![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
262 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Parts of the microscope
|

|
|
|
|
Microscope parts:
BASE |
solid, rests on the table
|
|
|
|
Microscope parts:
ARM |
angular portion of the frame that extends upward from the base
|
|
|
|
Microscope parts:
STAGE |
platform beneath the lenses
|
|
|
|
Microscope parts:
CLIPS |
hold slide in place
|
|
|
|
Microscope parts:
2 STAGE MANIPULATOR KNOBS |
beneath the stage moves slide forward/backward and left/right
|
|
|
|
Microscope parts:
CONDENSER LENS/IRIS DIAPHRAGM |
both under the stage; regulate the intensity of the light
|
|
|
|
Microscope parts:
FOCAL ADJUSTMENT KNOBS |
Coarse adjustment – larger knob
Fine adjustment – smaller knob |
|
|
|
Microscope parts:
REVOLVING NOSEPIECE |
circular attachment which houses the 4 objective lenses
|
|
|
|
Microscope parts:
OCULAR LENSES |
eyepiece- allows for additional 10X magnification
|
|
|
|
Microscope parts:
Objective lens 4X |
for scanning object
|
|
|
|
Microscope parts:
Objective lens 10X |
low power
|
|
|
|
Microscope parts:
Objective lens 40X |
high power
|
|
|
|
Microscope parts:
Objective lens 100X |
objects oil immersion
|
|
|
|
Microscope parts:
Ocular lenses |
eyepiece- allows for additional 10X magnification
|
|
|
|
Toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the body; above
|

|
Superior (cranial, cephalic)
|
|
|
Away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure or the body; below
|

|
Inferior (caudal)
|
|
|
Toward or at the front of the body; in front of
|

|
Anterior (ventral)
|
|
|
Toward or at the back of the body; behind
|

|
Posterior (Dorsal)
|
|
|
Toward or at the midline of the body; on the inner side of
|
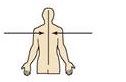
|
Medial
|
|
|
away from the midline of the body; on the outer side of
|

|
Lateral
|
|
|
Between a more medial and a more lateral structure
|
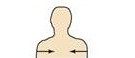
|
Intermediate
|
|
|
Closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
|

|
Proximal
|
|
|
Farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk; farther from point of reference or attached base
|

|
Distal
|
|
|
Integumentary System
|
Forms the external body covering, protects deeper tissues from injury, sit of cutaneous receptors/sweat and oil glands, synthesizes vitamin D
Contains: Hair, skin, nails |
|
|
|
Toward or at the body surface
|

|
Superficial (external)
|
|
|
away from the body surface; more internal
|

|
Deep/Internal
|
|
|
Skeletal system
|
Protects and supports body organs, provides a framework the muscles use to cause movement, stores minerals; blood cells form within bones
Contains: bones, cartilage, joints, ligaments, tendons |
|
|
|
Describe Anatomical Position
|
body is erect (standing), feet parallel to each other and flat on the floor, eyes directed forward, arms at sides with palms turned forward, thumbs pointing away from body
|
|
|

|
Vertical - Sagittal division into left and right halves
1. Midsagittal (median) equal left and right halves 2. Parasagittal unequal left and right halves |
|
|
|
Muscular System
|
Allows manipulation of the environment, locomotion, expression, maintains posture, produces heat
Contains: muscles |
|
|

