![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Water |
the most important molecule to life |
|
|
|
Hydrogen Bonding |
allows water molecules to stick together (cohesion), as well as with other substances (adhesion) |
|
|
|
Hydrophilic |
substances that have an affinity for water ex: ionic or polar molecules |
|
|
|
Hydrophobic |
substances that are repelled by water ex: oils |
|
|
|
Organic Molecules |
contain carbon. Referring in chemistry to the carbon compounds, many of which have been in some manner associated with living organisms. |
|
|
|
Inorganic Molecules |
do not contain carbon |
|
|
|
Macromolecules |
biological molecules are large molecules |
|
|
|
Monomers |
smaller parts that make up macromolecules |
|
|
|
Polymer |
another name for macromolecule (man monomers put together) |
|
|
|
Carbohydrates |
basic macromolecule group -Sugars (saccharides) and their polymers |
|
|
|
Monosacchardes |
important for: -fuel for cellular work -their carbon skeleton serves as raw material for the synthesis of other types of organic molecules (most common one is Glucose) |
|
|
|
Disaccharides |
the most common is sucrose. Plants transport their carbohydrates as sucrose |
|
|
|
Polysaccharides |
-polymers in which few hundred to a few thousand monosaccharides are linked together -some polysaccharides are use as storage material while others serve as building material. |
|
|
|
Storage Polysaccharides |
energy storage |
|
|
|
Starch |
a storage polysaccharide of plants. Consists entirely of glucose. |
|
|
|
Glycogen |
The storage polysaccharide of animals |
|
|
|
Structural Polysaccharides |
used for cell structure |
|
|
|
Cellulose |
a major component of the tough walls that enclose plant cells |
|
|
|
Chitin |
The carbohydrate used by arthropods (insects, spiders, crustaceans) to build their excoskeletons |
|
|
|
Lipids
|
a diverse group of compounds that share one important trait. ALL HYDROPHOBIC. non-polar bonds cause this behavior.
|
|
|
|
Fats
|
large molecules constructed of two kinds of small molecules, glycerol and fatty acids
|
|
|
|
Saturated Fats |
lack the double bonds and fit together closely.
|
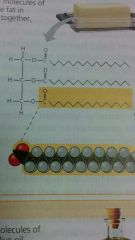
bacon, Grease and butter
|
|
|
Unsaturated Fats
|
have double bonds and thus have kinks in the fatty acid chains. these fats do not fit close together and are fluid at room temperature.
|
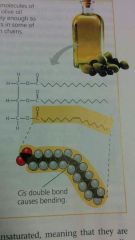
plants fats (corn and peanut oils) these fats are often referred to as oils.
|
|
|
Phospholipids
|
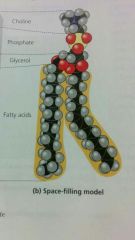
are structurally related to fats, but they have only 2 fatty acids rather than 3 and the 3rd carbon of glycerol is joined to a phosphate group (which has a negative charge). Thus they have a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails.
|
makes up the phospholipid bilayer
|
|
|
Steroids
|
are lipids that are characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four interconnecting rings. examples: cholesterol
|
|
|
|
Proteins
|
account for more than 50% of the dry weight of most cells, and they are instrumental in almost everything cells do.
|
|
|
|
Amino Acids
|
monomers of proteins.
1. a hydrogen 2. a carboxyl group 3. an amino acid 4. a side chain |
|
|
|
Proteins are formed when |
amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form a ploypeptide chain |
|
|
|
Two types of Nucleaic Acids |
1. DNA 2. RNA both are ploymers of repeated units called nucleotides. |
|
|
|
The Nitrogenous bases are |
Purines: adenine, guanine Pyrimidines: cytosine, thymine and uracil |
|

