![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
175 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What factors play a part in aeronautics? |
Newton's law of motion and universal gravitation, Bernoulli's principle, weight and balance, flight envelope factors, and aircraft axi. |
|
|
|
What does Isaac Newtons 3 laws of motion detail? |
Fundamental mechanics of motion |
|
|
|
What does newton's first law of motion focus on? |
Inertia |
|
|
|
What does newton's second law of motion focus on? |
Accelerated motion applied to a force |
|
|
|
What does newton's third law of motion focus on? |
Relationship of motion between any two objects |
|
|
|
What does the law of inertia state |
An object at rest tends to stay at rest and vise versa unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. |
|
|
|
What are the types of friction? |
-Sliding or kinetic friction -fluid friction -rolling friction - static friction
|
|
|
|
What is Sliding or kinetic friction |
One object sliding across another |
(Book on table) |
|
|
What is fluid friction? |
Object moving through gas or liquid |
Fish through water/ plane through air |
|
|
What is rolling friction |
Object rolling across another surface |
Bowling ball on alley |
|
|
What is static friction? |
Dude keeping an object at rest |
Trash can on floor |
|
|
What does the second law of motion state? |
When a body is acted upon by a constant force, its acceleration is inversely related to its mass but directly proportionate to the applied force |
|
|
|
What is a net force of an object equal to? |
Object mass times acceleration |
|
|
|
What does the equation that determines net force look like? |
F = ma |
|
|
|
What is one unit of force defined as? |
Newtons |
|
|
|
What is a newton? |
One unit of force |
|
|
|
What is mass weight in? |
Kilograms |
|
|
|
What is acceleration measured in? |
Meters per second per second or m / s / s or M / s squared |
|
|
|
What does m / s / s mean? |
Meters per second per second |
|
|
|
What does Newton's Third Law of Motion state? |
If two objects in interact, the force exerted by the first object on a second object is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force exerted by the second object on the first object |
|
|
|
Provide an example of Newton's third law of motion |
Tennis racket hitting a tennis ball is equal in magnitude and opposite the force exerted by the ball on the tennis racket |
|
|

|
B. The velocity of the object must be constant |
|
|
|
What does Newton's law of universal gravitation state? |
Particles attract every other particle in the universe with the force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them |
|
|

|
The force decreases by a factor of 16 or 4 x 4 |
|
|
|
What principle did Daniel Bernoulli device and relation to hydro Dynamics? |
Within a horizontal flow of fluid points are faster fluid speed will experience less pressure than points of slower fluid speed |
|
|
|
What is essential to the operation of braking and flight control systems? |
Accurate pressure flow of fluids |
|
|
|
Along with Hydro Dynamics what does Bernoulli's principle also apply to? |
Airflow during the basic phases of flight |
|
|
|
What are the basic phases of flight? |
Take off, flight and Landing |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a wing's curvature? |
Causes air to pass faster over the top of the wing than under the wing |
|
|
|
What is created when air passes faster on top of the wing ? |
Low pressure area |
|
|
|
What is created when air passes slower under the wing? |
High pressure area |
|
|
|
What produces lift for an airplane? |
High and low pressure areas |
|
|
|
What are the four forces of flight? |
Weight, lift, thrust and drag |
|
|

