![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Experiment |
Uses IV and DV to examine change |
|
|
Quasiexperimental |
Used when IV cannot be manipulated, but can be observed |
|
|
Case Studies |
Examine rare or interesting cases of 1 or more individuals. However, can't be applied to all settings or people |
|
|
Pure Research |
Motivated by curiosity to acquire more knowledge |
|
|
Applied Research |
Conducted to provide a benefit to humans |
|
|
CT Scan |
Uses an xray to produce an image of the brain at rest, a STATIC image |
|
|
MRI |
Uses a magnet and a radio frequency to produce a STATIC image of the brain |
|
|
PET Scan |
Uses radio dye to produce an image of the brain at work, a DYNAMIC image |
|
|
fMRI |
Produced similar to MRI, but fMRI provides an image of the working brain, DYNAMIC image. One of best methods |
|
|
Diffusion Tensor Imaging |
Produces images of the tracts or connections in the brain |
|
|
TMS |
Uses a magnet to activate areas of the brain. Most commonly used to treat depression |
|
|
EEG |
Records electrical activity of the brain by placing electrodes on the scalp. PROs: easy to administer, non-invasive. CONs: not good localization, not sure what part of brain is producing activity |
|
|
EMG |
Records muscular activity. Can be used in sleep studies or on studying emotion. |
|
|
EOG |
Records eye movements. Used in sleep studies or in studies looking at visual attention. |
|
|
Monism |
Your brain makes you who you are |
|
|
Dualism |
Your mind and spirit make you who you are |
|
|
Anterior/Posterior |
Front/Back |
|
|
Dorsal/Ventral |
Top/Bottom |
|
|
Medial/Lateral |
Middle/Outside |
|
|
Proximal/Distal |
Close/Far |
|
|
What cells make up the Nervous System? |
Glial Cells and Neurons |
|
|
What are the different parts of the neuron? |
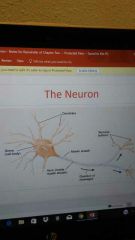
Dendrites, Soma (cell body), Myelin Sheath, Axon (inside myelin sheath), Terminal Buttons |
|
|
Soma (Cell Body) |
Keeps the cell functioning and holds the DNA |
|
|
Dendrites |
Receive stimuli in order for the cell to be active |
|
|
Myelin Sheath |
Myelin is the material that forms a layer around the axon of neuron. |
|
|
Axon |
Carries signals from the cell body to the terminal buttons |
|
|
Terminal Buttons |
Bulblike structures at the end of dendrites, contain neurotransmitters that carry the neurons message into the synapse |
|
|
Efferent Neurons |
Motory, exiting the brain |
|
|
Afferent Neurons |
Sensory, approaching the brain |
|
|
Frontal Lobe |
Personality, behavior, higher intellectual behaviors, cognition |
|
|
Parietal Lobe |
Receives and analyzes sensory information |
|
|
Occipital Lobe |
Vision |
|
|
Temporal Lobe |
Hearing, smell, learning, memory |
|
|
Cerebellum |
Motor learning, sequences of movement |
|
|
Spinal Nerves |
Cervical-8 Thoracic-12 Lumbar-5 Saeral- 5 Dorsal Root: coming in, sensory Ventral root: going out, motor |
|
|
Autonomic Nervous System |
Sympathetic: fight or flight Parasympathetic: feed or breed |
|
|
Meninges |
Connective tissues covering the brain and spinal cord. (Dura mater, arachnoid membrane, Pia mater) |
|
|
What do the brain and spinal cord develop from? |
Neural tube |
|
|
Why are pre-mature babies at risk for poor brain development? |
Its vulnerable because the brain cells aren't finished making connections, and outside stimuli |
|
|
Pruning |
Selective elimination of cells and cellular connections that are not being used.
Happens mainly to babies, also to adolescents |
|
|
Neurons and Stem Cells |
Seeds at which the nerves of the body grows Stem cells follow the neighbors Neuron cells already had a purpose |
|
|
Ventricle |
Cavity in brain containing cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) Four Ventricles: Two lateral ventricles (left and right) |
|
|
Neuron/Glial |
Neuron: basic unit of nervous system Glial: supportive function for neurons |
|
|
Reticular Formation |
Controls sensory information to isolate important things |
|
|
Tectum |
Produces dopamine, regulates motivation. Also plays a role in vision and hearing |
|
|
Hypothalmus |
Behavior, autonomic and endocrine functions. Temp, thirst, hunger, sleep, sex drive, Fighting, fleeing, feeding, formicating |
|
|
Hippocampus |
Long term memory, in Temporal lobe |
|
|
Nucleus Accumben |
Pleasure center of brain, reward system by releasing dopamine |
|
|
Prefrontal Cortex |
Anterior of frontal lobe, regulates personality |
|
|
Wernickes area |
Comprehending speech |
|
|
Brocas area |
Expressing speech |
|
|
Somatosensory cortex/strip |
Receives sensory information from body, touch, pain, temperature. |
|
|
Medulla |
Regulates breathing, heart and blood vessel function, digestion, sneezing, and swallowing |
|
|
Brain Stem |
Contains medulla oblagata and mid-brain pons. Associated with Sudden Infant Death Syndrome |
|
|
Tegmentum |
In midbrain, Motor movement in the eye, auditory and visual processing |
|
|
Pituitary gland |
Produces hormones |
|
|
Superior colliculi |
Receives major visual input through superficial layers.
In deep layers, receives audio.
Allows for visual-motor function (frog) |
|
|
Amygdala |
Regulates emotions and if memories are stored and where Can trigger anxiety |
|
|
Corpus Callosum |
Connects right and left hemispheres, communicates between the two sides. Sometimes cut to cure seizures |
|
|
Pons |
Controls sensation aspect of brain, key for dreaming during REM sleep. Controls rate of breathing. Relays signals from the forebrain to the cerebellum |
|
|
Spinal Nerves (two roots) |
Dorsal Root: to brain, sensory
Ventral Root: from brain, motor |
|
|
Cranial Nerves |
12 pairs, can be Sensory, Motor, or Sensory and Motor |
|
|
CNS location |
Brain and spinal chord. Sensory neurons |
|
|
PNS location |
Outside the skull and spinal chord...motor neurons |
|
|
Somatic Nervous System |
Interacts with the external, voluntary movements |
|
|
Autonomic Nervous System |
Regulates the body internally |
|
|
Nervous System Set-Up |
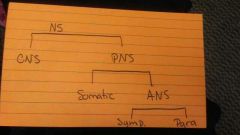
|

