![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
188 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What happens to nutrient macromolecules in an animal's digestive tract?
|
Protein --> Amino Acids
Sugars --> Monosaccarides Nucleic Acids --> Nucleotides Fats --> Glycerol & Fatty Acids |
|
|
Which of the following correctly lists the order of the parts of the human digestive system, from first to last contact with food matter
|
Mouth -> Pharynx -> esophagus -> Stomach -> small intestine -> large intestine -> rectum -> anus
|
|
|
The chemical digestion of carbohydrates begins in the ______ using a starch-digesting enzyme secreted by________.
|
Mouth by amylase which is secreted by the salivary glands
|
|
|
The epiglottis is a
|
a flap of cartilage and fibrous connective tissue which closes over the trachea when food is digested. open and close of epiglottis is caused by the larynx moving up (Close) and down (Open).
|
|
|
A drug that treats gastric ulcers by decreasing the pH of the stomach would most likely target
|
parietal cells since they produce H+ and Cl- ions to form HCl.
|
|
|
Which of the following mechanisms helps prevent the gastric juice from destroying the stomach lining?
|
mucous lining
|
|
|
The stomach mixes food with secretions of the stomach wall to form
|
chyme
|
|
|
In the digestive system, most nutrient absorption occurs in the
|
small intestine
|
|
|
Epithelial cells lining the intestine have surface projections that increase nutrient absorption. These projections are called
|
microvilli
Note: villi are the folds, microvilli are what are on the villi |
|
|
What is not a true about the function of the pancreas
|
Functions:
1. releases enzymes the help break down carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and nucleic acids. 2. releases alkaline solution rich in bicarbonate to neutralize the acidity of chyme as it enters the small intestine. 3. produces insulin and glucagon |
|
|
Bile is produced by the ________ and is used to________.
|
produced by the liver and stored by the gallbladder where it is released to emulsify fats and aid in their digestion
|
|
|
Which of the following nutrients is chemically digested only after it reaches the small intestine
|
Nutrients digested only in the SI :
Fats and Nucleic Acids Note : Carbs starts in the mouth and Protein starts in the stomach |
|
|
Nutrients absorbed by the intestines move directly to the liver, which
|
1. removes excess glucose from from blood and converts it to glycogen
2. synthesizes protiens such as plasma protiens, lipoprotiens (transport fat and cholesterol to body cells) 3. converts toxins (alcohol, weed, drugs) to inactive products that are secreted by urine. |
|
|
Altogether, the body secretes about 7 liters of water into the alimentary canal each day, of which ___ percentage gets reabsorbed by the _______.
|
90% gets reabsorbed by the small intestine and colon.
|
|
|
Organisms suffering from malnourishment have a diet deficient in
|
long term diet deficient in one or more essential nutrients.
|
|
|
Vitamins can be either
|
fat soluble (A,D,E,K) or water soluble (B, C)
thiamine = b1 riboflavin = b2 niacin = b3 |
|
|
Which of the following is associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease
|
high HDL levels, Low LDL levels
|
|
|
Which of the following options correctly lists the direction of carbon dioxide travel as it leaves the body
|
cappillaries, venules, veins, vena cavas, right atrium, right ventricle, pulmonary artery, lungs, out
|
|
|
Within the lungs, gas exchange occurs across
|
across the epithelium of the alveolar
|
|
|
The ________ is a passageway shared by both food and air.
|
pharynx
|
|
|
The maximum amount of air that a human can inhale and exhale is called the
|
vital capacity
avg: 3.4 L female 4.8 L male |
|
|
Inhalation in humans is achieved by
|
diaphragm contracts
intercostal muscles contract rib cage expands |
|
|
When you hold your breath, which of the following blood gas changes leads initially to the urge to breathe again?
|
high levels of CO2 which react with water to form carbonic acid which lowers the pH which is sensored by the medulla as well the the aorta and carotid arteries.
|
|
|
The oxygen-carrying capacity of one hemoglobin is
|
4 oxygen atoms per hemoglobin
|
|
|
Most CO2 is transported to the lungs
|
through the circulatory system.
|
|
|
What prompts a newborn baby to start to breathe
|
a CO2 rise in the fetal blood causes the blood pH to fall, stimulating the breathing control centers in the infants brain causing it to take its first breath
|
|
|
Blood is pumped from the heart to the pulmonary circuit by the
|
right ventricle
|
|
|
From the left ventricle, oxygen-rich blood flows through the
|
Aorta
|
|
|
During which phase of the heartbeat does the heart fill with blood?