|
Hey. Fluids moving out of points in a horizontal pipe at higher speed have lower pressure than fluids moving at a point at lower speeds |
|
|
|
What does EWCG stand for? |
Empty weight center of gravity |
|
|
|
What does MEW stand for? |
Manufacturer's empty weight |
|
|
|
What is a manufacturer's empty weight? |
Total weight of the aircraft as it was built |
|
|
|
What does MEW include? |
Systems and components required for flight only |
|
|
|
What does OEW stand for? |
Operating empty weight |
|
|
|
What is operating empty weight? |
Manufacturers empty weight plus weight of the crew, fluids, unusable Fuel and Equipment required for flight |
|
|
|
What doesAUW stands for? |
All up weight |
|
|
|
What is all up weight? |
Gross weight or total aircraft weight at any given moment during a flight |
|
|
|
Which weight decreases as fuel and fluids are consumed during operations? |
All up weight or aircraft gross weight |
|
|
|
What does MLW stand for? |
Maximum Landing weight |
|
|
|
What does the maximum Landing weight identify? |
Aircraft weight limit for landing |
|
|
|
What does exceeding this weight do? |
Increase stress on landing gear and may affect the distance required for a safe landing |
|
|
|
What does MZFW stand for? |
Maximum zero fuel weight |
|
|
|
What is maximum zero fuel weight |
Allowable weight of an aircraft with his conscience and it's included unusable fuel |
|
|
|
What does maximum zero fuel weight exclude? |
The weight of usable Fuel and any consumable fluids |
|
|
|
What does MTOW stand for? |
Maximum takeoff weight |
|
|
|
What is maximum takeoff weight? |
And aircraft weight limit for take off |
|
|
|
What does exceeding maximum takeoff weight limit do? |
Increase power required for takeoff, lengthen Runway distance needed for successful lift off, and places excess stress on aircraft structure |
|
|
|
What does MRW stand for? |
Maximum ramp weight |
|
|
|
What is maximum ramp weight? |
Weight limit for an aircraft a taxi or be towed on the ground |
|
|
|
What does the flight envelope and compass? |
Speed limits, altitude, and angle of attack required by any aircraft to maintain stable flight |
|
|
|
What may occur as a result of an incorrect combination of flight envelope factors? |
A stall |
|
|
|
What does the aircraft experienced during a stall? |
Decrease and lift and reduction and airspeed |
|
|
|
What does AOA stand for? |
Angle of attack |
|
|
|
What is the angle of attack? |
The angle between the direction of the airflow against the wing and the chord |
|
|
|
What is a Wings chord? |
An imaginary reference line that extends from the Leading Edge to the trailing edge of the wing |
|
|
|
What is an aircraft airfoil section design for? |
Maximum lift and fuel efficiency |
|
|
|
What creates low pressure above and high pressure below a wing as air passes? |
Curved Leading Edge |
|
|
|
What happens as air passes over the end of a wing or at the end of a helicopter rotor blade? |
The air changes Direction |
|
|
|
What is the change of direction of air called as it goes over the end of a wing or the end of a helicopter rotor? |
Down wash |
|
|
|
What does downwash help produce? |
Lift |
|
|
|
When would downwash be most visible relating to helicopters? |
Hovering over water |
|
|
|
How many control parts does a trailing edge of a wing have? |
2, aileron's and flaps |
|
|
|
What is drag? |
Air resistance experienced during flight |
|
|
|
What is Parasite drag? |
Objects on aircraft that produce drag ie flat tires, skin friction, rivets |
|
|
|
What is skin friction? |
Rough spot on the skin of the aircraft structure |
|
|
|
What types of drag are there? |
Parasite drag, profile drag, induced drag |
|
|
|
How is profile drag produced? |
Shape of the aircraft |
|
|
|
What is induced drag? |
When are flowing rapidly of top meat with slower are at the bottom creating a vortex |
|
|
|
What does induced drag depend on? |
Aircraft performance |
|
|
|
What happens to induced drag when lift, air speed and angle of attack increases? |
Induced drag increases |
|
|

|
D. An increase in angle of attack |
|
|

|
C. Air pressure is lower above the wing and higher below the wing |
|
|
|
What axes does an aircraft have? |
Longitudinal, lateral, and vertical |
|
|
|
What controls does the longitudinal axis Control? |
Roll (ailerons) |
|
|
|
What controls does the lateral axis Control? |
Pitch (elevators) |
|
|
|
What controls does a vertical axis control? |
Yaw (rudder) |
|
|
|
What does controlling the axis of the aircraft do? |
Keep the aircraft in trim |
|
|
|
What is trim? |
Aircraft desired position |
|
|
|
Where are Rudders located? |
Trailing edge of the wing |
|
|
|
Where are elevators located at? |
Rear portion of horizontal tail |
|
|
|
Where are Rudders located at? |
Rear portion of vertical tail |
|
|

