![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ephelids (Melanocytic Lesions)
|
Freckles
Lighten in winter and darken in summer Increased pigment at basal layer |
|
|
Melasma (Melanocytic Lesions)
|
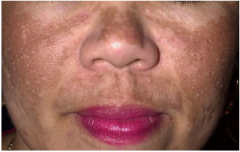
Mask of pregnancy
Diffuse patchy pigment on face Pigment in epidermis and/or dermis Hormonal. |
|
|
Vitiligo (Melanocytic Lesions)
|
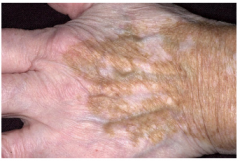
White patches
Complete loss of pigment Loss of melanocytes and pigment |
|
|
Albinism (Melanocytic Lesions)
|
Absence of pigment in skin, hair, and nails
Autosomal recessive Loss of pigment with normal appearing melanocytes |
|
|
Mongolian Spot (Melanocytic Lesions)
|
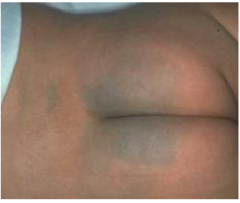
Bluish-gray lumbosacral patch in newborns
More common in pigmented races Resolves in early childhood (Present in neonates and then fades clinically). Sparse deep dendritic melanocytes (in dermis) |
|
|
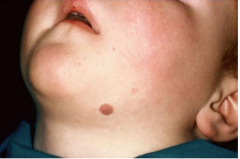
Cafe au Lait (Melanocytic Lesions)
|

Light brown patches
6 or more 0.5 cm in child --> neurofibromatosis 6 or more 1.5 cm in adolescence --> neurofibromatosis Increased pigment in basal layer |
|
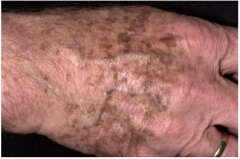
Lentigo (Melanocytic Nevus)
|
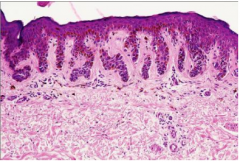
Macular pigmented lesions on sun exposed skin
Indication of photodamage Microscopic: Increased melanocytes at Dermal-Epidermal (DE) junction without nest formation. |
|
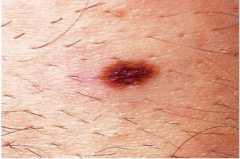
Junctional Nevus (Melanocytic Nevus)
|
Macular pigmented lesion
Microscopic: Nests of melanocytes along the DE junction |
|
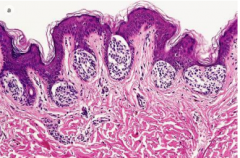
Compound Nevus (Melanocytic Nevus)
|
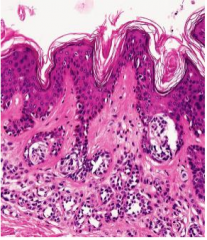
Slightly raised pigmented plaque
(Macular and Papular lesions clinically) Microscopic: Nests of melanocytes at DE junction and within the dermis |
|
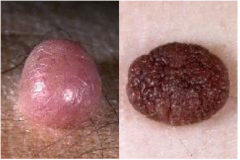
Intradermal Nevus (Melanocytic Nevus)
|
Papular lesions
Microscopic: Nests of melanocytes within the dermis |
|
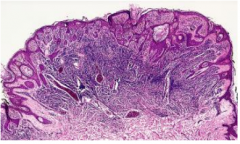
Spitz's Nevus (Melanocytic Nevus)
|
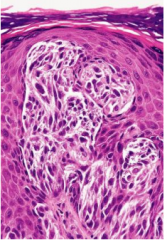
Papular regions of children
Histologically "benign juvenile melanoma" -- NOT! Microscopic: Epitheliod and spindle cell melanocytes can look atypical Nests often vertically oriented (Often confused with melanoma) |
|
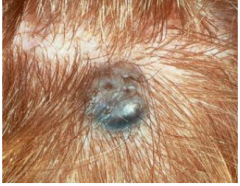
Blue Nevus (Melanocytic Nevus)
|
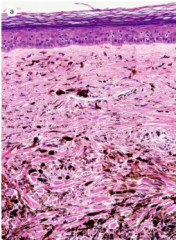
Bluish papule or macule
Deeper melanin appears blue due to Rayleigh scattering Microscopic: Heavily melanized dendritic melanocytes within the mid to deep dermis |
|
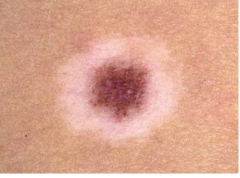
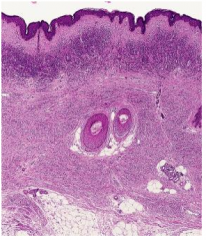
Halo Nevus (Melanocytic Nevus)
|
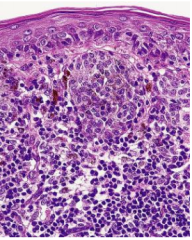
Depigmented zone around a nevus
Common (okay) in children Bad in elderly Microscopic: Lymphocytes surround benign nests of melanocytes |
|
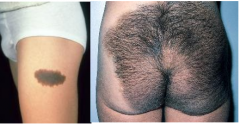
Congenital Nevus
|
Large "bathing trunk nevus" has increased risk of melanoma
