![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sakyamuni |
Common name used for the historical Buddha |
|
|
Samsara |
Cycle of rebirth |
|
|
Karma |
Law of action and consequence |
|
|
Dharma |
the Buddhist law of the cosmos |
|
|
Nirvana |
enlightenment (ultimate goal) |
|
|
Four Noble Truths |
Doctrine expounded in the first sermon of the Buddha |
|
|
Hinayana |
"lesser vehicle"; refers to older forms of Buddhism |
|
|
Mahayana |
"greater vehicle"; refers to complex forms of Buddhism that arise beginning in 1st c. BCE |
|
|
Bodhisattva |
Figure who has delayed the realization of nirvana in order to assist other people; a future Buddha. |
|

|
Pillars of Ashoka -- Topra, India. Ashoka was an emperor of the Mauryan dynasty who became a devout Buddhist and established many monuments as markers of faith. Prefers these markers to grand buildings. Large sandstone columns symbolize the Buddhist faith and the lion is a symbol of royalty. |
|
|
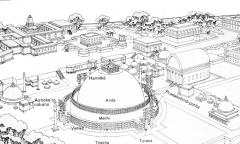
Buddhist Sanctuary -- Sanchi, India The stupa: dome-shaped structure that functions as a reliquary containing a relic of the Buddha. |
|

|
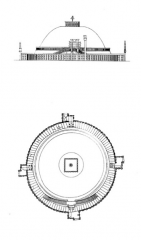
Great Stupa -- Sanchi, India It is thought that worshippers circumambulated from the east, moving clockwise like the path of the sun. |
|
|
Great Stupa -- Sanchi, India It is thought that worshippers circumambulated from the east, moving clockwise like the path of the sun. |
|

|
East Gate -- Sanchi, India The toranas, or gateways, mark a sacred boundary; they show scenes from the lives of the Buddha. |
|

|
East Gate -- Sanchi, India The female figure supporting the end of the beam is a yakshi, or female nature spirit. During this period, the Buddha was not represented in images. |
|

|
Chaitya Hall -- Karli, India The Chaitya Hall is a place of worship, and like the stupa, is a standard Early Buddhist building type. All carved out of a single mass of rock; long central space with stupa inside. |
|
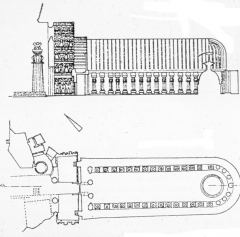
|
Chaitya Hall -- Karli, India The Chaitya Hall is a place of worship, and like the stupa, is a standard Early Buddhist building type. All carved out of a single mass of rock; long central space with stupa inside. |
|
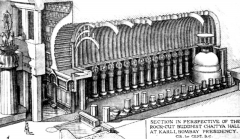
|
Chaitya Hall -- Karli, India Note the stupa at the inner end of the hall. The forms of the hall are based on wooden construction. |
|

|
Chaitya Hall -- Karli, India The shape of the columns recall the pillars of Ashoka from almost 400 years earlier. Similar to a basilica because it has aisles and a large central space for congregation. |
|

|
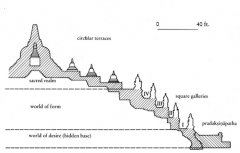
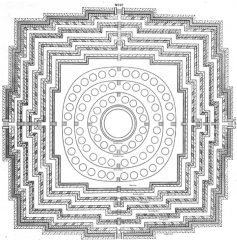
Borobudur, Java Largest Buddhist monument in world. In general, represents Buddhist cosmos as seen in 8th century. Multiple meanings: "world mountain"; madala; stupa; pilgrimage site. |
|

|
Borobudur, Java Largest Buddhist monument in world. In general, represents Buddhist cosmos as seen in 8th century. Multiple meanings: "world mountain"; madala; stupa; pilgrimage site. |
|
|
Borobudur, Java Pilgrimsview relief sculptures on square galleries as they rise from world of desire tothe sacred realm. |
|
|
Borobudur, Java Ultimate destination of spiritual journeyis nirvana. Different levels represent different realms of the Buddhistspiritual journey. Ultimate conclusion of the journey is the extinguishing ofthe individual and you become part of the larger cosmos – renter that perfectstate. |
|

