![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Types of Glia |
Macroglia (Astrocytes Oligodendricytes Schwann Cells) Microglia |
|
|
Neurons control |
Cells of CNS Informations processing and communication |
|
|
Astrocytes |
Provide structural matrix supporting neuronal networks. Control extra cellular chemical environment "blood-brain-barrier" |
|
|
Classes of neurons (3) |
Sensory Neurons- specialized to receive information from outside the world
Interneurons - act as bridges between the sensory and motor systems.
Motor Neurons- transmit commands from CNS directly to muscles and glands |
|
|
Dendrites |
Receive signals from adjacent Neurons |
|
|
Axons |
Transmit signals Axon hillock, terminal Myelination Nodes of ranvier |
|
|
Levels |
Circuit level Cellular level synaptic level Molecular level |
|
|
Neurotransmission |
1. Synthesis 2. Storage 3. Release 4. Receptor interaction 5. Inactivation 6. Re-uptake 7. Degradation |
|
|
Electrostatic force |
Opposite charges attract + and - |
|
|
Diffusion Force |
Molecules move from areas of high concentration to areas of lower concentration. |
|
|
Metabotropic receptors |
G protein causes ion channel to open and Ions pass through |
|
|
Ionotropic Receptors |
Channel opens and ions pass through after binding to ion channel |
|
|
What happens to neurotransmitters after they're released |
Diffusion Deactivation Enzymes Presunaltic Reuptake |
|
|
Extracellular fluid Intracellular fluid |
Extra = + Inter = - |
|
|
Depolarization |
(Increasingly negative) |
|
|
The interval in which no stimulus whatsoever can produce another action potential is known as the |
Absolute refractory period |
|
|
Diffusion and electrostatic pressure |
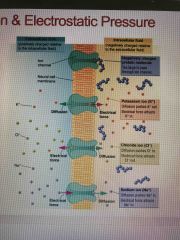
|
|
|
Closure of both voltage-dependent potassium and sodium channels results in |
Hyperpolarization |
|
|
The resting your own membrane allows ___ to cross freely |
Potassium |
|
|
Hypolarization |
Increasing positive |
|
|
Diffusion and electrostatic pressure |
|
|
|
What type of glia provides the structure for Neurons |
Astrocytes |
|
|
Mitochondria |
Extracts oxygen and pyurvic acid from sugar in the intracellular fluid. |
|
|
What types of glia supply myelin for the central nervous system |
Olgodendrocytes |
|
|
The most common structural neuron in the vertebrate nervous system is the |
Multipolar neuron |
|
|
What type of glia clean up dead cells and other debris |
Microglia |
|
|
The intercellular fluid of the resting neuron contains large numbers of |
Potassium ions |
|
|
The tendency for modules to distribute within a medium such as air or water is called |
Diffusion. |