|
diastole
|
|
|
Cardiac output is defined as the volume of blood pumped by a(n) ________ each time it contracts.
|
ventricle
|
|
|
Using a stethoscope, you listen to a beating heart and hear "lub-dup, lub-dup." These sounds are created by
|
closing of the heart valves
"lub" is from recoil of blood against av valves "dub" is recoil of blood against the semilunar valve |
|
|
The location of the heart's pacemaker is a specialized region of cardiac muscle called the
|
SA node
(sinoatrial node) |
|
|
Myocardial infarction, also called a heart attack,
|
damage or death of cardiac muscle tissue due to blocked coronary blood vessels.
|
|
|
Which blood vessels have the thinnest walls
|
cappillaries
|
|
|
As blood moves away from the heart to the tissues, the relative diameter of blood vessels ________, the blood pressure ________, and the velocity of blood flow ________.
|
diameter decreases
blood pressure decreases velocity of blood flow decreases |
|
|
Which of the following factors contributes to the flow of blood in veins
|
body movement (skeletal muscles pinch the veins during movement)
valves breathing (change in pressure in chest cavity allows large veins to expand and fill) |
|
|
Blood flow through capillaries is controlled and regulated by
|
precapillary sphincters
sphincter closed - blood goes straight through and bypasses cappilary bed sphincter open - blood goes throughout capillary bed |
|
|
Whether there is a net flow of fluid into or out of a capillary at a given point along its length depends upon
|
the difference between the blood pressure and the osmotic pressure.
HI BP + LO OP = fluid out of cappillary (arterial) HI OP + LO BP = fluid into capillary (venous) |
|
|
The liquid part of blood is called
|
plasma
|
|
|
Cells make up about what percentage of total blood volume?
|
45%
|
|
|
Which of these statements about erythrocytes is true?
|
-carry oxygen
-biconcave -lack nucleus - 250 million hg molecules on each = a billion oxygen molecules |
|
|
The drug aspirin works as a blood thinner by
|
it inhibits prostaglandin production which slows down blood clot formation
|
|
|
The drug Lipitor helps prevent cardiovascular disease by
|
Lipitor reduces the amount of LDL formed by limiting the amount of enzymes that create cholesterol.
|
|
|
Stratified squamous epithelium is well-suited for
|
is well suited to areas in the body subject to constant abrasion (skin, esopoghagus, mouth)
|
|
|
What is the least abundant leukocyte normally found in the bloodstream
|
Basophils
|
|
|
The drug Claritin is used to treat allergies by _____, thus preventing inflammation.
|
interfering with the action of histamine.
(histamine causes blood vessels to dilate and leak fluid which causes nasal irritation, itchy skin, and tears) |
|
|
Which of the following cells are phagocytes?
|
All of these are phagocytes:
-basophils -eosinophils -monocytes -macrophages -mast cells |
|
|
Neutrophils can be found where before an infection?
|
in the blood stream
|
|
|
Which of the following normally resides in the interstitial fluid of tissues, eating any bacteria and virus-infected cells they encounter?
|
macrophages
|
|
|
Which of the following are a group of about 30 proteins present in plasma that can directly attack and lyse bacteria?
|
complement proteins
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT one of the body's innate defenses against infection?
|
Innate- response is the same whether or not pathogen has been previously encountered.
External - skin, secretions, mucous membranes Internal - phagocytic cells, nk cells, complementry protiens, inflammitory response |
|
|
A doctor who detects a higher-than-normal amount of interferon in a patient would correctly conclude that
|
there is a viral infection since interferons are protiens that are produced by virus-infected cells that help other cells resist the virus.
|
|
|
When you cut yourself, the damaged cells immediately release chemical alarm signals, such as
|
histamine
|
|
|
Which of the following is an immediate effect of histamine release during inflammation?
|
induces neighboring blood vessels to dilate and become leakier blood flow to damaged area increases and blood plasma passes out of the leaky vessels
|
|
|
Bacterial infections can cause a serious, potentially fatal systemic inflammatory response called
|
sepsis
|
|
|
The major result of the inflammatory response is to
|
disinfect and clean injured tissues
|
|
|
The two main functions of the lymphatic system are
|
to return tissue fluid to the circulatory system and to fight infection
|
|
|
A substance that can elicit an immune response is called
|
antigen
|
|
|
The transfer of antibodies in breast milk to an infant is an example of ________ immunity.