|
Borobudur, Java Depicts tales from the lives of the Buddha. Thestories of the previous life of the Buddha tell about his generosity. As youmove through the building, you parallel the journey of Buddha. |
|

|
Borobudur, Java Depicts tales from the lives of the Buddha. The stories of the previous life of the Buddha tell about his generosity. As you move through the building, you parallel the journey of Buddha. |
|

|
Third Gallery -- Borobudur, Java Galleries from 2nd to 4th level tell story of a pilgrim's search for enlightenment. |
|

|
Fourth Gallery -- Borobudur, Java Galleries from 2nd to 4th level tell story of a pilgrim's search for enlightenment. |
|

|
Circular Gallery -- Borobudur, Java 72 stupas on top with life size figures of Buddha inside. |
|

|
View of statue inside stupa -- Borobudur, Java Thelarge stupa at the top may have held a great Buddha. |
|

|
View of statue inside stupa -- Borobudur, Java The large stupa at the top may have held a great Buddha. |
|
|
What building has the most in common with Borobudur? |
Ziggurat of Ur because it is a terrace mountain. Temple of Inscriptions, Palenque because both are storytelling monuments. |
|
|
Hinduism |
Hinduism,which boasts more followers than any religion except for Christianity andIslam, coalesced in the 1st millennium BCE in India. Hinduismarose from the Vedas, ancient Sanskrit texts that are thought to date to asearly as 1700 BCE. Hinduismshares certain important concepts with Buddhism, including karma, samsara, andmoksha (nirvana). In general, classic Hinduism promotes four goals •dharma(virtue) •artha(success) •kama(pleasure) •moksha(release) |
|

|
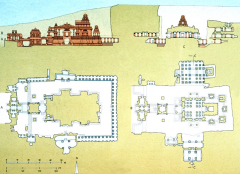
Kailasanatha -- Ellora, India Named for Mt. Kailash, the abode of Shiva and Parvati. Subtracted method of building. |
|

|
Kailasanatha -- Ellora, India Named for Mt. Kailash, the abode of Shiva and Parvati. Subtracted method of building. |
|

|
Kailasanatha -- Ellora, India Named for Mt. Kailash, the abode of Shiva and Parvati. Subtracted method of building. |
|
|
Kailasanatha -- Ellora, India Fromleft to right, the Kailasanatha hasan entry gate, a forecourt with two monolithic elephant sculptures, a nandishrine,and the main body of the temple. |
|

|
Kailasanatha -- Ellora, India Theupper left image shows the forecourt with elephant and pillar. The right imageshows the shikhara overthe garbha-griha. Inthe garbha-griha area large lingaand yoni,representing Shiva and Shakti. |
|

|
Kailasanatha -- Ellora, India The upper left image shows the forecourt with elephant and pillar. The right image shows the shikhara over the garbha-griha. In the garbha-griha are a large linga and yoni, representing Shiva and Shakti. |
|

|
Kailasanatha -- Ellora, India The upper left image shows the forecourt with elephant and pillar. The right image shows the shikhara over the garbha-griha. In the garbha-griha are a large linga and yoni, representing Shiva and Shakti. |
|

|
Kailasanatha -- Ellora, India The demon Ravana shaking Mt. Kailasa. Tells countless stories through sculpture. |
|
|
Kailasanatha is similar spatially to: |
Templeof the Feathered Serpent because they both have underground tunnels and tellstories of the creation of the world. Temple of Amun-Rebecause the idea of progression through a space. |
|

