD & LCX |
|
|
|
Right coronary artery becomes _______ |
Right posterior descending |
|
|
|
Leaflets of MV |
Anterior & Posterior |
|
|
|
Leaflets of TV |
Anterior & posterior & septal/ medial |
|
|
|
Leaflets of AV |
Right & left & non/ posterior |
|
|
|
Leaflets of PV |
Right & left & anterior |
|
|
|
The_______ is a continuation of the posterior AO root |
AMVL |
|
|
|
What is the most anterior chamber of the heart? |
RV |
|
|
|
What is the most anterior major vessel of the heart? |
PA |
|
|
|
What is the oxygen content of the right side and left side of the heart? |
Right- 75% Left- 95-100% |
|
|
|
What is the oxygen content of the coronary sinus |
Lowest O2 content in body <60% |
|
|
|
Frank starling law explains what? |
What comes in must come out |
|
|
|
Frank starling law increases fiber length/ tension T/F |
True |
|
|
|
Vaso- vasorum means |
Vessels of vessels |
|
|
|
Preload= volume overload and results in: |
Results in regurgitation and dilatation |
|
|
|
Afterload= pressure overload and results in: |
Results in stenosis and hyperteophy |
|
|
|
B-bump or B-notch indicates what? |
Increased LVEDP |
|
|
|
Where is B-bump or B-notch seen? |
On M-mode of MV after A wave/point |
|
|
|
The heart is a single tube around day _____ and forms completely by ____ days |
Tube at 22 days, completely formed by 43 days |
|
|
|
Foramen Ovale becomes: |
Fossa Ovale/Ovalis |
|
|
|
Is foramen ovale/ fossa ovale remains open it becomes: |
PFO |
|
|
|
Ductus arteriosus becomes: |
Ligmentum arteriosum |
|
|
|
If ductus arteriosus/ ligamentum arteriosum remains open, it becomes: |
PDA |
|
|
|
CO formula = |
HR x SV / 1000 |
|
|
|
Define cardiac output |
Amount of blood ejected w every minute |
|
|
|
Stroke volume formula = |
EDV- ESV |
|
|
|
Define Stroke volume |
Amount of blood ejected w every heartbeat |
|
|
|
What % of the max heart rate do we need for stress testing? |
85% |
|
|
|
Max HR formula= |
220-age |
|
|
|
Marfan’s is a _____ disorder and consists of what findings? |
Connective tissue disorder MVP Dilated aorta |
|
|
|
Down's syndrome/ Trisomy 21 consists of what findings? |
AV canal ASD VSD |
|
|
|
Noonan's syndrome is associated w______ |
PS |
|
|
|
Ehlers Danlo’s syndrome is a _______ disorder and consists of what finding(s)? |
Connective tissue disorder Dilatation of aorta |
|
|
|
Kawasaki's syndrome is due to |
Coronary aneurysms (think Micky Mouse in children) |
|
|
|
Takayatsu's arteritis is associated w: |
Multiple coarctations |
|
|
|
What causes MS |
Rh fever Parachute MV Double orifice MV |
|
|
|
Describe MS 2D findings |
Hockey stick Dilated LA Blood stasis/SEC/ smoke Thrombus formation in LAA PHTN RHF Normal/small LV |
|
|
|
MS will demonstrate a velocity of _____ |
>1.3 m/s and will be mosaic in color |
|
|
|
MVA formula = |
220/PHT |
|
|
|
Severe MS grading: |
<1cm2 >10 mmHg |
|
|
|
What are the causes of MR? |
MV apparatus (leaflets, chordae, annulus, papillary muscles, LV free wall below annulus) Dilated LV, MVP, veggies, thrombus, masses |
|
|
|
2D findings with MR |
Dilated LA and anything that could cause MR |
|
|
|
What are the causes of AS? |
Degenerative & calcification & BAV |
|
|
|
2D findings with AS: |
LVH, post stenotic dilatation of AO, dilated LA Thick/calcified leaflets, sclerosis, dining |
|
|
|
Velocity is _____ with AS |
>1.8 m/s or 2 and mosaic in color |
|
|
|
What is the formula for AVA |
LVOTd x .785 x LVOT TVI / AV TVI |
|
|
|
How to calculate pressure based on Bernoulli's? |
