![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which of following statements describes a difference between replication of DNA and transcription of RNA? |
Both strands of DNA are copied in replication, but usually only one is copied in transcription. |
|
|
Which of the following correctly describes a difference between RNA & DNA polymerases? |
DNA polymerases usually require a primes (i.e., they can only continue a strand, not start one), while most RNA polymerases do not. |
|
|
How do the core enzyme and the holoenzyme of RNA polymerase differ in E. coli? |
The holoenzyme includes the sigma (alpha) subunit, the core enzyme does not. |
|
|
RNA synthesis begins at the base in the DNA sequence designated by the following number: |
+1(plus one) |
|
|
Which of the following is not part of the core promoter? |
the UP element |
|
|
Which of the following offers the best description of a Pribnow box? |
A promoter consensus sequence located at approximately -10. |
|
|
Which of the following best describes the order of events at the promoter? |
closed complex --> open complex --> transcription initiation |
|
|
Chain termination occurs, in vivo, when: |
Either a hairpin loop forms or rho (p) is involved. |
|
|
What is the need for a primer strand in transcription? |
There is none. |
|
|
Which of the following is the best description of an operon? |
A group of genes under the control of a common promoter. |
|
|
Which of the conditions would result in the least amount of transcription of the lac operon? |
glucose lactose high low |
|
|
RNA transcribed from the coding strand instead of the template strand |
is called antisense RNA |
|
|
Which of the following RNAs is noted for having a "cloverleaf" structure? |
tRNA |
|
|
Which end of prokaryotic mRNA are protected from degradation? |
Neither end |
|
|
Which category of RNA carries amino acids for the process of translation? |
tRNA |
|
|
The majority of protein synthesis occurs in the |
cytoplasm |
|
|
Which amino acids have unique codons? |
trp, met |
|
|
Migration of DNA during electrophoresis is based |
mostly on the size of the molecule, since the ration of charge to mass is approximately the same, no matter how large the DNA is. |
|
|
Fluorescence and other luminescent methods of visualizing bands offer these advantages over methods dependent on radioactivity. |
These methods are both more sensitive and require no special license. |
|
|
Enzymes that seal nicks in DNA are called |
ligases |
|
|
A plasmid is |
a small circular DNA that is not part of a bacterial chromosome. |
|
|
The following steps are all involved in genetic recombination 1: Screening for cells that contain the recombined gene 2: Cutting the vector with restriction enzyme 3: Mixing the gene of interest with the vector 4: Isolating the gene of interest from its original source 5: Ligating the gene of interest and the vector together. |
4-->2-->3-->5-->1 |
|
|
How is human insulin produced by genetically engineered bacteria? |
DNA that goes for each of the two polypeptide chains is introduced into two different populations of bacteria. |
|
|
The "c" in cDNA stands for this word: |
Complementary |
|
|
In the polymerase chain reaction |
it is possible to amplify small amounts of DNA without cloning. |
|
|
The standard state usually used in biochemistry (deltaGº') includes |
all concentrations at 1 M, except for [H+], which is 10^-7 M. |
|
|
In general, catabolism |
is an oxidative process that releases energy |
|
|
Which is the oxidizing agent? |
NAD+ |
|
|
The energy released during metabolism of nutrients can be used to synthesize ATP from ADP and phosphate. |
True |
|
|
Metabolism takes place in stages |
and allows for efficient production and use of energy |
|
|
Haworth projection formulas |
are representations of the cyclic form of sugars; can show the distinction between the alpha and beta anomers |
|
|
In a Fischer projection, which chiral carbon determines whether the sugar is the D- or the L-isomer? |
highest numbered asymmetric carbon atom |
|
|
Diastereomers are |
non-mirror-image, non superimposable stereoisomers |
|
|
A pyranose is a sugar that |
contains a six-membered ring as part of its cyclic structure |
|
|
Which of the following groups is produced when an aldehyde is oxidized? |
Carboxyl |
|
|
Which of the following best describes the glycosidic bond in the disaccharide shown? (Graph) |
Alpha(2-4) |
|
|
Glycogen has a similar structure to amylopectin, but is less highly branched. |
False |
|
|
Plant starch includes amylopectin and cellulose |
False |
|
|
In humans, pyruvate can be converted to |
acetyl-CoA and lactate |
|
|
What is the net ATP yield per glucose during glycolysis? |
2 |
|
|
The phosphorylation of fructose 6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is the committed step in glycolysis because |
fructose 1,6-bisphosphate can undergo no other reactions than those of glycolysis |
|
|
Which enzyme is the key regulatory enzyme in glycolysis? |
Phosphofructokinase |
|
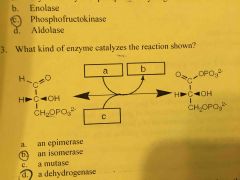
What kind of enzyme catalyzes the reaction shown? |
a dehydrogenase |
|
|
How many enzymes of glycolysis are control points for the pathway? |
3 |
|
|
During anaerobic metabolism in red blood cells, the carbons of glucose end up in |
lactic acid |
|
|
Thiamine pyrophosphate is a coenzyme |
involved in transfers of two-carbon groups |
|
|
Glycogen is mainly found in |
liver and muscle |
|
|
The compound uridine diphosphate glucose (UDPG) plays a role in |
glycogen synthesis |
|
|
Gluconeogenesis differs from glycolysis because |
the irreversible steps of glycolysis are bypassed different enzymes are involved biotin is required for gluconeogenesis and not for glycolysis All |
|
|
The Cori cycle involves the following |
Conversion of lactate produced in the muscle by regeneration of glucose in the liver. |
|

A chance to be a forensic scientist...... RFLP analysis has been requested |
The results indicate the accused is innocent |
|
|
Slight differences in a given gene between the two homologous chromosomes are called |
alleles |
|
|
Which of the following conditions is an example of how genetic engineering is currently used to increase food production? |
Genetically modified plants have been developed Genetically modified plants have been Hormones are given to cows to increase milk Genetically modified plants have been developed which are resistant to frost All |
|
|
In DNA sequencing, fragments to be analyzed are produced by |
selective interruption of DNA synthesis
|
|
|
In the conversion of glucose to pyruvate, how many of the actual steps involve electron transfer? |
1 |

