![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Carbohydrates are also known as.. |
sugars or saccharides. cellulose and starch. C, O, H |
|
|
How is a monosaccharide composed (think OHs and Carbonyls). Thereore, what is the general chemical formula of a monosac. |
at least three carbons, with ahydroxyl (–OH) on every carbon except one; thatremaining carbon has a carbonyl (C=O). Cn(H2O)n where n >or=3 |
|
|
What is the difference between an aldose and a ketose? What are they? |
If the carbonyl (shaded red) is at the end ofthe molecule, the monosaccharide is called an aldose, andif it is in the middle, it is called a ketose. |
|
|
What are trioses, tetroses, pentoses, hexoses andheptoses |
monos w/ 3-7 carbons |
|
|
What are some important functions of monos? |
The trioses form during glucose breakdown or synthesis. Ribose is a sugar that is part of RNA.Ribulose is important during photosynthesis. And glucose, galactose and fructose are energy sources |
|
|
What is the difference between alpha and beta glucoses (pentoses and hexoses in ring form)? |
The position of the new hydroxyl can be either below the planeof the ring opposite the CH2OH, making α-glucose, or above thering, making β-glucose |
|
|
What are dissacharides? How are they produced? what are the bonds between them called? |
Two monosaccharides can be covalently joined together. deydration reaction. glycosidic bonds- 2 OHs bond to make water and leave an oxygen connection the two monos. |
|
|
What are storage polys? what are structural polys? how do they differ? examples of each |
Storage polysaccharides are polymers of α-glucose that are used to store energy. example: starch and gycogen. Structural polysaccharides are used to build structuresfound in cells or tissues from many polymers of beta-glucose. example: cellulose and chitin |
|
|
What are lipids? |
Lipids are a large group of molecules that are mostly hydrophobic.They consist primarily of C-H and C-C bonds, which are strongnonpolar covalent bonds |
|
|
Are lipids true polymers? why or why not? |
no, becausethey cannot be made arbitrarily large the same way carbohydrates,proteins and nucleic acids can. |
|
|
What are the main three lipids we discussed in class? |
fats, phospholipids, and steroids. |
|
|
what do fats consist of? what are fatty acids. |
fatty acids joined to glycerol. Fatty acids are long HC chains with a carboxylic acid on one end. |
|
|
What is the difference bw saturated and unsaturated. give examples. Are double bonds usually cis or trans? What do cis bonds look like in the fatty acid? |
sat= no double bonds. ex: animal fat |
|
|
What is hydrogenation. How does this happen? What is sometimes made in this process? Bad fats ___ LDL cholesterol and ___ HDL cholesterol |
They can be made more solid by turning the double bonds intosingle bonds using a catalyst to add hydrogen. Trans fats are made sometimes. raise bad and lower good |
|
|
What are phospholipids? |
They make up cell membranes. They are similar to aglycerol with only two hydrophobic fatty acids attached (i.e. adiglyceride), but with additional functional groups that generatea hydrophilic region. |
|
|
What are steroids? |
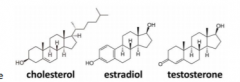
represent a class of molecules that are similar tocholesterol, which has a flat “planar” structure that isalmost all C or H |
|
|
What are proteins? |
representsone or more polypeptides that carry out a specific function that is dictated by their structure and shape. |
|
|
What is a polypeptide? every polypeptide corresponds to a ____. |
is a polymer of amino acids madeduring the process of translation. gene |
|
|
What is an amino acid? |
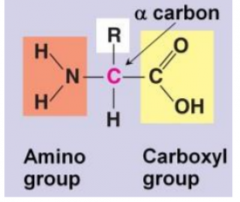
Amino acids have an amino on one side and a carboxyl on the other. A carbon in themiddle, called the α-carbon, is attached to these two groups plus a hydrogen and a sidechain (‘R’) |
|
|
What gives each amino acid its name? how many amino acids found in proteins in nature? |
The R' side chain. 20. |
|
|
How are polypeptides made. What bond is made? |
joined together bypeptide bonds in an overall dehydration reaction. The –OH of acarboxyl group will bond with the –H of an amino group to form awater molecule (H2O) and create a peptide bond. |
|
|
How can you quickly identify polypeptides? What is responsible for an enzymes catalytic activity? |
the NCC backbone. the shape of an enzyme which is dictated by its amino acid sequence. |
|
|
What are the four protein structure? describe each and how you could distinguish each. |
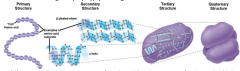
primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary. |
|
|
What are the two types of nucleic acids? what is the central dogma? |
ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid(DNA). DNA undergoestranscription to make messenger RNA (mRNA), which undergoes translation to makeprotein. |
|
|
What is a nucleotide? What are the three parts? |
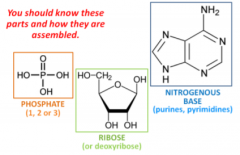
The nucleic acid building block. |
|
|
What is joined to each carbon (1'-5') |
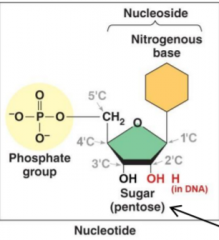
|
|
|
What are the 5 bases a nitrogenous base can be? How are they each categorized (2 options). What is the difference between these categorizations? |
adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), thymine (T) anduracil (U). The bases A and G are purines and have two rings, while C, T and U are pyrimidines and only have a single ring. |
|
|
How are nucleotides bonded?so that the backbone consists of alternating _____ and ______,with the________ attached to the _______ |
phosphodiester bonds. |
|
|
Polynucleotide strands can pair together by forming _____ bonds between functional groups on thenitrogenous bases. how do the bases pair? |
Hydrogen. AT (U in RNA), GC |
|
|
What are polymerases? |
Polynucleotide strands(DNA or RNA) are synthesized by enzymes called polymerases, using nucleoside triphosphates as buildingblocks, and a pre-existing DNA molecule as a template. |
|
|
How do the macromolecules relate? |
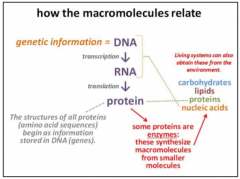
|
|
|
How does DNA and RNA store genetic info? |
as the order ofthe bases along the length of the molecules |

