![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cell theory |
• All animals and plants were made of cells • the cell is the basic unit for all organism • cells arise dorm only pre-existing cells |
|
|
Spontaneous generation |
False theory about life coming form non-living things |
|
|
Biogenesis |
The theory thay we use today to explain how life forms |
|
|
Redi |
Raw meat experiment |
|
|
Pasteur |
Chicken broth experiment |
|
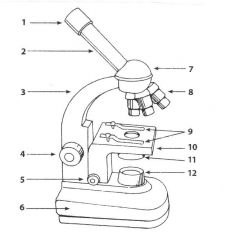
|
1. Ocular lens/eyepiece (10X) 2.body tube 3.arm 4.coarse adjustment knob 5.fine adjustment knob 6.base 7.revolving nose piece 8. Objective lenes 9.stage clips 10. Stage 11. Diaphragm 12.lamp |
|
|
Total mag |
Mag ocular lens 10x(the lens you look into) ×objective lens |
|
|
Nuclear envelope |
What surrounds the nucleus; has pores to allow the transport of materials |
|
|
Nucleus |
Contains DNA, the genetic material of the cell, and directs all cellular activities |
|
|
Cell membrane |
- protective barrier for the cell - regulates the passage of materials between the cell and it's environment |
|
|
Phospholipid bilayer |
Double layer of outward-facing phosphates and inward-facing fatter acids that form a cell membrane |
|
|
Cytoplasm |
- gel-like substance that contains nutrients and in which organelles are suspended |
|
|
Chloroplasts |
(ONLY FOUND IN PLANTS) - Green organelle that contains chlorophyll and is the site of photosynthesis |
|
|
Vacoules |
- storage space - plant cells have one and animals cells have many |
|
|
Vesicles |
Transport substances throughout the cell - Golgi apparatus transports things that need to be transported into vesicles |
|
|
Edoplasmic reticulum(ER) |
- Transport tubes - smooth ER does not contain ribosomes - rough ER does contain ribosomes |
|
|
Ribosomes |
Used to make proteins |
|
|
Lysomes |
Digestion centre for the cell |
|
|
Golgi apparatus |
Packages materials into vesicles so they can be transported in the cell |
|
|
Mitochondria |
- where cellular respiration happens - makes energy for the cell(powerhouse of the cell) |
|
|
Who coined the term "cells" |
Robert hooke |
|
|
Who created the compound microscope |
Janssen |
|
|
Compound microscopes |
Light microscope using more than one lens |
|
|
Who discovered the movement of different single called micro-organisms |
Leeuwenhoek |
|
|
Contrast |
The ability to see differences between structures due to differences in their capability to absorb light |
|
|
Resolution |
Distinguish between two structures that are very close together |
|
|
Contrast enhancing technique and fluorescence microscopy |
Provides information about molecules on the cells surface |
|
|
Transmission electron microscope (TEM) |
Uses a beam of electroms to produce images with fine details |
|
|
Diffusion |
The movement of molecules from am area of higher concentration to lower concentration |
|
|
Facilitated diffusion |
Diffusion of molecules across a membrane through binding to carrier proteins (does not require energy from ATP |
|
|
ATP |
Adenosine triphospate: - nucleotide that releases stored energy in a cell |
|
|
Rate of diffusion |
The relative movement of a particle in response to a concentration gradient |
|
|
Concentration gradient |
Difference within a given area between the highest and lowest concentrations of a particular chemical substance |
|
|
Passive transport |
- requires NO ENERGY - moves from high to low - moves WITH the concentration gradient |
|
|
active transport |
- requires energy (ATP) - Low to high AGAINST concentration gradient |
|
|
Selectively permeable |
A natural membrane that allows certain particles to press through it but excludes others (cell membrane is this) |
|
|
Semi-permeable |
- passage materials determined by size, charge, and solubility (used in osmosis) |
|
|
Osmosis |
The diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane |
|
|
Hypertonic |
More solute outside the cell; more water in the cell(Hyper = excessive) there's an excessive amount of water in the cell |
|
|
Hypotonic |
More solute inside the cell; more water outside(Hypo = less than normal), less water in the cell than Normal |
|
|
Isotonic |
Same concentration of solutes and water in solution as in cell |
|
|
Plasmolysis |
When cells lose water and shrink |
|
|
Cytolysis |
When cells gain water and swell/may even bursy |
|
|
Homeostasis |
State of equalinrium |
|
|
Channel proteins |
Pores for small water soluble particles to pass through - moves high to low |
|
|
Carrier proteins |
Attach to larger molecules, change shape and physically brings it inside the cell |
|
|
Endocytosis |
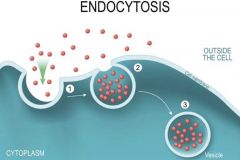
Movement into the cell Steps 1. Vesicles forms around particle 2. Cell membrane pinches off 3. Vesicles noe inside cell |
|
|
Exocytosis |
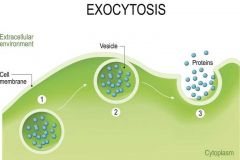
- movement out of the cell(for waste particles or cell products) Steps 1. Vesicles surrounds particle in cell 2. Moves to membrane and fuses with it 3. Vesicles ruptures, releasing contents |
|
|
What's the difference between an animal cell and a plant cell |
Plants have a cell wall and chloroplasts(photosynthesis) - Plants have one huge vacoule while the animal one has many |
|
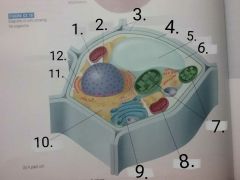
|
1.nucleus 2.nuclear envelope 3.cell wall 4.cell membrane 5.vacoule 6.cytoplasm 7.chloroplasts 8.Mitochondria 9.Golgi apparatus 10.smooth ER 11.ribosomes 12.rough ER |
|
|
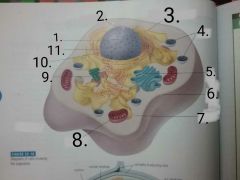
1.nucleus 2.nuclear envelope 3.smooth ER 4.lysosomes 5.Golgi apparatus 6.cell membrane 7.cytoplasm 8.Mitochondria 9. Centrioles 10.ribosomes 11.rough ER |
|
|
Surface area to volume ration |
SA:V |
|
|
Phototropism |
Direction plant growth in response to light (Positive)- leaves (Negative)- roots |
|
|
Gravitropism |
Directional plant growth in response to gravity (Positive)- roots, anything facing downwards (Negative)- stem, anything facing upwards |