|
passive
|
|
|
Which of the following cell types is responsible for humoral immunity?
|
B-cells which secrete antibodies into the blood and defend primarily against bacteria and viruses present in bodily fluids
|
|
|
Which of the following does NOT play a role in cell-mediated immunity?
|
certain t cells attack body cells that are infected with bacteria or viruses. other t-cells promote phagocytosis by other white blood cells and by stimulating the production of antibodies by B-cells
|
|
|
Clonal selection
|
an antigen encounters a particular antibody made specifically for that antigen. once that antibody is activated it makes clones of itself. it makes effector cells that combat the antigen as well as memory cells
|
|
|
When a B cell first interacts with its particular antigen, the B cell
|
the b-cell engulfs the antigen where it then breaks up the antigen into fragments and shows them at the cell surface. then a t-cell attaches to the b-cell and tells it to make clones of itself.
|
|
|
Which of the following choices best describes a memory cell
|
Memory B cells are B cells that although activated by the immune system, they are stored inside the circulatory system for later use, for long periods of time, possibly a whole lifetime. Like other cells such as helper T cells, killer T cells, and plasma cells they never become directly involved in the immune response to foreign objects in a living body. If a pathogen the body has already encountered invades, memory B cells can recognize the pathogen and start to divide. Quickly, they form a new generation of cells, and memory cells. The new generation kills off the pathogen so quickly the body does not become noticeably ill.
|
|
|
Which of the following distinguishes the secondary immune response from the primary immune response?
|
primary is when lymphocytes are exposed to an antigen for the first time. secondary is when the response is faster and stronger.
|
|
|
Which of the following statements about antibodies is false?
|
-are secreted by effector (plasma) cells
-y shaped -4 polypeptide chains (2 heavy and 2 light chains) - the two variable regions form an antigen-binding site |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a way in which antibodies work after they bind an antigen?
|
-Neutralization - blocks viral binding sites
-Agglutination - agglutinates the antigens -Precipitation - precipitation of dissolved antigens -Activation - activation of compliment system which leads to cell lysis |
|
|
The effector function of cytotoxic T cells involves
|
the release of cytotoxins into an infected cell which then causes the cell to go into apoptosis
|
|
|
What type of cell is required to activate both humoral and cell-mediated immunity?
|
T-cells
|
|
|
Which of the following is an effect of interleukin-2?
|
makes infection fighting cells multiply and mature
|
|
|
Which of the following types of cells does HIV preferentially infect?
|
helper t-cells
|
|
|
________ are responsible for coding for self-proteins that present antigens, as well as playing a role in organ transplantation.
|
major compatibility complex (MHC)
|
|
|
. ________ is/are produced and secreted by _________ during an allergic reaction, triggering an inflammatory response.
|
histimine that is produced by mast cells
|
|
|
Which is NOT accurate about the innate and acquired immune defenses?
|
innate includes skin, mucous membranes, phagocytic cells, etc. responds the same to every attack
acquired is specific to the invader by responding to antigens |
|
|
Which of the following physiological responses occurs in the human body when it becomes overheated?
|
-sweating
-dilation of blood vessels -dressing for warmth |
|
|
The transfer of heat from arteries carrying warm blood past veins returning cooler blood is an example of
|
countercurrent heat exchange
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT associated as source of nitrogen-containing waste?
|
aquatic animals - ammonia
mammals/amphibians - urea birds/reptiles/insects - uric acid |
|
|
Which of the following converts ammonia to urea
|
the liver by a metabolic cycle that combine ammonia and carbon dioxide
|
|
|
The kidney helps regulate blood pH by altering the secretion and reabsorption of
|
secretion of H+ and reabsorbtion of HCO3-
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a homeostatic function of the excretory system?
|
1. Maintain volume of extracellular fluid
2. Maintain ionic balance in extracellular fluid 3. Maintain pH and osmotic concentration of the extracellular fluid. 4. Excrete toxic metabolic by-products such as urea, ammonia, and uric acid. |
|
|
Through which of the following structures does urine leave the bladder
|
urethra
|
|
|
Which of the following correctly lists the structures in the kidney in the order in which fluid flows through them?
|
glomerulus that is inside the bowmans capsule. then goes to proximal tubule. down the loop of henle. to the distal tubule. to the collecting duct. to the renal pelvis. to the ureter.
