![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are some examples of monosaccharides? |
Glucose, galactose, fructose |
|
|
|
What are some examples of disaccharides? |
Sucrose, lactose, and maltose |
|
|
|
What are some examples of polysaccharides? |
Glycogen and starch |
|
|
|
What are the functions of carbohydrates? |
Energy storage and digestion |
|
|
|
What are the three types of lipids? |
Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Cholesterol |
|
|
|
What are the components of a triglyceride and what is its function? |
One glycerol and three fatty acids. Stores energy; provides protective structural padding |
|
|
|
What are the components of a phospholipid and what is its function? |
A phosphorus containing unit, two fatty acids. Forms cell membranes |
|
|
|
What are the components of cholesterol and what are its functions? |
Four carbon rings at the core. Transports lipids, stabilizes cell membranes, is basis of steroid hormones. |
|
|
|
What are the two types of proteins? |
Structural proteins and functional proteins |
|
|
|
What are proteins composed of? |
Amino acids |
|
|
|
What do structural proteins do? |
Form structures of the body (fibers) |
|
|
|
What are the three types of nucleic acids? |
DNA, RNA, ATP |
|
|
|
What are the components of a nucleic acid? |
Nucleotides |
|
|
|
What is the function of DNA? |
It contains information (genetic code) for making proteins |
|
|
|
What is the function of RNA? |
It serves as a copy of a portion of the genetic code during protein synthesis |
|
|
|
What is the function of ATP? |
It transfers energy from nutrient molecules to power work in the cell |
|
|
|
Where are simple squamous cells located in the body? |
Alveoli of lungs, lining of blood and lymphatic vessels |
|
|
|
Where are stratified squamous cells located? |
Surface of the lining of the mouth and esophagus, surface of skin (epidermis) |
|
|
|
Where are simple cuboidal tissues located? |
Glands, kidney tubules |
|
|
|
Where are simple columnar tissues located? |
Surface layer of stomach, intestines, parts of respiratory tract |
|
|
|
Where are pseudostratified tissues located? |
Surface lining of trachea |
|
|
|
Where are stratified transitional tissues located? |
In the urinary bladder |
|
|
|
What kind of tissue is skeletal tissue? |
Striated voluntary muscle tissue |
|
|
|
What kind of tissue is cardiac tissue? |
Striated involuntary muscle tissue |
|
|
|
What kind of tissue is smooth? |
Non-striated involuntary (visceral) muscle tissue |
|
|
|
Where are skeletal tissues located? |
In muscles that attach to bones, eyeball muscles, upper third of esophagus |
SKELETAL= bones SkEletal StriatEd= Eyeball, Esophagus |
|
|
Where is smooth muscle located? |
Walls of digestive respiratory and genitourinary tracts, walls of blood vessels and large lymphatic vessels, ducts of glands, intrinsic eye muscles (Iris and ciliary body), arrector muscles of hairs |
|
|
|
Where is nervous tissue located? |
Brain, spinal cord, nerves |
|
|
|
What are the 11 body systems? |
Muscular, urinary, respiratory, digestive, endocrine, reproductive, skeletal, lymphatic, integumentary, nervous, circulatory |
MURDERS LINC |
|
|
What are the major organs in the nervous system? |
Brain, spinal cord, cranial nerves and branches, peripheral nerves and branches, sense organs |
|
|
|
What are the major organs in the endocrine system? |
Hypothalamus, pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid gland, pancreatic islets, ovaries, testes, other glands |
HPPTPOTO |
|
|
What are the major organs of the cardiovascular system? |
Heart, arteries, veins, capillaries |
If your heart malfunctions, it could wreak HAVoC on your system |
|
|
What are the major organs of the lymphatic/ immune system? |
Lymph nodes, lymph vessels, thymus, spleen, tonsils, other lymphoid organs |
LLTST |
|
|
What are the major organs of the respiratory system? |
Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs |
Nobody pleads Larry to bring lunch |
|
|
What are the major organs of the digestive system? |
Mouth, pharynx, stomach, teeth, tongue, liver, small intestine, salivary glands, esophagus, pancreas, anus, appendix, gallbladder, rectum, large intestine, |
Mom's pharmacy said that to live, she should eat plants and, amazingly, gross red liver |
|
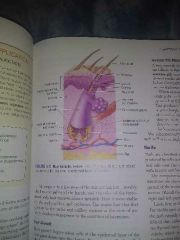
