![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the three assumptions of the Behaviourist Approach? |
• Humans are born like a blank slate
• Behaviour is learned through conditioning
• Humans and animals learn in similar ways |
There are four terms |
|
|
Describe the process of Classical Conditioning |
A UCS provokes a UCR. A NS is then introduced and is presented with the UCS. The NS then produces a CS which is identical for the UCR.
Therefore associating the previous Response with a different Stimulus |
|
|
|
What can happen after classical conditioning which lowers it's effectiveness |
Extinction, Spontaneous Recovery, Generalisation or Discrimination |
|
|
|
What is Operant Conditioning? |
Shaping behaviour through reinforcement |
|
|
|
Social Learning Theory says you're more likely to imitate someone if?
Who said this? |
• Same gender • Similar age • Powerful/High status • Friendly/Likable
Said by Albert Bandura |
|
|
|
Give three ways of accessing the unconscious |
• Dream analysis • Rorschach Inkblot test • Free association |
|
|
|
What can the process of conditioning teach us? |
• We can shape behaviour • We start as a "blank slate" • If we can elicit a response, we can eradicate it |
|
|
|
For Aversion therapy give its use, aim and an example |
To treat addictions
Aim: To condition the patient to associate an undesirable behaviour with an aversive (negative) response
E.g. An Alcoholic given emetics to make then feel sick when they drink alcohol |
|
|
|
For Systematic Desensitisation give its use, aim and an example |
To treat phobia
Aim: To slowly introduce a phobia by using a hierarchy of fear then using relaxation techniques whilst moving along this hierarchy
E.g. Slowly making a person go near a spider whilst controlling their breathing |
|
|
|
What does N-NURDS stand for? Why is it useful? |
Nature/Nurture Nomothetic/Idiographic Usefulness Reductionism/Holism Determinism/Free Will Scientific
Used to remember points when evaluating Approaches |
|
|
|
Give the mnemonic to remember the Psychosexual stages of development and what they stand for |
Old Age Pensioners Love Guinness
Oral Anal Phallic Latency Genital |
|
|
|
Give the assumptions of the Psychodynamic Approach |
• Influence of Childhood Experiences
• Unconscious Mind
• Tripartite Personality |
|
|
|
Give the stages of the Oedipal Complex |
1. Boy focuses sexual energy onto his mother
2. Sees father as threat and gets jealous
3. Boy fears that if father finds out, he'll castrate him (Castration Anxiety)
4. He realizes the only way to possess his mother is to become his father
5. Boy internalizes his father which becomes his superego and his desire for his mother becomes desire for other women |
|
|
|
Give the stages of the Electra Complex |
1. Realises doesn't have a penis
2. Gets penis envy, blames her Mother
3. Becomes attracted to Father who has a penis
4. Sees Mother as a rival for father
5. Girl identifies with Mother but penis envy isn't as strong as castration anxiety so girls have a weaker Superego |
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of the unconscious mind? |
• Not logical • Can't determine between real external and internal events • Seeks pleasure • Causes dreams and parapraxes |
|
|
|
Give the three assumptions of the Biological Approach |
• Evolutionary Influences
• Localisation of brain functions
• Neurotransmitters |
|
|
|
Define the two therapies used in the Biological Approach and an example of each |
Psychosurgery: Operating on the brain to control/treat mental disorders
E.g. Lobotomy
Chemotherapy: Using chemicals to alter the way thats the brain works to control/treat mental disorders
E.g. Morphine for pain |
|
|
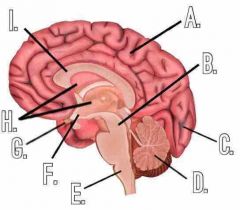
Name the parts of the brain labelled and what they do (except B, G and H) |
A. Cerebrum - Site of intelligence, learning, memory, personality and ability to reason
B. Midbrain
C. Visual Cortex - Associated with sight
D. Cerebellum - Coordinated movement and balance
E. Medulla Oblongata - Reflex control of breathing, heart rate and pressure
F. Hypothalamus - Coordinates automatic nervous system, thirst, hunger and aggression
G. Pituitary Gland
H. Ventricles