|
|
|
During filtration in the glomerulus, which of the following will enter Bowman's capsule from the bloodstream?
|
all of these enter:
H2O NaCl HCO3 H+ Urea Glucose Amino Acids some drugs |
|
|
The kidney helps regulate blood pH by altering the secretion and reabsorption of
|
secretion of H+ and reabsorbtion of HCO3-
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a homeostatic function of the excretory system?
|
1. Maintain volume of extracellular fluid
2. Maintain ionic balance in extracellular fluid 3. Maintain pH and osmotic concentration of the extracellular fluid. 4. Excrete toxic metabolic by-products such as urea, ammonia, and uric acid. |
|
|
Through which of the following structures does urine leave the bladder
|
urethra
|
|
|
Which of the following correctly lists the structures in the kidney in the order in which fluid flows through them?
|
glomerulus that is inside the bowmans capsule. then goes to proximal tubule. down the loop of henle. to the distal tubule. to the collecting duct. to the renal pelvis. to the ureter.
|
|
|
During filtration in the glomerulus, which of the following will enter Bowman's capsule from the bloodstream?
|
all of these enter:
H2O NaCl HCO3 H+ Urea Glucose Amino Acids some drugs |
|
|
Urine flows from the collecting duct into the
|
renal pelvis
|
|
|
The overall process that refines and concentrates the filtrate and ultimately returns water and valuable solutes to the blood is known as
|
reabsorbtion
|
|
|
What region(s) of the nephron has its major function as water readsorption
|
loop of henle and collecting duct
|
|
|
Where along the nephron is glucose reabsorbed from the filtrate back into the blood?
|
in the proximal tubule
|
|
|
Why must water that has moved to the interstitial fluid in the medulla be quickly removed from the interstitial fluid?
|
because it will lower the concentration gradient in the medulla so less water will be reabsorbed.
|
|
|
What is the function of urea reabsorption in the collecting ducts of the kidney
|
so that it can add to the concentration gradient of the renal medulla
|
|
|
When you are dehydrated, blood levels of ADH
|
increase the levels of adh since the kidneys now want to reabsorb as much water as possible.
|
|
|
ADH acts on
|
the collecting ducts by opening the pores so that the water can be reabsorbed
|
|
|
Consumption of alcohol
|
inhibits the release of ADH which is why drinking causes excessive urinary loss and dehydration
|
|
|
How are hormones distributed to tissues, and what determines which cells hormones will affect?
|
hormones are released by endocrine glands and neurosecretory cells. the hormones then travel through the blood stream to the target cell. the receptor protein on or in a cell determines if a certain cell is affected by a hormone. (lock and key)
|
|
|
non steroid hormones are synthesized from
|
These are amino acid derived hormones. they include hormones made from protiens, peptides, and amines.
these hormones are hydrophilic |
|
|
list the sequence of events in the cell-signaling process in the correct order.
|
Reception - Signal Transduction - Response
Water Soluble Hormone- -hormone binds to receptor -signal transduction pathway is activated (converts extracellular signal to intracellular signal) -final relay molecule activates a protien that carries out the cells response Steroid Hormone- -hormone goes through cell membrane and binds to receptor in cytoplasm or nucleus -the hormone receptor complex attaches to specific sites on the cells DNA -this stimulates transcription of DNA to RNA to Proteins. (steroid hormones work by turning genes on or off) |
|
|
A target cell that is affected by a particular steroid hormone would be expected to have
|
-receptor protein inside the cell.
-hormone receptor complex |
|
|
The hormones secreted in response to long-term stress orginiate from the ____, and their release is stimulated by ___.
|
adrenal cortex and is stimulated by ACTH
|
|
|
Which of the following hormones stimulates and maintains metabolic processes?
|
Thyroid Hormones
(thyroxine T4 , triiodothyronine T3) |
|
|
Which of the following hormones targets the kidneys, which leads to an increase in retention of water and salts (sodium ions), an increase in blood volume, and increase in blood pressure?
|
mineralcorticoids (aldosterone)
|
|
|
The ______is an endocrine gland that raises blood calcium levels by targeting _______ with its hormone.
|
parathyroid raises blood calcium levels by releasing PTH which targets osteoclast thus increasing the blood calcium levels
|
|
|
Which of the following hormones targets (affects) the greatest variety of cell types
|
Hormones that target all body cells:
-T4 -T3 -gluccocorticoids (GH targets all soft tissues and bones) |
|
|
If levels of thyroxine are below homeostatic levels, how will the body respond?
