![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Meaning and types of budgets |
Financial plan for the future * Income* Expenditure * Profit |
|
|
Variances formula and how answer is expressed |
Actual - Budgeted Fav = More profit Adv = Lower profit |
|
|
What ways can budgets be set |
* Historical budgeting - Update from previous year * Zero based budgeting - plan from nothing, based on new proposals and more accurate. |
|
|
Budgeting ADV/DIS |
* Control in & out
* Delegate to departments = motivated * Staff motivated to meet targets * Restrictive decisions * Time consuming - updating * Does not focus on issues e.g. product * Rivalry of departments
|
|
|
Causes of cash flow problems |
* Low profit * Too much stock * Too much production capacity * Seasonal demand * Allowing too much Cr * Growing fast * Unexpected changes in the business |
|
|
Methods of improving cash flow ST & LT |
ST: * Debt factoring* Lower costs * JIT stock * CL - Overdraft (delay payments) * Sell surplus NCA or sale and leaseback * Improve efficiency & productivity * Increase LTL & Equity * Reduce spend on NCA * Better credit control on TR (e.g T&C, Cr check, disc for early)
|
|
|
Debt factoring |
* Third party buys TR at a discount (usually 5%)
* They chase the debts * Short term inflow
|
|
|
Net Profit Margin |
Net profit/Revenue x 100
How profitable business is high = better |
|
|
ROCE |
Net profit/Capital employed x 100
Return on investment |
|
|
Ways to improve profit |
* Increase quantity sold D/O demand
* Raise prices D/O price elasticity of demand * Reduce VC D/O quality * Reduce FC D/O quality & output decrease? * Increase output (economies of scale) D/O spare capacity, demand?
|
|
|
Hierarchy |
Levels where each level is responsible for level below |
|
|
Tall hierarchy |
* More layers * Narrow span of control * More control * Less delegation * Longer communication * More staff = Higher cost |
|
|
Flat hierarchy |
* Few layers * Wide span of control * More delegation * Faster communication * Less staff = Less cost |
|
|
Span of control |
No of people who report directly to a manager Narrow: * Less* Monitor more closely * Could de-motivate * More * Good for routine tasks * Indepandance |
|
|
De/Centralised |
Centralised: * Senior staff make decisions* Delegate more responsibility |
|
|
Delayering |
Removing layers of management from the hierarchy. * Faster communication & decisions* Lower costs * Redundancies could demotivate * Less opportunity for promotion |
|
|
Delegation Empowerment |
Delegation - assign tasks to workers Empowerment - enabling employees to make decisions once reserved for managers e.g. deal with customer complaints (links to decentralisation) |
|
|
Delegating ADV/DIS |
Assignment of responsibility to others to carry out specific activities. * Reduce management stress* Managers can focus on key tasks * Subordinates motivated * Potentially better decisions * Some businesses should not delegate * Depends on quality/experience of workforce * Could increase workload/stress on subordinates |
|
|
Workforce roles |
* Director
* Manager * Team Leader * Supervisor
|
|
|
Labour Productivity |
Output per period/No of employees |
|
|
Staff Turnover |
No of staff leaving/no of staff employed x100 |
|
|
Absenteeism |
No of staff absent/Total number of staff x100 |
|
|
Recruitment process |
* Vacancy
* Job description (Responsibility & Job title) * Person specification (qualifications, perso) * Advertise job * Process applications * Shortlist * Interview
|
|
|
Internal Recruitment |
Job given to staff already employed, involves promotion or reorganisation. * Cheap & quick* Familiar with business * Limits new ideas * Resentment from employees not chosen * Creates another vacancy |
|
|
External Recruitment |
Employed from outside the business * New ideas* More workers to choose from * Wide range of experience * Longer process * Expensive (ad's & interviews) * Still may not find a good candidate
|
|
|
Selection |
* Interviews * Assessment centres * Tests |
|
|
On-the-job Training |
Training in the workplace (Demonstration, shadow, mentor) * Easy* Cost effective * Productive * Meet colleges * Trainer quality? * Bad habits could be passed
|
|
|
Off-the-job Training |
Training away from workplace (courses, webinars) * Specialist skills* Intensive * Expensive * Lost working time & output * May still need induction
|
|
|
What is motivation and the advantages of it? |
The will to work * Better productivity* Better quality & customer service * Lower absenteeism & staff turnover * Lower training and recruitment costs
|
|
|
Financial Motivation |
Used more in tall structure * Salary* Bonuses * Commission * Perks |
|
|
Non-Financial Motivation |
Used more in flat structure * Empowerment* Promotion * Better communication * Better working environment * Teamwork * Job enrichment (challenging & interesting tasks) * Job enlargement (more tasks of similar complexity)
|
|
|
Maslow |
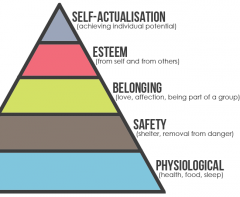
Hierarchy of needs People need basics first and have specific needs.