|
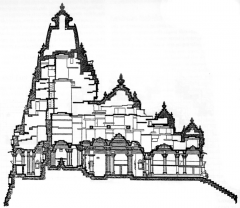
Khandariya Mahadeva -- Khajuraho,India The temple is devoted to Shiva. Illustratesthe marriage of Shiva and Parvati,and more generally the union of male and female energies. |
|
|
Khandariya Mahadeva -- Khajuraho, India The temple is devoted to Shiva. Illustrates the marriage of Shiva and Parvati, and more generally the union of male and female energies. |
|
|
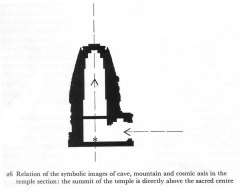
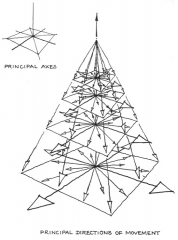
Khandariya Mahadeva -- Khajuraho, India The temple represents a mountain and a mandala, or sacred diagram. Inthis vision of Mt. Meru, thepinnacle represents the origin from which the cosmos eminates. |
|
|
Khandariya Mahadeva -- Khajuraho, India The temple represents a mountain and a mandala, or sacred diagram. In this vision of Mt. Meru, the pinnacle represents the origin from which the cosmos eminates. |
|
|
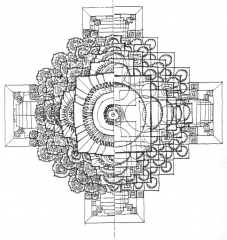
Khandariya Mahadeva -- Khajuraho, India The main tower, or skihara, is built over the most important space. |
|

|
Khandariya Mahadeva -- Khajuraho, India |
|
|
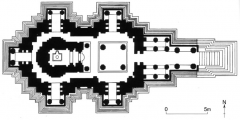
Khandariya Mahadeva -- Khajuraho, India Theinnermost chamber served as the sanctuary to which Shiva could be calledthrough rituals. Inmany Hindu temples, elaborate rituals focused onthe treatment of the deity, who was ritually wakened, dressed, and fed. |
|
|
Whatbuildings most resembled Khandariya Mahadevain terms of ritual use? |
Temple 1, Tikal because of the mountainsand connection between basic form. Old Temple, Chavinde Huantarbecause of famous pillar statue which allows two worlds to connect. |
|

|
Khandariya Mahadeva -- Khajuraho, India Thegeometric perfection of the Khandariya Mahadeva andother temples reflected the structure of the cosmos. |
|
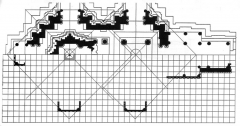
|
Khandariya Mahadeva -- Khajuraho, India The geometric perfection of the Khandariya Mahadeva and other temples reflected the structure of the cosmos. |
|
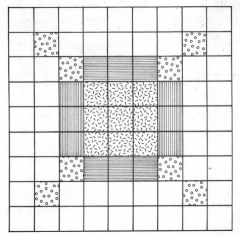
|
Khandariya Mahadeva and mandalas Likea mandala, the plan of the temple was organized according to a strict geometrichierarchy. Temples and mandalas both could be seen as manifestations of cosmicorder. |
|

|
Khandariya Mahadeva -- Khajuraho, India In Hinduism, aestheticpleasure is seen as one of the four goals. At this temple, there are strong tantricinfluences. Tantrictradition typically involves the worship of shakti,the female energy inhabiting all divinities. |
|

|
Khandariya Mahadeva -- Khajuraho, India Sculpturesrepresent the union of Shiva and Shakti, the male andfemale energies. |
|

|
Khandariya Mahadeva -- Khajuraho, India Sculptures represent the union of Shiva and Shakti, the male and female energies. |
|

|
AngkorArea -- SiemReap, Cambodia |
|
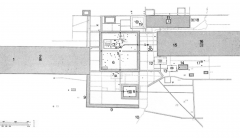
|
Angkor Area -- Siem Reap, Cambodia Shadedareas are artificial reservoirs and canals that hold religious and utilitarianmeanings. |
|
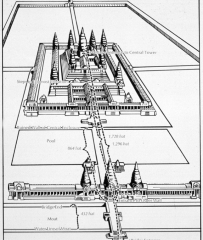
|
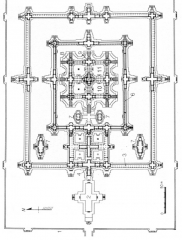
Angkor Wat -- Siem Reap, Cambodia Dedicatedto Hindu god Vishnu (religion of the Khmer kingdom is blend of Hinduism andBuddhism). |
|
|
Angkor Wat -- Siem Reap, Cambodia Dedicated to Hindu god Vishnu (religion of the Khmer kingdom is blend of Hinduism and Buddhism). |
|

