![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The largest phylum among all animal phyla.
|
Arhtropoda
|
|
|
The success of arthropods is probably the result of very helpful adaptations such as
|
Flexible body segmentation
External and light skeleton Jointed very adaptable appendages |
|
|
Many Arthropods undergo a very complex developmental process called
|
metamorphosis
|
|
|
Metamorphosis
|
Developmental process where vastly different physiological, morphological, behavioral and ecological stages of an individual will appear sequentially through their ontogeny.
|
|
|
Arthropod classification is based on
|
Modification of their appendages and body regions.
|
|
|
1) Uropod
2) Telson 3) Abdomen 4) Tergum 5) Cephalothorax 6) Carapace 7) Compound Eye 8) Antenna 9) Rostrum 10) Cheliped 11) Walking legs (Pereopods) 12) Swimmerets (Pleopods) |
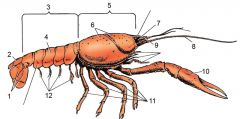
Label
|
|
|
1) Telson
2) Uropod 3) Anus 4) Abdomen 5) Testis 6) Heart 7) Cephalothorax 8) Stomach 9) Brain 10) Rostrum 11) Eye 12) Antenna 13) Digestive gland 14) Copulation swimmeret 15) Swimmerets |
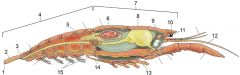
Label
|
|
|
Hemimetabolism
|
Incomplete metamorphosis. The development of certain insects that includes three distinct stages: the egg, nymph, and adult (imago) stage. The organism goes through gradual changes with no pupal stage.
|
|
|
Holometabolism
|
Complete metamorphosis. These insect groups go through four stages: embryo, larvae, pupa, and adult (imago).
|
|
|
Tegnata
|
segment grouped together
|
|
|
These are marine, spiny-skinned, slow moving, voracious animals
|
Phylum Echinodermata
|
|
|
This phylum has bilateral symmetrical larvae which change into adults that have pentamerous radial symmetry.
|
Echinodermata
|
|
|
This phylum is a true coelomate and deuterostomes
|
Echinodermata
|
|
|
This phylum has a water vascular system unique to the organisms
|
Echinodermata
|
|
|
This phylum has organisms which are coelomates, segmented, deuterostomes, bilaterally symmetric, dorsal hollow nerve cord, longitudinal flexible supportive rod (notochord), pharyngeal gills, and a postanal tail.
|
Chordata
|
|
|
Subphylum ____ is the largest and most familiar group of Phylum ____ which have the notochord partially or totally replaced by cartilage or bone.
|
Vertebrata, Chordata
|
|
|
Vertebrata are seperated by
|
The adaptations of the cranium (protection to the brain)
|
|
|
These lower veretebrates are seperated from the rest of the phylum.
|
Jawless fishes and cartilaginous fishes
|
|
|
Fish have which:
Spine, Tail, Jaws, Opposable thumb |
Spine, Tail, Jaws
|
|
|
Monkey has which:
Spine, Tail, Jaws, Opposable thumb |
Spine, Tail, Jaws, Opposable thumb
|
|
|
Lamprey has which:
Spine, Tail, Jaws, Opposable thumb |
Spine, Tail
|
|
|
1) Tentacles
2) Tube feet |
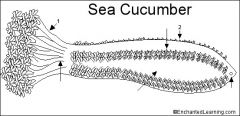
Label
|
|
|
1) Madreporite
2) Location of anus 3) Arm 4) Spine 5) Pedicellariae 6) Dermal branchiae (skin gills) 7) Ambulacral grooves 8) Mouth 9) Peristome 10) Retracted Tube feet 11) Extended Tube feet |
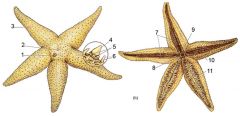
Label
|
|
|
1) Eye spot
2) Intestinal caeca 3) Anus 4) Pyloric caecum (digestive gland) 5) Ambulacral ridge 6) Pyloric stomach 7) Cardiac stomach 8) Gonads |
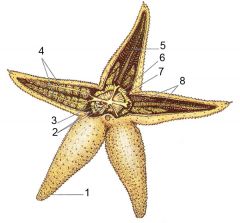
Label
|
|
|
1) Stone canal
2) Madreporite 3) Ring canal 4) Radial canals 5) Ampullae |
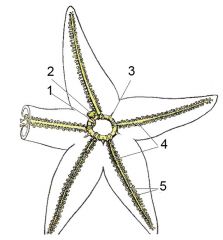
Label
|
|
|
1) Ampulla
2) Gonad 3) Coelom 4) Spines 5) Digestive gland 6) Ossicles of endoskeleton (beneath epidermis) 7) Radial canal 8) Transverse canal 9) Ambulacral groove 10) Tube foot |
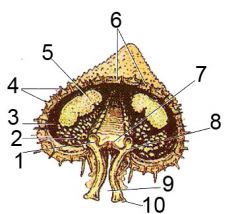
Label
|
|
|
How many segments do chilopoda have?
|
15-173
|
|
|
How many segments do diplopoda have?
|
11-60
|
|
|
This Class has a Head and a Trunk
|
Chilopoda, Diplopoda
|
|
|
This Class has a Head, Thorax, and Abdomen
|
Insecta
|
|
|
This Class has a cephalothorax and abdomen
|
Malacostraca
|
|
|
This Class has a Prosoma and Opisthosoma
|
Arachnida, Merostomata
|
|
|
Describe the tagmatization of Malacostraca
|
cephalothorax, abdomen
|
|
|
Describe the tagmatization of arachnida
|
prosoma, opisthosoma
|
|
|
Describe the tagmatization of merostomata
|
prosoma, opisthosoma
|
|
|
Describe the tagmatization of chilopoda
|
head, trunk
|
|
|
Describe the tagmatization of diplopoda
|
head, trunk
|
|
|
Describe the tagmatization of insecta
|
head, thorax, abdomen
|