|
the anterior pituitary will constantly be making TSH which will lead to goiter
|
|
|
A diet deficient in iodine can lead to a goiter because of
|
thyroxine cannot be made. because of this the negative feedback, the anterior pituitary keeps releasing TSH causing the thyroid gland to enlarge
|
|
|
consequence of excessive secretion of parathyroid hormone?
|
(parathyroid hormone stimulates osteoclasts which break down bones)
-weak bones -osteoporosis |
|
|
pairs of hormones that have antagonistic effects
|
calcitonin & PTH
epinephrine & norepinephrine |
|
|
When the concentration of glucose in the blood rises following digestion of a meal, what is the hormonal response?
|
insulin is secreted by the pancreas. insulin stimulates the uptake of glucose by cells. in the liver and muscles, the glucose is stored as glycogen.
|
|
|
What is the metabolic abnormality that underlies the characteristic symptoms of Type I diabetes?
|
the beta cells in the pancreas are not producing insulin. so insulin is not present to tell the cells to metabolize the glucose which leads to
-hypoglycemia -lethargy -glucose in urine |
|
|
______ occurs because body cells fail to respond adequately to insulin, and is treated by taking ______
|
type II diabetes is treated eating well and exercising.
|
|
|
functions of epinephrine?
|
increases heart rate & blood pressure
blood glucose levels rise muscles become energized vessels dilate bronchioles dilate |
|
|
The chemical Bisphenol A (BPA), found in some plastics, acts as an endocrine disruptor by miming the action of the hormone
|
estrogen
|
|
|
Which organ secretes hormones that target the liver to breakdown glycogen, the bronchioles in the lungs to dilate, the blood vessels in the intestines to constrict?
|
adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine in the fight or flight response to stress
|
|
|
Which of the following hormones can suppress the body's immune system when administered for extended periods of time?
|
gluccocorticoids
|
|
|
Which of the following is true regarding the function of the pituitary gland?
|
functions of the pituitary gland:
-releases hormones -controls secretions from other glands (hypothalmus is the master controler of endocrine system, hypothalmus makes ADH and oxytocin) |
|
|
Fertilization in the female reproductive tract most often takes place in the
|
oviduct
|
|
|
The embryo implants in the ________ of the uterus
|
embryos implant in the lining of the uterus
|
|
|
After being produced in the testes, sperm mature further in a structure called the
|
sperm mature in the epididymis
|
|
|
Which of the following produces a thick fluid containing fructose, which is used for energy by sperm?
|
the seminal vesicles
|
|
|
Which of the following statements comparing spermatogenesis and oogenesis is true?
|
comparison of spermatogenisis and oogenisis
both use FSH and LH |
|
|
Menstruation (the shedding of the endometrial lining of the uterus)
|
occurs when the endometrium of the uterus breaks down. this is caused by low levels of estrogen and progestrone
|
|
|
In human females, the ovarian cycle begins when
|
FSH secretion begins causing primary follicles to grow
|
|
|
Which of the following hormones stimulates the growth of an ovarian follicle?
|
FSH
|
|
|
A sharp increase in which one of the following triggers ovulation and development of the corpus luteum?
|
LH
|
|
|
The function of a sperm cell's acrosome is to
|
the acrosome stores enzymes that "dig" into the egg
|
|
|
Which of the following serves as an impenetrable barrier that prevents more than one sperm from fertilizing an egg?
|
the vitelline layer
|
|
|
Which of the following results from cleavage?
|
cleavage partitions the zygote so that there are several cells each with its own nucleus. it creates the blastula which is a multicellular embryo. its is also an organizing process because it sets up the embryo for gastrulation
|
|
|
The embryonic tissue layer produced during gastrulation that forms the digestive tract, pancreas, and liver is called
|
the endoderm forms the digestive tract
(ectoderm is skin and nervous, mesoderm is skeletal and muscle) |
|
|
Retinoic acids-based prescription drugs should not be taken by women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant because they interfere with the process of _______.
|
it interferes with gastrulation
|
|
|
Which of the following defines apoptosis?
|
programmed cell death
|
|
|
When does the human blastocyst implant in the wall of the uterus?
|
a week after conception
|
|
|
What would happen if the chorion failed to secrete human chorionic gonadotropin?
