![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sensory (afferent) neurons |
transmit sensory information from receptors to CNS |
|
|
Motor (efferent) neurons |
transmit motor information from CNS to muscles and glands |
|
|
CNS (central nervous system) |
brain and spinal cord (olfactory and optic nerves) |
|
|
PNS (peripheral nervous system) |
nerve tissue and fibers outside CNS |
|
|
Somatic Nervous System |
sensory and motor neurons in skin, joints, muscles |
|
|
Autonomic Nervous System |
controls automatic body processes |
|
|
parasympathetic nervous system |
conserve energy; resting and sleeping states |
|
|
sympathetic nervous system |
stress; fight-or-flight |
|
|
meninges |
thick sheath of connective tissue protecting the brain |
|
|
dura mater |
outermost layer of meninges |
|
|
arachnoid mater |
middle layer of meninges |
|
|
pia mater |
innermost layer of meninges |
|
|
hindbrain |
balance, motor coordination, breathing, digestion |
|
|
rhombencephalon |
hindbrain |
|
|
myelencephalon |
during embryonic development, becomes medulla oblongata |
|
|
metencephalon |
during embryonic development, becomes pons and cerebellum |
|
|
pons |
sensory and motor pathways between cortex and medulla |
|
|
cerebellum |
posture, balance, coordination |
|
|
midbrain |
receives sensory and motor information |
|
|
mesencephalon |
midbrain |
|
|
superior colliculus |
in midbrain, receives visual sensory input |
|
|
inferior colliculus |
in midbrain, receives auditory sensory input (reflex to sudden noises) |
|
|
forebrain |
complex perceptual, cognitive, behavioural processes, emotion and memory |
|
|
prosencephalon |
forebrain |
|
|
telencephalon |
during embryonic development, becomes cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, limbic system |
|
|
diencephalon |
during embryonic development, forms thalamus, hypothalamus, posterior pituitary, pineal gland |
|
|
basal ganglia |
smooth movement |
|
|
cerebellum |
coordinated movement |
|
|
cerebral cortex |
complex perceptual, cognitive, and behavioural processes |
|
|
hypothalamus |
hunger and thirst; emotion |
|
|
inferior and superior colliculi |
sensorimotor reflexes |
|
|
limbic system |
emotion and memory |
|
|
medulla oblongata |
vital functioning (breathing, digestion) |
|
|
reticular formation |
arousal and alertness |
|
|
thalamus |
sensory relay station |
|
|
frontal lobe |
executive function, impulse control, long-term planning, motor function, speech production |
|
|
prefrontal cortex |
long-term planning |
|
|
primary motor cortex |
motor function |
|
|
broca's area |
speech production |
|
|
parietal lobe |
sensation of touch, pressure, temperature, pain; spatial processing, orientation, manipulation |
|
|
somatosensory cortex |
sensation of touch, pressure, temperature, pain |
|
|
occipital lobe |
visual processing |
|
|
temporal lobe |
sound processing, speech perception, memory, emotion |
|
|
auditory cortex |
sound processing |
|
|
wernicke's area |
speech perception |
|
|
visual system, dominant hemisphere |
letters, words |
|
|
visual system, nondominant hemisphere |
faces |
|
|
auditory system, dominant hemisphere |
language-related sounds |
|
|
auditory system, nondominant hemisphere |
music |
|
|
language, dominant hemisphere |
speech, reading, writing, arithmetic |
|
|
language, nondominant hemisphere |
emotions |
|
|
movement, dominant hemisphere |
complex voluntary movement |
|
|
movement, nondominant hemisphere |
- |
|
|
spatial processes, dominant hemisphere |
- |
|
|
spatial processes, nondominant hemisphere |
geometry, sense of direction |
|

|
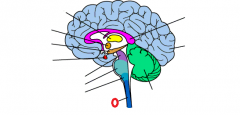
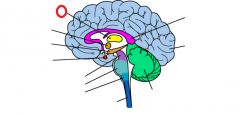
cerebellum |
|
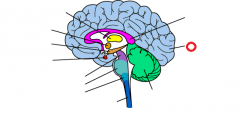
|
cerebral cortex |
|
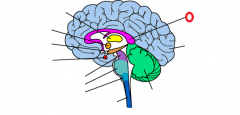
|
corpus callosum |
|
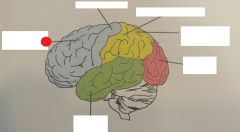
|
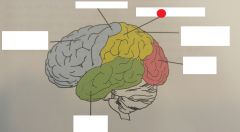
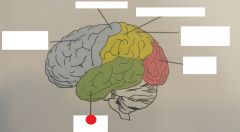
frontal lobe |
|
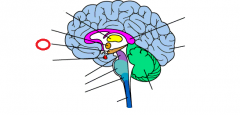
|
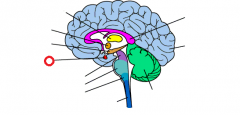
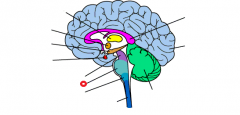
hippocampus |
|
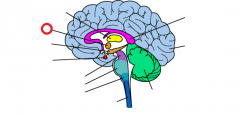
|
hypothalamus |
|
|
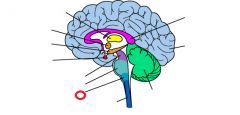
medulla |
|
|
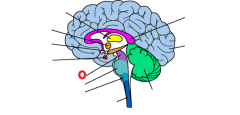
midbrain |
|
|
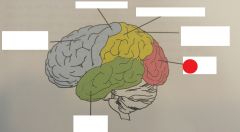
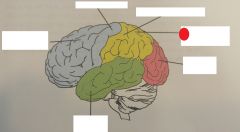
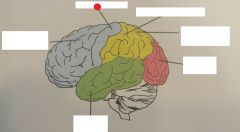
occipital lobe |
|
|
parietal lobe |
|
|
pituitary |
|
|
pons |
|
|
primary motor cortex |
|
|
primary somatosensory cortex |
|
|
spinal cord |
|
|
temporal lobe |
|
|
thalamus |