|
Angkor Wat -- Siem Reap, Cambodia Concentricenclosures with taller, denser buildings at center represent idea of the world(or cosmic) mountain. |
|

|
Angkor Wat -- Siem Reap, Cambodia Concentric enclosures with taller, denser buildings at center represent idea of the world (or cosmic) mountain. |
|

|
Entrance, Angkor Wat -- Siem Reap, Cambodia |
|

|
Front Elevation, Angkor Wat -- Siemp Reap, Cambodia |
|

|
Section, Angkor Wat -- Siemp Reap, Cambodia |
|

|
Central Tower, Angkor Wat -- Siemp Reap, Cambodia |
|

|
View from Central Tower, Angkor Wat -- Siemp Reap, Cambodia |
|

|
Churning of the Sea of Milk, Angkor Wat -- Siemp Reap, Cambodia Galleriesof Angkor Wat are covered by narrative reliefsdrawn from sacred texts. Here Vishnu directs the churning of the sea of milk asdevas (gods) and asuras (demons) use a naga, or serpent, to produce the elixirof immortality. |
|

|
Churning of the Sea of Milk, Angkor Wat -- Siemp Reap, Cambodia |
|

|
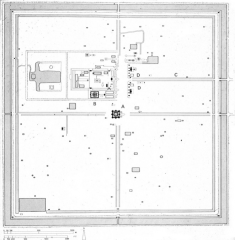
Angkor Thom Newcity/district founded by Jayavarman VIIto provide religious protection for the Khmer capital. |
|
|
Angkor Thom New city/district founded by Jayavarman VII to provide religious protection for the Khmer capital. |
|

|
Causeway and Gate, Angkor Thom -- Siemp Reap, Cambodia Statuesof railing may represent churning of the sea of milk or rainbow linking humanand divine worlds. |
|

|
Causeway and Gate, Angkor Thom -- Siemp Reap, Cambodia Statues of railing may represent churning of the sea of milk or rainbow linking human and divine worlds. |
|
|
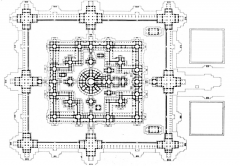
BayonTemple, AngkorThom -- SiemReap, Cambodia Layoutrelated to ideas of cosmic mountain and sacred diagrams. |
|

|
Bayon Temple, Angkor Thom -- Siem Reap, Cambodia Layout related to ideas of cosmic mountain and sacred diagrams. |
|

|
Bayon Temple, Angkor Thom -- Siem Reap, Cambodia |
|

|
Bayon Temple, Angkor Thom -- Siem Reap, Cambodia |
|

|
Bayon Temple, Angkor Thom -- Siem Reap, Cambodia Colossalfaces depict bodhisattvas. Bodhisattvas: Buddhist entities that assist in the journey to enlightenment. |
|

|
Bayon Temple, Angkor Thom -- Siem Reap, Cambodia Colossal faces depict bodhisattvas. Bodhisattvas: Buddhist entities that assist in the journey to enlightenment. |
|

|
Relief Sculpture, Bayon Temple, Angkor Thom -- Siem Reap, Cambodia Reliefsculpture lines walls as at Angkor Wat, but here most scenes are of battles andeveryday life rather than religious subjects. |
|

|
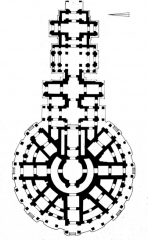
Central Sanctuary, Bayon Temple, Angkor Thom -- Siem Reap, Cambodia As atAngkor Thom, overall composition and central temple represent the cosmicmountain. Statue of Jayavarman VII found in central chamber. |
|
|
Central Sanctuary, Bayon Temple, Angkor Thom -- Siem Reap, Cambodia As atAngkor Thom, overall composition and central temple represent the cosmicmountain. Statue of Jayavarman VII found in central chamber. |