I. Corpus Callosum - Connects hemispheres |
|
|
|
Who created the GAS theory? When? |
Hans Selye
1936 |
|
|
|
What does the GAS theory stand for and why |
General: Same response despite stressor
Adaptive: Body's way of adapting to cope
Syndrome: Range of responses, not just one |
|
|
|
What are the three stages of the GAS theory? Describe each |
1. Alarm (First 48h) - Cortisol decreases immune response - Adrenaline increases heart rate, blood pressure, strength, sugar from liver (energy)
2. Resistance - Effects from Adrenaline stay elevated
3. Exhaustion - Control over immune system is lost so the chances of contracting disease increases |
|
|
|
How can the Nervous System be split down? Describe each part |
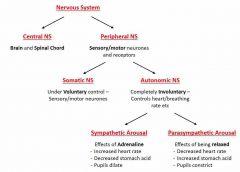
|
|
|
|
What are the long and short term effects of stress? |
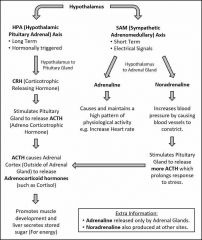
|
HPA and SAM axis |
|
|
What can chemotherapy drugs be used to do? |
• Block receptors
• Making membranes impermeable so vesicles fusing
• Stop pathways selectively
• Enhance signaled |
|
|
|
For three drugs give: - What they do - How they do it - What they treat |
Morphine - Controls experience of pain - Imitates action of endorphins - Treats severe pain
Chlorpromazine - Reduces symptoms - Blocks dopamine receptor sites - Schizophrenia
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) - Reduces sadness - Blocks return of Serotonin to pre-synaptic membrane - Treats depression |
|
|
|
Describe the mechanism of Natural Selection |
1. Variation in appearance or abilities
2. Competition for resources e.g. Food, mates, space
3. There are more offspring born than can survive
4. Organisms better suited survive and pass on their genetics |
|
|
|
Are humans more likely to show adaptive or non-adaptive behaviour and why? |
Non-adaptive because we don't just have to consider survival and we have spare time |
|
|
|
How can Phobias be seen as an evolutionary advantage? |
Those scared of something dangerous are more likely to avoid it and survive |
|
|
|
How can Phobias be seen as an evolutionary advantage? |
Those scared of something dangerous are more likely to avoid it and survive |
|
|
|
How does the EEA explain the formation of the large human brain? |
• Evolved in response to social interactions
• Those better at forming alliances and good relationships survived
• Genes relating to these characteristics were passed on |
|
|
|
What theory did Trivers (1972) come up with? What does it suggest |
Parental Investment Theory
Male mammals less selective as they spend less time with offspring. Females are more selective as they invest more time |
|
|
|
What does the EEA say males and females seek? |
Both seek more fertile and healthy mates
Fertility can be detected in females who have a thin waste, red lips, soft skin
Females seek males who are resourceful i.e. Food, shelter, security |
|
|
|
How do brain chemicals effect relationships? |
They can alter our emotions and perceptions of others so effect how we feel about another person |
|
|
|
What are Dopamine and Oxytocin? How do they effect relationships |
Dopamine = Neurotransmitter
When you achieve a relationship "goal" dopamine is released and you experience a natural high
Oxytocin = Hormone
Chemical released when you're pleased to see someone. You get used to high levels so the absence of your partner reduces the levels and causes a feeling of longing. |
|
|
|
What are the main ways of knowing? (Give mnemonic)
Which are science based on and why? |
All Insects Eject Raisins
Authority Intuition Experience Reason
Science it based on experience and reason. Authority and Intuition can lead to incorrect knowledge |
|
|
|
The BPS ethical guidelines are split into what four principles? Briefly describe each |
Respect - Don't discriminate - Confidentiality - Aware of ability to withdraw
Competence (Capability) - Make ethical decisions - Know when to seek advice - Stop if professional ability is damaged
Responsibility - Avoids risks to you/client - Know when to stop care for patients - Protect and debrief participants
Integrity (Honesty) - Be truthful and accurate - Avoid exploitation - Maintain personal boundaries - Address any ethical misconduct |
|