|
HCG maintains the production of estrogen and progestrone. if estrogen and progestrone levels become low, menstration occurs causing the embryo to be aborted.
|
|
|
Which of the following structures contributes to the structure of the placenta as well as completely surrounding the embryo?
|
the chorion
|
|
|
Which of the following processes dominates the third trimester of human development?
|
the growth of the fetus. everything to make sure it can survive outside the womb. the circulatory, respiratory, skeletal, and muscle systems grow.
|
|
|
The hormone _____ is made by the ______ and stimulates contraction of both uterine
|
oxytocin is made by the hypothalmus
|
|
|
After implantation of an embryo, ___ is secreted by the embryo into the bloodstream and targets the ________ in order to maintain the endometrial lining of the uterus.
|
HCG is released and is used to target the corpus luteum in the ovary
|
|
|
Which of the following options correctly lists the three stages of labor in the order in which they occur?
|
1. dilation of cervix
2. expulsion of baby 3. delivery of placenta |
|
|
A diet deficient in folic acid can lead to
|
spina bifida
|
|
|
What is the first effect of a spike in estrogen before ovulation?
|
it exerts positive feedback on the pituitary to release bursts of FSH
|
|
|
After ovulation but before menstruation, the levels of _____, which targets the brain to prevent re-entry into the ovarian cycle.
|
estrogen and progestrone
|
|
|
Which of the following statements about resting potential is true
|
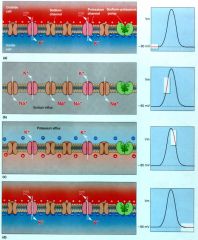
|
|
|
The major divisions of the autonomic nervous system are the
|
-Sympathetic
-parasympathetic -enteric |
|
|
What part of a neuron is involved in receiving a stimulus from another cell
|
dendrites
|
|
|
Multiple sclerosis results from an immune system disorder that primarily involves
|
the scarring and destruction of the mylin sheaths surrounding axons
|
|
|
Once an action potential is triggered, the first major chemical change is
|
the interior of cell become more positive since Na ion flow in.
|
|
|
Action potentials relay different intensities of information due to the
|
frequency of the signals
|
|
|
The gap between the transmitting and receiving neurons in a chemical synapse is known as the
|
the synaptic cleft
|
|
|
Which of the following statements about the sodium-potassium pump is false?
|
The sodium-potassium pump functions much like a revolving door. Its main job is to keep sodium ions (NA+) outside of the cell and keep potassium ions (K+) inside of the cell. With the addition of energy from an ATP molecule, the sodium potassium pump moves three sodium ions out of the cell and moves two potassium ions into the cell with each turn. The goal of this process is to return, or keep, the cell at a resting state, or resting potential.
|
|
|
Which of the following statements about the voltage-gated sodium ion channel is false?
|
voltage gated sodium ion channels open and close depending on the changes in membrane potential.
|
|
|
When an action potential reaches the end of an axon, vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane, releasing neurotransmitters. This process of vesicle fusion and neurotransmitter release directly requires
|
an action potential
|
|
|
Which division of the human nervous system carries signals to skeletal muscles?
|
the peripheral nervous system
|
|
|
The autonomic nervous system
|
regulates the internal environment ex: digestive system, cardiac, excretory and endocrine systems.
|
|
|
Which of the following results from stimulation by the parasympathetic nervous system?
|
all of the following occur:
-slows heart -stimulates digestion -stimulates urination -constricts pupils -stimulates saliva production |
|
|
Which of the following results from stimulation by the sympathetic nervous system?
|
all of the following occur:
-pupils dilate -bronchi dilates -heart rate increases -stimulates epinephrine and norepinephrine release -stimulates glucose release -inhibits digestion and urination |
|
|
The cerebral cortex is part of the
|
the forebrain along with the cerebrum and diencephlon
Midbrain- part of brainstem Hindbrain- Pons, cerebellum, medulla oblangata |
|
|
A physician friend of yours is telling you about a patient with a head injury who suddenly stopped breathing. Your friend explains that the bony rim was pressing against the breathing center. You guess that the "bony rim" (whatever that is) must have been exerting pressure in the region of the
|
medulla oblangata
|
|
|
The drug Prozac is an example of an SSRI, used to treat depression. SSRIs work by
|
it blocks the removal of serotonin from the synapse which increases the amount of time it is available to the receiving cell.