Small form not strongly associated with melanoma Microscopic: Benign melanocytes extend more deeply into dermis and even subcutaneous tissues. |
|
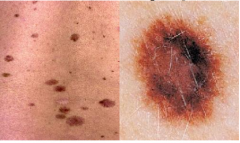
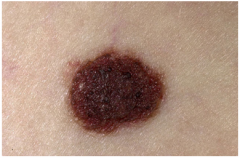
Dysplastic Nevus (Melanocytic Nevus)
|
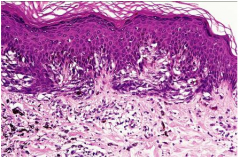
Larger irregular morphology (often larder than most moles -- can be confused with melanoma)
Heritable Melanoma Syndrome (sparse and low risk) Controversial Diagnosis (could be atypical nevus or Clark's nevus) Microscopic: Atypical melanocytes (in junctional nests with disordered organization) Nests steam horizontally Severely atypical treated as melanoma in situ |
|
|
Nevus
|
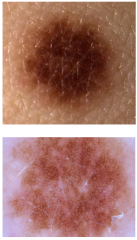
Slightly irregularity of border and color
Dermoscopy reveals a fine reticular pigment network without atypical features. |
|
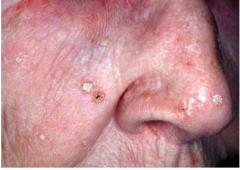
Actinic Keratosis
|
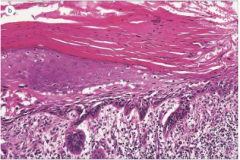
Scaly/hyperkeratotic lesions on sun exposed skin--(hard and spiny feel it)
Considered pre-cancerous, but only about 1% evolve to SCC. Microscopic: Atypical keratinocytes in lower epidermis Underlying solar elastosis (bluish dermis) Overlying parakeratosis (retained nuclei) Treatment: cryogenic surgery (liquid nitrogen) fluorouracil cream |
|
|
Seborrheic Keratosis (treatment is unnecessary, they just look gross)
|
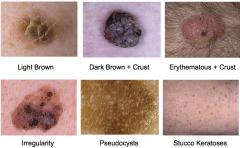
Appear as one gets older -- most commonly in elderly
Can show in younger if there is a strong genetic tendency in family Stuck on lesions -- keratotic with varying shades of brown, but can be skin colored or even erythematous Can be rough or smooth surface and be large or small May have keratotic pores or pseudocysts Sometimes inflamed or bleeding from picking Not limited to sun exposed surfaces (Feel "velvety" when compared to actinic keratosis) Microscopic: Epidermal hyperplasia Orthokeratosis (no retained nuclei) Horn pseudocysts -- cysts connect to the surface like this |
|
|
Acanthosis Nigricans (need to treat the internal disease or obesity)
|
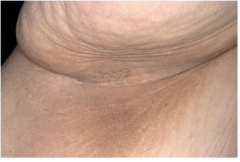
Most common in obesity but rarely associated with internal tumors (or diabetes, auto-immune diseases, familial, and medication reactions)
Clinically velvety brown plaques -- usually in the axillae. (Sometimes associated with skin tags-acrochordons) Microscopic: papillomatosis and orthokeratosis |
|
|
Fibroepithelial Polyps
|
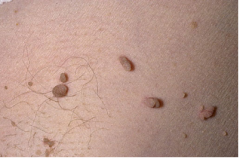
Also known as acrochordons
Skin tags More common in obesity involving neck, axillae, and groin areas. Can be associated with Acanthosis Nigricans. Microscopic: epidermis covering an polypoid fibrovascular core Can be treated with cyrogenics |
|
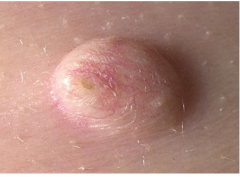
Epidermoid Cysts
|
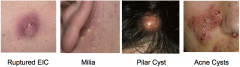
Sometimes referred to as "sebaceous cysts"--NOT!
Expansion of hair follicle forms epithelial lining. Also forms EICs from trauma Pilar cysts has trichilemmal keratinization arises from the lower region of the hair follicle Acne cyst results from follicular rupture |
|
|
Sebaceous Hyperplasia
|
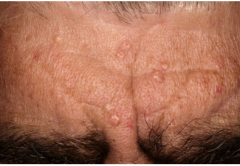
Common in middle and elderly men.