|
C. Elevators along the lateral axis |
|
|
|
What is of extreme concern for Pilots when flying? |
Atmospheric pressure |
|
|
|
How much does air weigh? |
14.7 PSI |
|
|
|
What does Humidity and low air density levels due to aircraft capabilities? |
Reduce capability for power, thrust and lift |
|
|
|
What happens when the intake of an engine receives less air? |
Propellers become inefficient and thin air applies less force on the wings resulting in less than maximum lift |
|
|
|
What are some factors that affect aircraft performance? |
Altitude, pressure, temperature, and humidity |
|
|
|
What is a pressure altimeter in a cockpit automatically calibrated to? |
29.92 to inches of Mercury (Hg) |
|
|
|
What must a pilot do after departing an Airfield to ensure the correct pressure altitude of the aircraft is displayed for the destination Airfield? |
Reset pressure altitude indicator |
|
|
|
What may occur if pressure altitude indicator is not reset after departing an Airfield? |
Aircraft maybe at a lower altitude than what is displayed in the altimeter |
|
|
|
At what temperature do all aircraft perform more efficiently? |
Cold temperature |
|
|
|
Why do aircraft perform more efficiently in cold temperature? |
Cold Air is denser than warm air |
|
|

|
C. High air density increases engine performance |
|
|
|
What is the main section of an aircraft that holds the crew, passengers and cargo? |
Fuselage |
|
|
|
Along with holding Wings, tail, engines, and landing gear, what use does the fuselage provide? |
Stabilisation of an aircraft during flight |
|
|
|
What are the two main types of aircraft structure |
Truss and monocoque |
|
|
|
What does a truss structure consists of? |
Welded steel tubing longerins separated by diagonal members |
|
|
|
What is a monocoque structure consists of? |
Thin sheets of aluminum alloy curved to fit the shell of a fuselage |
|
|
|
What is the skin of a monocoque structure designed to do? |
Whith stands the stress of loads and minimize total weight of aircraft |
|
|

|
The weight and strength of a material |
|
|
|
What is a low wing structure? |
Wings attached to bottom of fuselage |
|
|
|
What is a high wing structure? |
Wings attached to top of fuselage |
|
|
|
What is a mid wing structure? |
Wings attached to middle of fuselage |
|
|
|
What is a cantilever design? |
One where no external braces are required |
|
|
|
What is semi-cantilever design? |
External braces are attached to wing |
|
|
|
What aircraft usually have semi-cantilever design? |
Smaller fixed wing |
|
|
|
What is a plane with two levels of wings? (Top and bottom) |
Biplane |
|
|
|
What wing angles assist in stabilization? |
Dihedral and anhedral |
|
|
|
What do dihedral and anhedral do? |
Assist in stabilization |
|
|
|
What angle does dihedral point? |
Up |
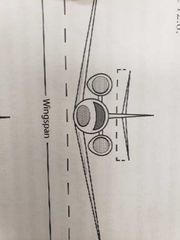
|
|
|
What angle does anhedral point? |
Down |
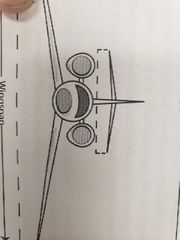
|
|
|
What happens when the measurement of the chord line and the camber line differ greatly? |
Curvature of wing provides more lift |
|
|
|
In reference to the airfoil, what is thickness? |
Percentage of wing chord |
|
|
|
In reference to the airfoil, what is a chord? |
Distance between leading and trailing edge |
|
|
|
In reference to the airfoil, what is the camber line? |
Amount of curvature in the wing |
|
|
|
How many types of planforms are there? |
4- Rectangular Elliptical Tapered Swept |
|
|
|
Describe rectangular planform |
Simplest, highly efficient |
|
|
|
Where is rectangular planform used? |
Light general aviation |
|
|
|
Describe elliptical planform |
Most efficient with lowest possible induced drag |
|
|
|
Describe the tapered planform |
Cross between regular and elliptical, better lift, moderate efficiency |
|
|
|
What do aircraft with tapered wings have? |
Wide range of speeds |
|
|
|
What position is a swept planform and why? |
Tapered back to reduce drag |
|
|
|
What type of swept planforms are there? |
Slightly swept Moderately swept Sharply swept |
|
|
|
What disadvantages exist for swept wing planforms? |
Tendency to twist under stress |
|
|
|
What swept style wing is found on supersonic aircraft? |
Delta wing |
|
|
|
What advantages does a delta wing have? |
Very strong and can carry high volume of fuel |
|
|
|
What type of sweep is a delta wing? |
Highly swept triangular type |
|
|
|
What does the delta wing have that other swept wings dont? |
High incidence of induced drag |
|
|

