![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Behaviourism 1 |
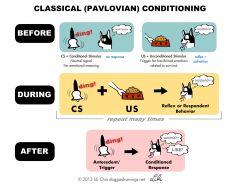
|
|
|
Behaviourism 2 |
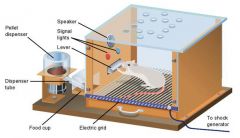
Skinner 1948 Neutral operants responses from the environment that neither increase nor decrease the probability of behavior being repeated Reinforcers: responses from the environment that increase the probability of behavior being repeated. Reinforces can be either positive or negative Punishment: responses from the environment that decreases the likelihood of a behavior being repeated. punish,et weakens behavior. |
|
|
Schema theory (retrieval) |
Bransford and johnson (1972) Bartlett argued that schematic influences were erected mostly during retrieval. This idea was tested by having participants listen to a long speech containing 18 discreet ideas. There were 3 conditions No title given before Title given after Recalled No title: 2,8 ideas on average Title before: 5.8 Title after: 2.5 |
|
|
Schemas and eyewitness testimony |
(loftus and palmer 1974) Participants asked to watch 7 clips of car accidents 7 clips were different length ,5 - 39 seconds after each clip a number of questions were asked, including one leading question. these question yielded different answers How fast (MPH) were the cars going when they: contacted: 31,8 hit: 34 bumped: 38,1 collided:39,3 smashed: 40,8 We are influenced by the way we are asked questions, as works reflect recalling memory. Different schemata get activated depending on the words which are used. |
|
|
Stress effect on recall |
Iglebaek et al (2003) Tested the idea that being at the scene had the additional stress that could affect recall had two groups of participants look at live staged robbery(n62) or the same scene on video (n64). They found that the video group had higher average recall than the live group Conclusion: past research might be underestimating the effect of stress in a real life situation. |
|
|
Stress effect on recall |
loftus (1987) Weapons effect Condition 1: no weapon; man with greasy hand emerged holding a pen. Condition 2: weapon; a man emerged holding a paper knife with blood on it. People li allocated their attention to the weapon which led to them recalling the first conditions man more accurately. |
|
|
Multi store model of memory |
Peterson and peterson (1959) participants memorize consonant triplets (gro,bjw etc) to memories. presented one at a time then asked to count 3 digit numbers backwards before recall. counting task took 3,6,9,12,18 seconds between conditions as time increased performance became progressively worse Supports MSM Problems. random letters are not important thus it's not a fair test of memory. |
|
|
Multi store model of memory (short term memory) |
Glanzer and cunitz (1966) Serial position words with delayed (DFR) and immediate (IFR) free recall Participants presented with 15 words to memorise Half in IFR condition half in DFR condition (30) second delayIn DFR rehearsal was prevented by counting backwards Results were recorded using serial position curve(ie rates of recall for each word were recorded in the order that they were presented) |
|
|
Levels of processing |
Craik and Tulving (1975) Participants were shown a list with 60 words along with each word the were shown one of three questions each testing a different level of processing similar to: Was the word in capital letters or lowercase?Does the word rhyme with (another word) Does the word fit in the following sentence They found that participants were better able to recall words which had been "processed more deeply". |
|
|
Aprasial of emotion |
Speisman E al 1964 Participants watched a film of aboriginal boys undergoing a puberty rite (circumcision=4 conditions accompanied by a soundtrack Trauma: pain of the boys and sharp knife emphasised Denial: Boys anticipation of entering manhood focused on, de emphasising painful aspects. Intellectualization: Ignored emotional aspects of the film and looked at culture and traditions silent: no soundtrack Trauma highest lowest intellect and silent middle denial |
|
|
Aprasial of emotion |
Smith and lazarus 1993 Asked participants to identify with a character the Character had poor performance on an important course. two conditions: either they were accountable for poor performance or the teacher was to blame results were as you would expect. |
|
|
Emotion |
Herrald and Tomak 2002 Investigate anger shame and pride had participants express an opinion of someone related to their study. Emotions were induced as a confederate would express something in line with lazarus Eg: you should have worked harder if that's an issue you did really well in that situation don't think anyone cares you feel that way. |
|
|
Unconscious processing |
Öhman 2000 Presented pictures of spiders and snakes to those who fear them and those who did not One condition allowed the participants to consciously process the image one presented the image for 30 MS followed by a neutral, meaning no conscious processing could take place. indicated that they had a fear response though they were not consciously aware of images. |
|
|
Unconsious processing |
Whalen et al 1998 fMRI experiment stimuli used were aces showed a fear expression for 30 MS followed by a neutral expression (same subject in pic) subjects did not report seeing the expression however,activation was found in the amygdala (associated with fear and flight or fight response) |