4V^2 (use any velocity, can be TR, PI, AI, MR) |
|
|
|
What are the causes of AI? |
Dilatation Endocarditis Marfan's Stenosis Dissection Trauma |
|
|
|
What are 2D findings with AI? |
Stressing for AI: dissection, diastolic flutter of AMVL, LV dilatation |
|
|
|
What are the causes of AI? |
Dilatation Endocarditis Marfan's Stenosis Dissection Trauma |
|
|
|
With severe AI, what valves open and close early? |
MV closes early, AV opens early |
|
|
|
What are the causes for PS? |
Congenital> TOF, noonans, pulm atresia
|
|
|
|
What is the Fontan procedure |
Done fore TV and PV atresia Done for hypoplastic LV & RV |
|
|
|
The goal of the Fontan procedure is to do what? |
Redirect vena cava blood flow to pulmonary artery |
|
|
|
What is the Mustard procedure? |
Done for transposition of the great vessels (TGA) |
|
|
|
What is the goal of the Mustard procedure |
Redirect vena cava flow to the LA> LV> Lungs |
|
|
|
Why is the Senning procedure done? |
Done for TGA Known as atrial switch |
|
|
|
Why is the Jatene procedure done? |
Done for TGA Known as arterial switch |
|
|
|
Ball in cage is known as the __________ prosthetic valve |
Ball in cage= Starr-Edwards |
|
|
|
St Jude is knows as __________ prosthetic calve |
St Jude= bileaflet |
|
|
|
Tilting disk is known as ________ prosthetic valve |
Tilting disk= Bjork- Shiley |
|
|
|
Medtronic Hall is a __________ type of prosthetic valve |
Mechanical |
|
|
|
The Carpentier-Edward is known as a ________ valve |
Bioprosthetic |
|
|
|
With prosthetics, velocity of flow will be higher than normal T/F? |
T |
|
|
|
What are prosthetic valves likely to develop? |
Endocarditis Pannus Thrombus formation Dehiscence Artifacts |
|
|
|
P- wave = |
Atrial kick |
|
|
|
QRS = |
Vent depolarization (vent systole) |
|
|
|
T wave = |
Vent repolarization (vent diastole) |
|
|
|
Order of electrical pathway through the heart |
SA node>AV node>Bundle of His>Rt/Lt bundle branches>Purkinje network |
|
|
|
What is normal sinus rhythm: beats and on EKG |
60-100 bpm UprightP waves following QRS, Lead 2 |
|
|
|
HR below 60 means what? |
Bradycardia |
|
|
|
HR above 100 means what? |
Tachycardia |
|
|
|
_____ valves open after IVRT |
AV valves-MV & TV |
|
|
|
______ valves open after IVCT |
Semilunar valves- AV & PV |
|
|
|
IVRT consists of a pressure change while volume does not change. The pressure in the ________ drops below the pressure in the ________ |
Ventricles Atria |
|
|
|
During IVCT, pressure changes but volume stays the same. All valves are ______ |
ALL valves closed |
|
|
|
During IVCT the pressure in the ________ is higher than the pressure in the _______ |
Ventricles Aorta and PA |
|
|
|
EDV is measured on the _____ wave of the EKG |
R wave |
|
|
|
ESV is measured on the _____ wave in EKG |
T wave |
|
|
|
What does COCO stand for? |
MV & TV Close AV & PV Open AV & PV Close MV & TV Open |
|
|
|
What is the best view to visualize an ASD? |
Subcostal |
|
|
|
What is the most common ASD? |
Secundum |
|
|
|
Where is secundum ASD locates? |
Fossa ovale area, mid-septum |
|
|
|
This type of ASD is associated with AV canal |
Primum |
|
|
|
Where is a primum ASD located? |
Close to AV valves |
|
|
|
Describe Fetal circulation: foramen ovale |
Increase in LAP closes flap and foramen ovale becomes fossa ovalis. If it doesn’t close it becomes the patent foramen ovale PFO |
|
|
|
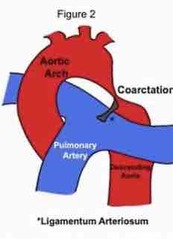
Describe fetal circulation: ductus arteriosus |