|
Frontal (Coronal)
division into anterior and posterior halves; at right angles to sagittal plane |
|
|
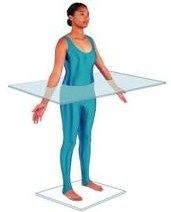
|
Horizontal - Transverse (cross-section)
Parallel to ground; division into top and bottom halves; superior and inferior halves |
|
|
|
Nervous System
|
Fast-acting control system of the body, responds to internal and external changes by activating appropriate muscles and glands
Contains: Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors |
|
|
|
How many bones are in the adult skeleton?
|
206
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Endocrine System
|
Glands secrete hormones that regulate body cell processes
Contains: Pineal glands, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, thymus, adrenal gland, pancreas, ovaries/testes |
|
|
|
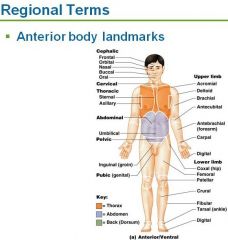
Nasal
|
nose
|
|
|
|
Oral
|
mouth
|
|
|
|
Cardiovascular System
|
Transport blood, carry nutrients/wastes/oxygen to the body
Contains: heart, blood vessels |
|
|
|
Cervical
|
neck
|
|
|
|
Acromial
|
the very top point of the shoulder
|
|
|
|
Lymphatic System
|
Picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to the blood, disposes of debris in the lymphatic stream, houses lymphocytes, involved in immunity
Contains: red bone marrow, thymus, lymphatic vessels, thoracic duct, spleen, lymph nodes, tonsils, lymphoid tissue |
|
|
|
Axillary
|
armpit
|
|
|
|
Abdominal
|
abdomen
|
|
|
|
Respiratory System
|
Keeps blood supplied with oxygen and removes CO2
Contains: nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, lungs, bronchi |
|
|
|
Brachial
|
upper arm
|
|
|
|
Antecubital
|
anterior elbow
|
|
|
|
Digestive System
|
Breaks down food into absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution to body cells, eliminates indigestible foodstuffs as feces
Contains: oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus, accessory structures (teeth, salivary glands, liver, pancreas) |
|
|
|
Antebrachial
|
forearm
|
|
|
|
Pelvic
|
pelvis
|
|
|
|
Urinary System
|
Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body, regulates water/electrolytes/pH
Contains: kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra |
|
|
|
Carpal
|
wrist
|
|
|
|
Pollex
|
thumb
|
|
|
|
Reproductive System
|
Production of offspring.
Male: prostate, penis, testes, scrotum, ductus deferens Female: mammary glands, ovaries, uterus, vagina, uterine tubes |
|
|
|
Palmar
|
palm
|
|
|
|
Digital
|
fingers/toes
|
|
|
|
Pubic
|
genital
|
|
|
|
Patellar
|
anterior knee
|
|
|
|
Crural
|
Anterior leg (shin region)
|
|
|
|
Pedal
|
foot
|
|
|
|
Tarsal
|
ankle
|
|
|
|
Frontal
|
forehead
|
|
|
|
Orbital
|
eye
|
|
|
|
Buccal
|
cheek
|
|
|
|
Mental
|
chin
|
|
|
|
Sternal
|
breastbone
|
|
|
|
Thoracic
|
chest
|
|
|
|
Mammary
|
breast
|
|
|
|
Umbilical
|
navel
|
|
|
|
Coxal
|
hip
|
|
|
|
Inguinal
|
groin
|
|
|
|
Femoral
|
thigh
|
|
|
|
Fibular/Peroneal
|
side of leg
|
|
|
|
Hallux
|
big toe
|
|
|
|
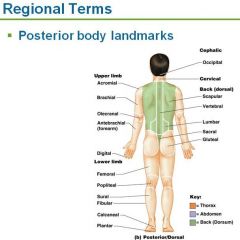
Cephalic
|
head
|
|
|
|
Manus
|
hand
|
|
|
|
Otic
|
ear
|
|
|
|
Occipital
|
Back of head and base of skull
|
|
|
|
Vertebral
|