|
|
|
Herzberg |
Hygiene Factors: * Working conditions* Policy * Pay * Job enrichment & empowerment * Personal achievement & growth |
|
|
Taylor |
Scientific management People are in it for the money (should be paid on a piece-rate basis) |
|
|
Mayo |
Human relations More productive & motivated if: * Interaction* Teamwork * Socialising * Democracy |
|
|
Unit costs |
Total cost/output |
|
|
Capacity utilisation |
Output/capacity x100 * 100% = low quality & cant produce more * 90% good (economies of scale & low unit cost) * Can increase capacity by buying new machine |
|
|
How to add capacity to cope with extra unexpected demand |
Should predict demand but can add capacity by: * Subcontract* Overtime * Temporary * Part time staff * Manage stocks more effectively * Rationalisation |
|
|
Ways to improve productivity |
* Training (disrupt prod in ST)
* Motivation * More/Better capital equipment * Better quality raw materials = less waste |
|
|
Quality and how it affects a business |
Meets needs and expectations of customers High quality: * Lower costs (less waste, ads & complaints)* More revenue (rep, USP = charge more) * More profit * Cheaper * More complaints/wastage * Loose customers to competitors
|
|
|
Quality control & assurance |
Quality control: * Errors are unavoidable,* Inspectors check at end (high cost) * Quality built into production process * The whole organisation works toward it * Motivated employees |
|
|
TQM |
* Whole workforce working towards the highest possible quality
* Committed * Training to improve * Costly * Extra work could demotivate, but could offer staff rewards. * Better reputation, customer loyalty, USP, charge more, higher profits. |
|
|
ISO 9000 |
* Quality standard which proves quality
* Can be used as a marketing tool |
|
|
Kaizen continuous improvement Cell production JIT |
* Continuously examining ad improving quality and productivity
* Teams responsible for doing part of prod process, motivate * Reduces cost, need reliable suppliers |
|
|
Customer service and how it affects the business |
The way a business looks after its customers Good customer service * USP* Charge more * Repeat purchase & loyalty * More competitive * More sales * Word of mouth * Marketing tool |
|
|
Factors choosing supplies and how they can improve operational performance |
* Price (lower costs)
* Quality (satisfy customers, less waste) * Payment terms (improve cash flow) * Reliability (No delays) * Flexibility & Capacity (meet unexpected demand & JIT) * Few suppliers = economies of scale but dangerous |
|
|
Types of technology and ADV |
Robotics * Fast* Better productivity & quality * Less waste * More efficient, better decisions, lower admin cost * Faster internal/External * With customer online, loyalty card, direct marketing. |
|
|
Technology DIS |
* Constant updates
* Staff training to operate (cost) * Higher initial cost * Redundancies * Could de-motivate |
|
|
Marketing & Marketing Mix |
Marketing identifies, anticipates and satisfies customers needs and wants.
4P's Marketing mix can be influenced by finance, technology and market research 4P's need to work together
|
|
|
Niche and mass marketing |
Niche: * Small segment of larger market with specific needs and wants* Target particular customers * Less production * Charge more, high margins * USP * General targeting * Majority of market * High production * Success from low cost operation or leading brands
|
|
|
B2B marketing |
Requires relationships and after sales to succeed |
|
|
Product |
* Innovate (High risk, £R&D, High rewards. USP)
* Replace existing product * Imitate Can be Influenced by Technology, competitors actions & skills of managers and owners. |
|
|
Product Life Cycle |
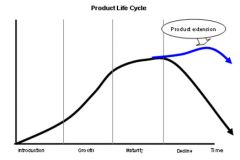
Product extention could involve a new market, re-design or promotion. |
|
|
Boston Matrix |
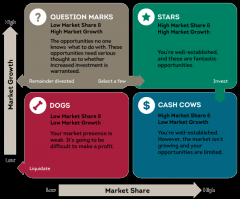
|
|
|
Price (7 types) |
Skimming - High price to maximise profit Penetration - Low price to gain market share Leader - Powerful brand that sets price Taker - Buyers dictate price (milk prod to Tesco) Predatory - Sell at loss to kill competition Loss Leader - Loss to attract to other products Psychological - high price = high quality, 99p |
|
|
Price elasticity of demand |
* PED 0 = Perfectly Inelastic (demand does not change at all)
* PED less than 1 = Inelastic (Demand barely changes) * PED more than 1 = Elastic (demand changes)
(However other factors also affect demand e.g. ads, season) |
|
|
Price elasticity of demand formula |
% Change in demand/% Change in price |
|
|
Place (types of selling & distribution) |
* Direct selling
* Indirect selling * Can use several e.g. online * Choose to suit needs and maximise profit * Depends on product e.g. high quality = exclusive stores, milk = everywhere. * Each party (e.g. retailer) called an intermediary |
|
|
Promotional mix |
The promotional techniques a business uses * PR - media* Branding - image that is recognisable * Merchandising - POS, Logo * Sales promotion - BOGOF * Direct selling - salesman * Advertising * Depends on lifecycle e.g. intro = more, competition, budget and product. |
|
|
Competitiveness depends on |
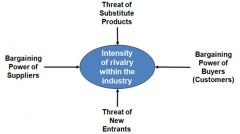
Monopoly Oligopoly Perfect competition
|
|
|
Methods of improving competitiveness |
* Marketing
* USP * Differentiate * Reduce costs * Customer service * Quality * Training * Better reputation = lower marketing costs & loyal customers = higher sales & profit |
|
|
Work out percentage changes |
Difference/Original x100 |
|
|
Exam tips |
* Think how and why when analysing * Always keep in context and use calculated figs when you can * Should lead back to point after analysed * Think about how it will affect other functional areas |
|
|
Efficiency Productivity |
Efficiency - resources used in production (e.g. materials) to get low cost per unit. Productivity - how much is produced in a certain amount of time, relation between inputs and outputs |
|
|
Finance |
Budgets Cash flow Measuring and increasing profit |
|
|
HR |
Organisational structure Recruitment selection and training Motivation |
|
|
Operations |
Capacity Quality Suppliers Customer service Technology |
|
|
Marketing |
Niche and mass Product Promotion Pricing Place Competitiveness |