|
C. Chord line |
|
|
|
What does a powerplant encompass? |
Engine Propellers Induction Exhaust Electrical Cooling Lubrication Fuel systems |
|
|
|
Referencing newton's third law of motion, what must an aircraft do to generate lift? |
Create enough thrust to generate lift that overcomes drag |
|
|
|
How is thrust accomplished? |
Converting the exploding gas-air mixture into mechanical energy |
|
|
|
What shape do propellers and fans use? |
Airfoil shape |
|
|
|
What does the airfoil shape propeller and fans produce? |
"Left" in the forward direction |
|
|
|
What kind of engine is used for aircraft not exceeding 250mph? |
Reciprocating engine |
|
|
|
What engine do larger more powerful aircraft use? |
Gas turbine engine |
|
|
|
What engine do aircraft traveling at high altitudes(<30k feet) use? |
Turbo supercharged reciprocating engine |
|
|
|
What engine do aircraft operating at mach 1 or higher use? |
Turbojet engine |
|
|
|
How do engines operate at takeoff? |
Maximum performance |
|
|
|
What happens to power when climbing? |
It is cut back then reduced to a fuel efficient level when cruising level |
|
|
|
What type of propellers are there? |
Fixed pitch Variable pitch Pusher propeller |
|
|
|
Which sets pitch on fixed pitch propellers? |
Manufacture |
|
|
|
What does a variable pitch propeller allow a pilot to do? |
Adjust blade pitch during flight |
|
|
|
Where is a pusher propeller located? |
Behind aircraft facing to the rear |
|
|
|
What does a push propeller do? |
Pushes aircraft forward by directing thrust backwards instead of pulling aircraft forward |
|
|
|
What does a propellers pitch affect? |
The way it cuts into the air, producing air mass |
|
|

|
D. 4,666.67 thp |

|
|
|
When must landing gear support aircraft? |
Takeoff Landing Ground navigation |
|
|
|
What landing gear types are there? |
Tail wheel Tandem Tricycle |
|
|
|
When is a tail wheel landing gear system used? |
When main landing gear is forward center of gravity |
|
|
|
What is a tail wheel beneficial for? |
Landing on non-paved runways |
|
|
|
What landing gear has both main and tail portion landing gear mounted along the longitudinal axis? |
Tandem |
|
|
|
What does tandem landing gear support? |
Use of very flexible wings |
|
|
|
What landing gear style supports increased braking ability, higher landing speeds and better visibilty? |
Tricycle |
|
|
|
What kind of gear does tricycle landing gear have? |
Main and nose landing gear |
|
|
|
How is nose gear used on smaller planes? |
Mechanical linkage (rudders) |
|
|
|
How is nose gear used on larger aircraft? |
Hydraulic power |
|
|
|
What improves landing gear tire saftey? |
Having multiple wheels on each main gear |
|
|

|
A.1 B.2 C.3 C.4 (the center of gravity is forward NOT the landing gear!) |
|
|
|
What is the rear tail section of an aircraft called? |
Empenage |
|
|
|
What does an empenage do? |
Provides stability |
|
|
|
What does an empenage consist of ? |
Rudders Vertical stabilizers Horizontal stabilizer Trim tabs Elevators |
|
|
|
What empenage components are part of the vertical tail structure |
Rudders Vertical stabilizer |
|
|
|
What do rudders do (aside from control yaw)? |
Keep aircraft in coordinated flight |
|
|
|
What does the vertical stabilizer do? |
keeps aircraft from yawning back and forth |
|
|
|
What components are part of the horizontal tail structure? |
Elevators Horizontal stabilizer |
|
|
|
What does the horizontal stabilizer do? |
Prevent the aircraft from pitching up and down |
|
|
|
What type of control are trim tabs? |
Secondary |
|
|
|
What do trim tabs do? |
Offset undesirable attitude and relieve pressure on controls |
|
|
|
What relationship do trim tabs and elevators have? |
Inverse. Going up on trim puts elevators down (a/c goes down) Going down on trim puts elevators up (a/c goes up) |
|

