![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Superior |
Part that is above another part, closer to the head. |
|
|
|
Medial |
Towards the midline of the body |
|
|
|
Distal |
Further from point of attachment. When dealing with limbs (arms/legs). |
|
|
|
Inferior |
Closer to the feet. Opposite of superior. |
|
|
|
Proximal |
Structure that is nearer to trunk or main part of body. |
|
|
|
Anterior |
Toward the front of the body (belly surface( another word is ventral) |
|
|
|
Lateral |
Away from the midline of body. |
|
|
|
Posterior |
Toward the back of surface. Another word is dorsal. |
|
|
|
Deep |
Further from surface of skin. |
|
|
|
Peripheral |
Part that is located away from center. |
|
|
|
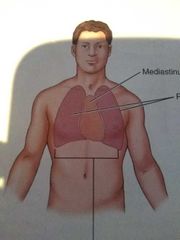
What is the mediastinum and where is it located? |
The mediastinum is the space that contains the heart, thymus gland, and part of the esophagus, trachea, blood vessels attached to the heart.
It is located in the thoracic cavity. One of 2 compartments. |
|
|
|
Where is the axilla located? |
Armpit |
|
|
|
What is inside the dorsal cavity? |
The dorsal cavity (located in the back of body) contains 2 divisions. Cranial cavity: contains the brain Vertebral (also called spinal) cavity: contains spinal cord. |
|
|
|
What is inside the ventral cavity? |
Similar to the dorsal cavity it has two divisions and is located in the front of the body. 1. Thoracic cavity 2. Abdominopelvic cavity |
|
|
|
Describe the frontal plane. |
The frontal plane divides the body anterior and posterior. This plane creates a front part of the body and a back part of the body. The front plane is also called the coronal meaning crown. |
|
|
|
Describe the sagittal plane. |
The sagittal plane divides the body lengthwise and makes a right and left portion.
Midsagittal refers to a completely equal division. Sagittal or parasagittal refers to an unequal division. |
|
|
|
Where is the inguinal area of the body? |
This area is often called the groin and is the area where the thigh meets the trunk of the body. |
|
|
|
What does the term cephalocaudal mean? |
It refers to assessment head to toe. |
|
|
|
What type of tissue needs to be stretchy and why? |
Transitional epithelia These tissue are primarily found in organs that need to stretch like bladder. |
|
|
|
What does the term carcinogenic mean? |
Cancerous |
|
|
|
Which type of tissues are arranged like the tile on a floor? Or fish scales? |
Squamous epithelium |
|
|
|
What are endocrine glands? |
Ductless glands that secrete hormones directly into the blood stream. |
|
|
|
What are exocrine glands? |
Glands that produce and secrete substances on the epithelial surface. By way of ducts. Ex: sweat, salivary, mammary. |
|
|
|
Describe neuroglia |
They are the most abundant nerve cells that are located in the central nervous system. Play protect insulate nourish and generally care for delegate neurons. They do not conduct nerve impulses but they do participate in phagocytosis. To the most common astrocytes and ependymal cells. |
|
|
|
What is the job of an astrocyte? |
They are the star-shaped cells that are most abundant of the glial cells. They support the neurons structurally and cover the entire surface of the brain to help form a protective barrier called the blood-brain barrier. it prevents toxic substances in the blood from entering the nervous tissue of the brain or spinal cord. |
|
|
|
What are the sutures in a cranial cavity? |
The coronal suture The squamous suture Lambdoidal suture |
|
|
|
What is a hinge joint and which ones are there? |
A hinge joint allows for movement similar to the movement of two boards joined together by a hinge it allows for movement in one direction and increases the angle at the hinge or decreases. Elbows knees and fingers. |
|
|
|
What is the term for losing your hair? |
Alopecia |
|
|
|
What type of gland secretes vernix in fetus? |
Sebaceous glands |
|
|
|
Normal body temperature? |
97.0 to 100.0 |
|
|
|
Name the 8 cranium bones? |
Frontal Parietal (2) Temporal (2) Occipital Sphenoid Ethmoid |
|
|
|
Name the 14 facial bones? |
Mandible Maxilla (2) Palatine (2) Zygomatic (2) Nasal (2) Vomer Lacrimal (2) Inferior concha (2) |
|
|
|
Steps in Tissue Repair |
1. A deep wound to the skin severs blood vessels causing blood to fill wound. 2. Blood clot forms and as it dries it forms a scab. 3&4. Process of tissue repair begins. Scar tissue forms in deep layers. 5. At the same time surface epithelial cells multiply and fill the area between the scar tissue and scab 6. When the epithelium is complete the scab detaches. |
|
|
|
Vasodilation |
Veins open, flushing blushing to skin. |
|
|
|
Vasoconstriction |
Vein constrict, makes you pale. |
|
|
|
Which tissue is Avascular? |
Epithelial tissue |
|
|
|
What joint does the coxal and the femur meet? |
Coxal joint? |
|
|
|
3 examples of connective tissue membranes? |
Synovial Periosteum Meninges Fascia Perichondrium |
|
|
|
What type of tissues serves as a reservoir of energy for body? |
Adipose tissue |
|
|
|
Describe a ligament? |
A dense fibrous connective tissue that crosses joints and attaches bone to bone. |
|
|
|
What is vernix caseosa? |
Cream-cheese like substance covering the skin of the fetus |
|
|
|
Where is the thermostat of the body located? |
In the hypothalamus |
|
|
|
What is a subcutaneous layer also known by? |
Hypodermis layer |
|
|
|
How does a baby produce heat? |
Nonshivering thermogenesis |
|
|
|
What are eccrine glands? |
Also known by sweat glands that are widely distributed throughout the body |
|
|
|
Which layer of skin has The receptors for touch pressure and pain? |
Epidermis |
|
|
|
What is the difference between apocrine and eccrine glands? |
Apocrine = sweat gland that is an endocrine. Eccrine = sweat gland that is an exocrine gland |
|
|
|
Define pronation. |
Turning the forearm to the palm of your hands looks at the floor. |
|
|
|
Define supination? |
Turn in your hand so the palm of your hand face upward |
|
|
|
What is it called when the foot movement is opposite of plantar flexion? |
Dorsiflexion |
|
|
|
What is another name for the metacarpalphalangeal joints? |
Knuckles |
|
|
|
How are the joints in the skull classified? |
Immoveable joints |
|
|
|
What is the term for the area in an infant skull that has not been converted to bone. |
Fontanels |
|
|
|
What are the muscles that perform the kicking a football motion? |
Quadriceps fermoris |
|
|
|
What is the energy source for muscle contraction? |
Creatine phosphate |
|