Umbilicated pale yellowish papules Benign tumor of sebaceous glands |
|
|
Syringoma
|
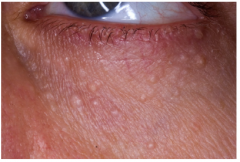
Seen under the eyes of women
Small skin colored papules Benign tumor of eccrine sweat glands |
|
|
Nevus Sebaceous
|
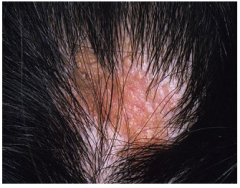
Birthmark lacking hair when on scalp
Prepubertal may appear smooth yellow/orange Adolescent has cobblestone surface Adult form in prone to basal cell carcinoma. |
|
|
Adenoma Sebaceum
|
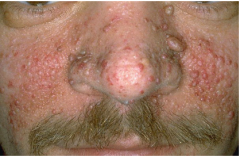
Central facial papules
One manifestation of Tuberous Sclerosis Angiofibromas, histologically. |
|
|
Neurofibroma
|
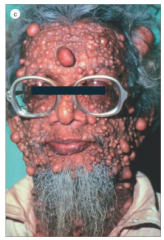
Von Recklinghausen's
Solitary lesion more commonly Spindle cell tumor of Schwann cells and fibroblasts |
|
|
Xanthelasma
|
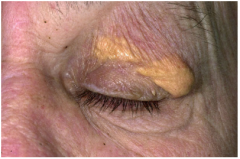
Yellowish plaques on eyelids
Not strongly associated with increased lipids -- other xanthomas associated with increased lipids (associated with lipid disorders) Foamy histiocytes contain the lipid. |
|
|
Trichilemmona
|
Indicative of Cowden Syndrome/ Breast Carcinoma
|
|
|
Sebaceous Adenoma
|
Multi-Torre Syndrome/mult CA
|
|
|
Dermatofibroma
|
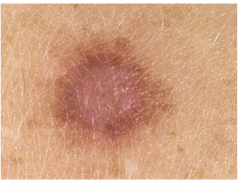
Common in the legs of women, most common growth in the knee in young adults, may arise from former arthropod bite
Brownish papule with "dimple sign" Benign fibrohistiocytic tumor Microscopic: bland fibrohistiocystic dermal proliferation; histiocytes may contain hemosiderin pigment from ingestion of hemoglobin |
|
|
Keratoacanthoma (GET RID OF THIS)
|
Rapidly growing "volcanoe-like" lesion with keratin center
Sometimes resolve spontaneously Rare metastasis -- take it out immediately? Resembles squamous cell carcinoma histologically Microscopic: Glassy well differenciated keratinocytes form a cup-like depression |
|
|
Angiomas (Mesenchymal Tumors)
|
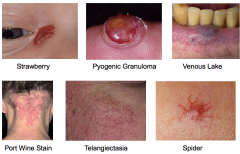
Capillary blood vessels in the dermis
Cherry angiomas most common Strawberry angiomas in children often resolve spontaneously Pyogenic granuloma is a traumatic variant Port wine stains are very common in the form of a "stork bite" on posterior neck Venous lakes occur on lips and ears Telangiectasia of face is more commonly due to sun damage than rosacea |
|
|
Keloid (Tumor-Like Lesions)
|
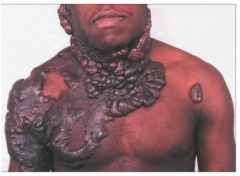
Hypertrophic scars that extend beyond initial injury
More common in African-American Microscopic: broad bands of collagen Can be treated with corticosteroids |
|
|
Lipoma (Mesenchymal Tumors)
|
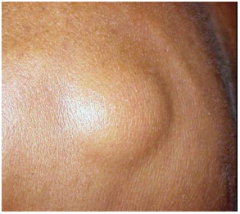
Expanded fat lobules below the dermis encapsulated within a thin fibrous capsule
Soft mobile subcutaneous mass Solitary or multiple Stable size When tender = angiolipoma |
|
|
Verruca (Warts)
|
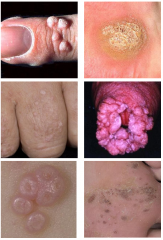
Verruca -- common warts; seeds = microhemorrhage
Plantar warts -- common warts "pounded inward" Verruca plana -- flat warts Condyloma accuminatum -- gential, STD, HPV 6, 11 most common Molluscum Contagiosum -- pox virus, not HPV -- children and STD in adults Mosaic warts -- extensive plantar involvement |
|
|
Heritable Melanoma Syndrome (Melanocytic Nevus)
|
Associated with Dysplastic Nevus
But actually: 100 nevi, large and irregular Associated of family history |