spinal column
|
|
|
|
Scapular
|
shoulder blade
|
|
|
|
Dorsum/Dorsal
|
back
|
|
|
|
Olecranal
|
posterior elbow
|
|
|
|
Lumbar
|
lower back, lateral to spine (also called "loin")
|
|
|
|
Sacral
|
between hips (butt crack and slightly above)
|
|
|
|
Gluteal
|
buttocks
|
|
|
|
Perineal Region
|
region between anus and external genitalia (pelvic floor)
|
|
|
|
Popliteal
|
Posterior knee
|
|
|
|
Sural
|
calf
|
|
|
|
Calcaneal
|
heel
|
|
|
|
Plantar
|
sole of foot
|
|
|
|
cheek area
|
buccal
|
|
|
|
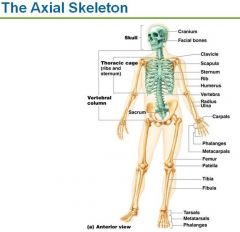
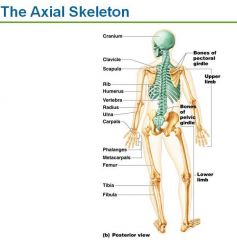
The Skeleton is divided into 2 large body regions
|
Axial and Appendicular Skeleton
|
|
|
|
The Axial Skeleton contains 3 regions
|
Skull, Vertebral Column and Thoracic Cage
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Appendicular Skeleton contains
|
Pectoral/Shoulder Girdle, Arms, hands, Pelvic/Hip Girdle, legs, and feet
|
|
|
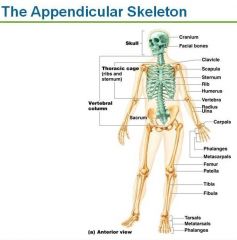
|
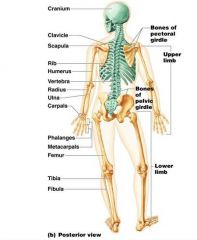
|
|
|
|
Name the 2 large Body Cavities
|
Dorsal (back) body cavity and
Ventral (front) body cavity |
|
|
|
Dorsal body cavity contains
|
Cranial (skull) cavity protects the brain and the Vertebral (spinal) cavity protects the spinal cord
|
|
|
|
Ventral body cavity contains
|
Thoracic cavity protects heart, lungs and others
Abdominoplevic cavity - liver, digestive system,urinary organs and reproductive structures |
|
|
|
Body Cavities
|
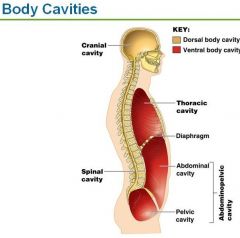
|
|
|
|
4 abdominopelvic quadrants
|
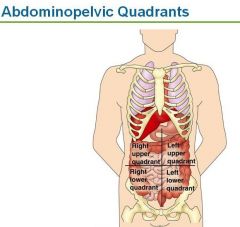
|
|
|
|
Nine abdominopelvic regions
|
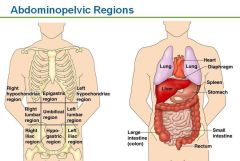
|
|
|
|
Dorsal Body Cavity
|
Protects the organs of the nervous system (brain and spinal cord)
Contains cranial and vertebral cavities |
|
|
|
Cranial Cavity
|
cavity of the skull
contains: brain |
|
|
|
Vertebral/Spinal Cavity
|
cavity within the vertebral column
contains: spinal cord |
|
|
|
Ventral Body Cavity
|
anterior body cavity containing the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities, houses the visceral organs
|
|
|
|
Viscera
|
internal organs
|
|
|
|
Thoracic Cavity
|
cavity surrounded by the ribs and chest muscles, contains pleural and pericardial cavities
|
|
|
|
Pleural Cavities
|
cavities housing the lungs
|
|
|
|
Superior Mediastinum
|
cavity containing the esophagus and trachea within the thoracic cavity
|
|
|
|
Pericardial Cavity/Medial Mediastinum
|
central thoracic cavity
contains: heart |
|
|
|
Diaphragm
|
thin muscle attached to the inferior boundary of the rib cage, important in breathing, separates the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
|
|
|
|
Abdominopelvic Cavity
|
inferior cavity of the body trunk, containing the abdominal and pelvic cavities
|
|
|
|
Abdominal Cavity
|
superior cavity of the abdominopelvic cavity
contains: stomach, intestines, spleen, liver, pancreas, large intestines, small intestines, greater omentum, mesentary |
|
|
|
Pelvic Cavity
|
inferior cavity of the abdominopelvic cavity, within the bony pelvis
contains: urinary bladder, internal reproductive organs, rectum |
|
|
|
