![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Atom |
smallest unit of matter that still contains properties of an element Contains: Nucleus-Protons & Neutrons, and Electron Cloud- Electrons
|
|
|
Mass |
amount of matter and energy in a given object |
|
|
Matter |
anything that has mass and takes up space is composed of elements |
|
|
Element |
is a substance entirely made up of one type of atom |
|
|
What is a subatomic particle? |
Building Blocks of an atom: protons, neutrons and electrons |
|
|
An atom is composed of --------,--------,&---------. |
Protons, neutrons, and electrons |
|
|
The nucleus contains the ------,&------. |
Protons and Neurons |
|
|
The ------ are found in the electron cloud |
Electrons |
|
|
Protons: Charge: Mass (weight): Location: |
Protons: Charge: Positive (+) Mass (weight): 1 AMU Location: Nucleus |
|
|
Neutrons: Charge:
Mass (weight): Location: |
Neutrons: Charge: NONE
Mass (weight): 1 AMU Location: Nuecleus |
|
|
Electrons: Charge:
Mass (weight): Location: |
Electrons: Charge: Negative(-) Mass (weight):0 Location: Electron Cloud
|
|
|
How does an atom gain a charge? |
When it loses or gains an electron |
|
|
What are two types of charges? |
postive(+) & negative(-) |
|
|
What is an ion? |
an atom with a charge |
|
|
What are the two types of ions? |
cation & anion |
|
|
Cation |
positively charged atom |
|
|
Anion |
negatively charged atom |
|
|
What is an isotope? |
an atom with a different number of neutrons and protons |
|
|
What is atomic mass? |
the mass of an atom of a chemical element in AMU |
|
|
Define the tem molecule. |
two or more atoms joined together |
|
|
Give an example of a molecule |
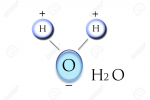
H20 Polarization S- O ---- ---- H H S+ S+ |
|
|
What is electronegativity? |
-the name for the force that causes polarity -an atoms affinity for an electron -the more electronegative an atom is, the more affinity it has on an electron |
|
|
What element is the most electronegative? |

|
|
|
What is a chemical bond? |
-the connections between the atoms in a compound - the lasting attraction between atoms that enable the formation of a chemical compounds |
|
|
Name three types of chemical bonds? |
Polar Covalent, Non polar Covalent, & Ionic |
|
|
What happens when an ionic bond forms? |
-(bond between two atoms) -an electron is striped away from one atom and gained by the other -resulting in two oppositely charged atoms *the atom with the highest electronegativity takes the electron* |
|
|
What is the difference between a polar and non polar covalent bond? |
Polar-two atoms unequally share their valence electrons & Non Polar-two atoms equally share their valence electrons |
|
|
What is a Hydrogen bond? |
a weak attraction between hydrogen and another oppositely charged atom |
|
|
Example of a hydrogen bond? |
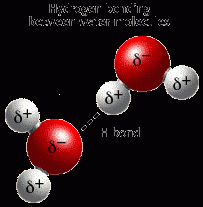
|
|
|
Cohesion VS Adhesion |
Cohesion-water sticks to water VS Adhesion-water sticks to something else |
|
|
Define and give example: Acid |
-any species that donates H ions in solution -A chemical that releases (H^+1) ions |
|
|
Define and give example:
Base |
-any species that donates -OH in solution -A chemical that accepts (H^+1) ions |
|
|
Define and give example:
pH |
Power of Hydrogen Scale on which acids and bases are measured |
|
|
Define and give example: Buffer |
-a species that maintains pH -a chemical that accepts/releases (H^+1) as necessary to keep pH constant |
|
|
Covalent Bond |
forms when two atoms share 2 or more valence electrons strength depends on the number of electron pairs shared by the atoms |
|
|
What is a molecule? |
-representing the smallest fundamental unit of a chemical compound that can take part in a chemical reaction -a group of two or more atoms bonded together -can bond together to form larger molecules |
|
|
Carbon can bond to ---- other atoms. |
Four |
|
|
A Hydrocarbon is composed of ---- and ---- atoms. |
Hydrogen, Carbon |
|
|
Hydrocarbons are ---- molecules. |
Organic |
|
|
A monomer is composed of ---- and are ---- ---- for polymers. |
molecules, building blocks |
|
|
Polymers are composed of ----. |
Monomers |
|
|
Poly means----. |
many |
|
|
Mono means ----. |
one |
|
|
Mer means ----. |
unit. |
|
|
------ ------ are found on monomers and are involved in chemical bonding of one monomer to another. |
Functional Groups |
|
|
Name the four Functional Groups. |
Hydroxyl, Carbonyl, Carboxyl, Amino |
|
|
Draw the following Functional Group: Hydroxyl |
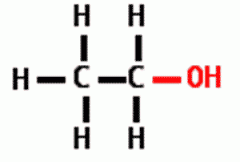
|
|
|
Draw the following Functional Group:
Carbonyl |

|
|
|
Draw the following Functional Group:
Carboxyl |

|
|
|
Draw the following Functional Group:
Amino |
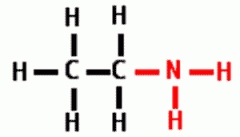
|
|
|
What is the formula for the three monosaccharides? |
C6 H12 O6 |
|
|
Name the three monosaccharides (and where the stem from). |
Glucose (Plant Sugar), Fructose (Fruit Sugar), Galactose (one or the other). |
|
|
What is the bond between two monosaccharides called and what does it form? |
Glycosidic Linkage, Disaccharides |
|
|
Glucose bonded to Glucose |
Maltose |
|
|
Glucose bonded to Fructose |
Sucrose (table sugar) |
|
|
Glucose bonded to Galactose |
Lactose (milk sugar) |
|
|
Name three Polysaccharides. |
Glycogen, Starch, and Cellulose |
|
|
---- is the storage form of ---- in animals; stored in the muscle and liver tissue. |
Glycogen, Glucose |
|
|
---- is the storage form of ---- in Plants. |
Starch, Glucose |
|
|
---- is the main component of the fibril in the ridged plant cell wall. |
Cellulose |
|
|
A ---- ---- is a chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule, releasing a molecule of water (H2O).
|
Peptide Bond |
|
|
A ---- ---- is a type of reaction used to bond monomers together and results in a chemical bond and a water molecule. This reaction is the opposite of Hydrolysis. |
Dehydration Synthesis (Reaction) |
|
|
------ is used to break a polymer in to two separate pieces and is the opposite of a dehydration reaction. |
Hydrolysis |
|
|
What are the four main biological marco molecules? |
1)Cabohydrates 2)Lipids 3)Proteins 4)Nucleic Acid |
|
|
Sacchar means ---- and mono means ----, so a monosaccharide is a ---- ----. |
sugar, single, single sugar |
|
|
What types of atoms are found in a carbohydrates molecule? |
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen |
|
|
Why are CHO important? |
Brain can only use glucose to produce energy. Primary Source of Energy for Energy Production. |
|
|
Are CHO essential? What does the term essential mean? |
NO, but still important. Vital to life. |