Ductus arteriosus closes and becomes ligament in arteriosum within 21 after baby is born. If it does not close it becomes patent ductus arteriosus PDA |
|
|
|
Visceral layer of the heart continuous with _______ |
Continuous with epicardium |
|
|
|
Visceral _________ Parietal _________ |
Inner Outer |
|
|
|
Layers of the parietal |
Epi-Myo -Endo |
|
|
|
Most anterior chamber of the heart? |
RV |
|
|
|
Most anterior chamber of the heart? |
RV |
|
|
|
Most posterior chamber of the heart? |
LA |
|
|
|
Most right sided chamber of the heart |
RA |
|
|
|
Most inferior chamber of the heart? |
LV |
|
|
|
Name the 2 grooves |
1- AV/atrioventricular groove 2-interventricular groove known as coronary sulcus |
|
|
|
Name the 2 grooves |
1- AV/atrioventricular groove 2-interventricular groove known as coronary sulcus |
|
|
|
What does the coronary sinus drain into? |
RA |
|
|
|
Pulmonary circulation begins and ends where? |
Starts PA and ends in plum veins. Low pressure |
|
|
|
Systemic circulation begins and ends where |
Starts in Aorta and ends in IVC/SVC |
|
|
|
_______carry blood to the heart |
Veins |
|
|
|
_______carry blood to the heart |
Veins |
|
|
|
_______ carry blood away from the heart |
Arteries |
Think Ateries Away |
|
|
What are the first vessels of the ascending aorta? |
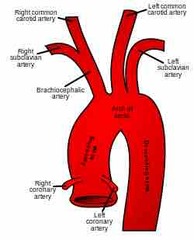
RCA and LCA |
|
|
|
It is not true that all veins carry oxygenated blood |
False |
|
|
|
Stroke due to one thing from the left side can be due to an embolic event. T/F |
False- left side stroke cannot be due to clots from the legs or embolic events because they involve the right side only |
|
|
|
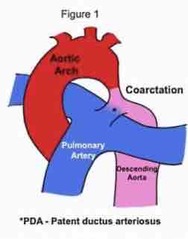
Where is the aortic isthmus? What commonly occurs here? |
Aortic isthmus is the area of the descending aorta just after the left subclavian artery. It is common for coarctations to occur here |
|
|
|
Coronary arteries fill mainly in _________ |
Diastole (think Mercedes Benz sign- valve must be closed) |
|
|
|
In general, RCA feeds what wall/s? |
Inferior |
|
|
|
In general, LAD feeds what wall/s? |
LAD= Triple A Anterior, Anteroseptal, Apical |
|
|
|
In general, LAD feeds what wall/s? |
LAD= Triple A Anterior, Anteroseptal, Apical |
|
|
|
In general, LCX feeds what wall/s? |
Later walls |
|
|
|
Eustachian=________ |
Fossa |
|
|
|
Eustachian=________ |
Fossa |
|
|
|
Thebesian=_________ |
Coronary sinus |
|
|
|
Infundibulum refers to what region? |
The region in the RVOT just before the pulmonic valve |
|
|
|
Pulmonary veins drain into the______ |
LA |
|
|
|
____________ is a continuation of the AMVL |
Posterior aortic root |
|
|
|
What view visualizes the posterior leaflet of the TV? |
RVIF view is the only view to visualize the posterior leaflet |
|
|
|
What are the LV walls visualized in PLAX? |
Anteroseptal and inferolater Cannot visualize apical wall segment |
|
|
|
B bump on MVIF pattern is indicative of ________ |
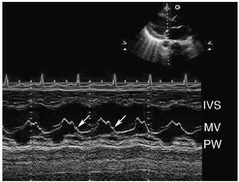
Increased LVEDP |
|
|
|
QRS |
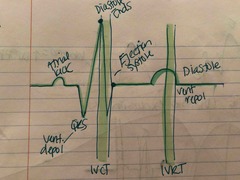
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What happens during IVCT and IVRT |
No volume change All valves closed |
|
|
|
Systole last from _____ to________ |
J point to end of T wave |
|
|
|
Systole last from _____ to________ |
J point to end of T wave |
|
|
|
Diastole lasts from ________ to _______ |
End of T wave to R wave |
|
|
|
The purpose of Ca during IVRT is to initiate what? |
Cardiac contraction Ca ions increase cardiac contraction |
|

