![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
rectovesical (pouch)*** lies where?
Development of the Urinary Bladder |
In males, the base of the bladder lies between the rectum and the pubic symphysis
superior to the prostate, and separated from the rectum by the rectovesical (pouch)*** excavation. |
|
|
|
In males, the base of the bladder lies between the rectum and the pubic symphysis. It is superior to the prostate, and separated from the rectum by the =
|
rectovesical (pouch)*** excavation.
|
|
|
|
In females, the bladder sits
|
anterior to the vagina.
separated from the uterus by th vesicouterine excavation |
|
|
|
In females, the bladder sits inferior to the uterus and anterior to the vagina. It is separated from the uterus by the =
|
vesicouterine excavation.
|
|
|
|
In males, the base of the bladder lies between the _____ and the ____ ____. It is superior to the _____ , and separated from the _____ by the ____ ____.
*** |
rectum
pubic symphysis prostate rectum rectovesical excavation. |
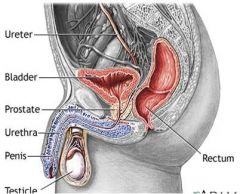
In males, the base of the bladder lies between the rectum and the pubic symphysis. It is superior to the prostate, and separated from the rectum by the rectovesical (pouch)*** excavation.
|
|
|
In females, the bladder sits inferior to the ____ and ____ to the ____ . It is separated from the ____ by the _____ _____.
|
uterus
anterior vagina uterus vesicouterine excavation. |
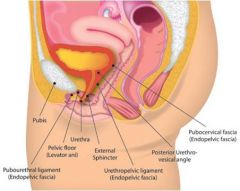
In females, the bladder sits inferior to the uterus and anterior to the vagina. It is separated from the uterus by the vesicouterine excavation.
|
|
|
The internal floor of the bladder includes a triangular area called the
|
trigone
|
|
|
|
trigone has three openings at each of its angles =
|
ureters =
neck = urethra = |
attached to the two posterior openings
anterior opening, at the apex of the trigone, Neck leads to the urethra |
|
|
wall of the bladder consists of
|
four bundles of smooth muscle fibers interlaced.
|
detrusor muscle
(which surrounds the bladder neck) and comprise what is called the internal urethral sphincter. |
|
|
Know layers of myo in urinary bladder ***
6ct |
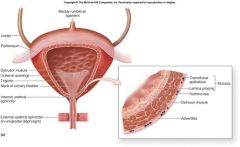
Mucosa
Transitional Epithel. Lamina Propria Submucosa Detrusor (smooth myo) Adventitia |
|
|
|
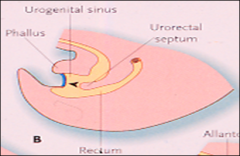
***The urinary bladder is formed from the
|
upper portion of the urogenital sinus
which is continuous with the = |
allantois
|
|
|
____ ____ is between atlantois & rectum.
|
Urectal septum
is between atlantois & rectum |
|
|
|
Urectal septum is between =
|
atlantois & rectum
|
|
|
|
Female
development of the urogenital sinus into the urinary bladder and definitive urogenital sinus describe pictured layout = |
-Allantois is at the anterior superior
-leads into urinary bladder -bladder turns inferior making a boomerang shape -ureter is at the bend -halfway between bend inferior to the end is the seminal vesicle on posterior wall -on the anterior side just distal to seminal vesicle is the pelvic part of urogenital sinus -at the end is the definitive urogenital sinus -Inferior to the above structure is the anorectal canal |
|
|
|
male
the definitive urogenital sinus develops into the penile urethra. The prostate gland is formed by buds from the urethra and seminal vesicles are formed by budding from the ductus deferens. Describe the picture layout = |
-Urachus at the superior end
-the urinary bladder -near the end is the ureter -at the end is the ductus deferens -prostate -prostatic and membranous urethra -penile urethra -Anorectal canal |
|
|
|
Female
urogenital sinus forms into the = 2ct |
Urinary bladder
definitive urogenital sinus |
|
|
|
Female
Urinary bladder definitive urogenital sinus comes from = |
urogenital sinus
|
|
|
|
Male
definitive urogenital sinus develops into the = The buds from the urethra form = Budding from the ductus deferens forms = |
Penile urethra
Prostate gland Seminal vesicles |
|
|
|
Male
Structures are formed from: Penile urethra= Prostate gland = Seminal vesicles = |
definitive urogenital sinus
buds from the urethra Budding from the ductus deferens |
|
|
|
The lower ends of the ____ ____ become incorporated into the _____ ____ of the bladder to form the _____ of the bladder.
|
mesonephric ducts
posterior wall trigone |
|
|
|
The mesonephric ducts eventually open into the =
|
urogenital sinus below the =
|
bladder.
|
|
|
The transitional epithelium lining the urinary bladder is derived from =
*** |
endoderm of urogenital sinus.
|
|
|
|
Urinary sinus
Trigone bladder DBL up from = |
-upper portion of the urogenital sinus
-mesonephric ducts -endoderm of urogenital sinus |
***The urinary bladder is formed from the upper portion of the urogenital sinus, which is continuous with the allantois.
The lower ends of the mesonephric ducts become incorporated into the posterior wall of the bladder to form the trigone of the bladder. The transitional epithelium lining the urinary bladder is derived from ***endoderm of urogenital sinus. |
|
|
***
After birth, the allantois degenerates and becomes the = |
urachus
forming the = |
median umbilical ligament. ***
If it persists it communicates w the = cavity of the bladder |