Hair follicle |
I assume you studied. Good job |
|
|
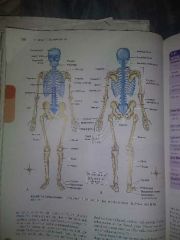
Human skeleton |
I assume you have studied this. Good job. |
|
|
|
What are the three ear bones? |
Malleus, incus, stapes |
|
|
|
What are the cranial bones? |
Frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, sphenoid, ethmoid |
|
|
|
What are the face bones? |
Nasal, zygomatic, maxilla, , mandible, lacrimal, vomer, inferior nasal concha, palatine |
New Zealand makes men look very inferior in Palestine |
|
|
What are the bones of the vertebral column? |
Cervical, thoracic vertebrae, lumbar vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx |
Cows think lunch should be chicken |
|
|
Which ribs are true ribs? |
The upper seven pairs, attached to the sternum by costal cartilages |
|
|
|
Which ribs are false ribs? |
The lower five pairs (first three are false, lower two floating) |
|
|
|
What are the three parts of the sternum? |
Manubrium, body, xiphoid process |
|
|
|
What are the 8 bones of the upper extremities? |
Clavicle, scapula, humerus, radius, ulna, carpal bones, metacarpals, phalanges |
Basically the shoulder and arm bones |
|
|
What are the eight bones of the lower extremities? |
Coxal bone, femur, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsal bones, metatarsals, phalanges |
|
|
|
which of the following is not a mucous membrane? a. lining of the respiratory tract, b. lining of the blood vessels, c. lining of the digestive tract, d. all the above are examples of mucous membranes |
B |
|
|
|
The layer of the epidermis that contains cells full of keratin is the: a. dermal papillae b. stratum germinativum c. stratum corneum d. subcutaneous layer |
C. Stratum corneum |
|
|
|
The layer that is below the dermis and contains fat and blood vessels is called the: a. subcutaneous layer b.superficial faccia c. hypodermis d. all of the above |
D. All of the above |
|
|
|
Epithelial membranes do not include a. cutaneous membranes b. synovial membranes c. serous membranes d. mucous membranes |
B. Synovial membranes |
|
|
|
Which type of skin cancer is a slow-growing malignant tumor of the epidermis? |
Squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
|
The receptor in the skin that detects pressure is the... |
Pacini corpuscle |
|
|
|
The part of the hair that begins from a small cap shaped cluster of cells is called the... |
Hair papilla |
|
|
|
The upper region of the dermis containing parallel rows of tiny bumps is called the... |
Dermal papillae |
|
|
|
The very fine and soft hair of newborns is called the... |
Lanugo |
|
|
|
Damage to the dermal epidermal junction can result in the formation of fluid-filled... |
Blister |
|
|
|
What are the five main functions of the skin? |
Protection, temperature regulation, sense organ activity, excretion, synthesis of vitamin d |
|
|
|
The bones of the spine are examples of... |
Irregular bones |
|
|
|
The total number of phalanges in the body is... |
56 which bone does not contain one of the paranasal sinuses |
|
|
|
The terms haversian system and _____________________ refer to the same structure |
Osteon |
|
|
|
Which bone does not contain one of the paranasal sinuses? a. mandible b. maxillary c. frontal d. ethmoid |
The mandible |
|
|
|
What hormone decreases calcium in the bone? |
Parathyroid hormone |
|
|
|
Which hormone increases mineralization of bone? |
Calcitonin |
|
|
|
What are the five main functions of the skeletal system? |
Support, protection, movement, storage, hematopoiesis |
|
|
|
Going from Superior to inferior the sequence of the vertebrae is... |
Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum, coccyx |
|
|
|
Bone forming cells |
Osteoblasts |
|
|
|
Bone reabsorbing cells |
Osteoclasts |
|
|
|
Mature bone cells |
Osteocytes |
|
|
|
What part of the body does the gastrocnemius move? |
Lower extremities (plantar flexes ankle) |
|
|
|
What kind of contraction occurs when the muscle contracts but does not shorten? |
An isometric contraction |
|
|
|
what kind of muscle contraction occurs when the muscle contracts and shortens and the insertion and moves towards the point of origin? |
In isotonic contraction |
|
|
|
Endurance training leads to |
An increased number of blood vessels to the muscle |
|
|
|
Strength training leads to an increased number of_____________ |
Myofilaments |
|