|
|
|
When a stimulus to a sensory receptor cell occurs more frequently (such as increased sweetness on a taste receptor), this results in
|
a stronger perception of a sense
(the more frequent stimulus results in increasing sweetness) |
|
|
Sensory receptors that release neurotransmitteres when its protrusions move or changes shape are called
|
mechanoreceptors more specifically stretch receptors.
|
|
|
You exercised to the point that you were breathing heavily. Your heavy breathing was the result of ________ relaying information about the amount of CO2 an O2 in your blood to the brain, which ultimately resulted in your increased rate of breathing.
|
internal chemoreceptors in some arteries.
|
|
|
The cochlea is
|
a coiled structure found in the inner ear that contains fluid and the organ of corti
|
|
|
What is NOT found in the inner ear?
|
all of these are in the inner ear:
-cochlea -organ of corti (hearing organ) -basilar membrane (floor of middle canal in cochlea) -semicircular canals (balance) |
|
|
Which of the following choices lists structures involved only in the sense of hearing
|
all are involved with hearing:
-eardrum -hammer, anvil, stirrup -oval window -cochlea -organ of corti |
|
|
Which of the following structures is involved in the human sense of balance
|
semicircular canals
|
|
|
When looking at a close-up object, the ciliary muscles __________, making the lens __________.
|
ciliary muscles contract making the lens more rounded
|
|
|
What is a difference between the sensory receptor cells used for the human sense of smell and sense of taste
|
taste receptors release neurotransmitter, triggering action potentials carried to the brain by sensory neurons. Olfactory receptors are modified sensory neurons.
|
|
|
of the following options correctly lists the order in which structures within the ear transfer a sound wave during hearing?
|
-auditory canal
-eardrum -hammer, anvil, stirrup -oval window -cochlea -organ of corti -auditory canal |
|
|
Which part of a bone contains the cells that produce white blood cells
|
the shaft made of compact bone which surrounds the central cavity where yellow bone marrow is stored
|
|
|
The shoulder joint where the humerus meets the shoulder girdle is an example of
|
ball and socket joint
|
|
|
When blood calcium levels are too low, the parathyroid glands releases PTH, which targets _____, causing them to ____ their activity.
|
osteoclasts causing them to increase their activity
|
|
|
Muscles are connected to bones by
|
tendons
|
|
|
Structurally, a sarcomere is
|
is from one Z line to the next Z line
|
|
|
A thin filament consists of
|
actin molecules
|
|
|
Which of the following options lists muscle components in the correct order from largest to smallest?
|
correct order:
-muscle -muscle fibers -myofibrils -sarcomeres |
|
|
During muscle contraction
|
the thin filament (actin) slides across the thick filament (myosin).
|
|
|
describe the power stroke of muscle contraction
|
1. ATP binds to myosin head in its resting position
2. Myosin hydrolyzes ATP to ADP releasing energy that extends the myosin head towards the actin 3. the myosin head and actin latch onto one another. 4. ADP and phosphate are released causing the myosin head to return back to its "resting position" thus causing the actin to move with the head towards the center |
|
|
Which event during muscle contraction is most closely associated with the use of ATP energy?
|
the power stroke
|
|
|
The neurotransmitter found at the synapse between nerves and human skeletal muscle cells is
|
acetylcholine
|
|
|
The calcium that triggers muscle contraction does so by binding to
|
its binds to troponin so that the tropomyosin moves away from the myosin binding sites
|
|
|
What is found in muscle fibers that contains an extra supply of oxygen used for ATP production?
|
glucose since it is used for aerobic respiration
|
|
|
What is stored in the sarcoplasmic reticulum
|
calcium ions
|
|
|
The drug Botox, which is a bacterial toxin, is used to paralyze facial muscles. How does it specifically work to prevent muscle contraction?
|
it blocks the transmission of acytlcholine from nerves to muscles so that muscles cannot contract and stay smooth.
|
|
|
The role of calcium in muscle contraction is to
|
to bind to troponin in order to move tropomyosin out of the way so that the myosin head can perform the power stroke.
|
|
|
According to the sliding filament model of muscle contraction, a sarcomere contracts when its
|
the myosin head attches to actin and drags it as it return back to its resting position.
|
|
|
Changes occur within a sarcomere during muscle contraction. One change is that the
|
-myosin head pivots back and forth
-calcium binds to troponin thus causing tropomysin to move out of the way of the binding site -ATP gets hydrolyzed to ADP and phosphate |