Serous Membrane/Serosa
|
double-layered membranes within the ventral body cavity; lines the walls and folds over and lines the inner organs
|
|
|
|
Parietal Serosa
|
membrane lining the cavity walls
|
|
|
|
Visceral Serosa
|
membrane covering the organs in the body cavity
|
|
|
|
Serous Fluid
|
lubricating fluid separating the serious membranes which allows the organs to slide without friction
|
|
|
|
Peritoneum
|
serosa lining in the abdominal cavity and abdominal organs
|
|
|
|
Pleura
|
serosa lining in the pleural cavities; lines thoracic cabity and covers the lungs
|
|
|
|
Pericardium
|
serosa lining in the pericardial cavity and heart
|
|
|
|
Umbilical Region
|
centermost abdominopelvic region, surrounding the navel
contains: large & small intestines |
|
|
|
Epigastric Region
|
top-centre abdominopelvic region
contains: stomach, liver, small intestine, pancreas |
|
|
|
Hypogastric/Pubic Region
|
bottom-centre abdominopelvic region
contains: urinary bladder, small intestine, appendix, large intestine |
|
|
|
Right Iliac/Inguinal Region
|
bottom right abdominopelvic region
contains: small intestine, large intestine, appendix |
|
|
|
Left Iliac/Inguinal Region
|
bottom left abdominopelvic region
contains: large & small intestine |
|
|
|
Right Lumbar Region
|
middle right abdominopelvic region
contains: large and small intestines |
|
|
|
Left Lumbar Region
|
middle left abdominopelvic region
contains: large & small intestines |
|
|
|
Left Hypochondriac Region
|
top left abdominopelvic region
contains: large intestine, small intestine, spleen, stomach |
|
|
|
Abdominopelvic Regions (name)
|
epigastric, R/L hypochondriac, umbilical, R/L lumbar, hypogastric/pubic, R/L iliac/inguinal
|
|
|
|
Right Hypochondriac Region
|
top right abdominopelvic region
contains: liver, gall bladder, small intestine, large intestine |
|
|
|
List smaller body cavities
|
Oral and Digestive cavities
Nasal cavities Orbitial cavities - eyes Middle ear cavities Synovial cavities - movable joints |
|
|
|
What are the 3 main regions of an animal cell?
|
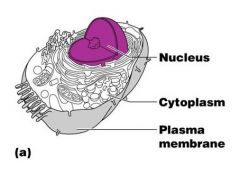
|
|
|
|
The Nucleus
|
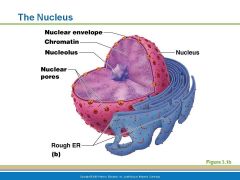
|
|
|
|
Nucleus
Function |
Control center of a cell; contains genetic material;
DNA deoxyribonucleic acid will duplicate during interphase Nucleus will divide into two daughter cells |
|
|
|
Nuclear Envelope aka Nuclear Membrane
Location Function |
double membrane barrier that has a fluid filled space between the layers, surrounds the jellylike fluid called nucleoplasm around the nucleus. Keeps DNA save
|
|
|
|
Nuclear Pores
location function |
penetrate through the fused regions of the nuclear envelope aka nuclear membrane allows substances to pass through
|
|
|
|
Nucleoli
Location Function |
Dense spherical bodies in the cell nucleus involved with ribosomal subunit synthesis (makes the ribosomes which will migrate out of the nucleus to the cells cytoplasm)
|
|
|
|
Chromatin
Location Function |
Structures in the nucleus that carry the hereditary factors (genes DNA) when not dividing are scattered throughout the nucleus
|
|
|
|
Structure of the plasma membrane
|
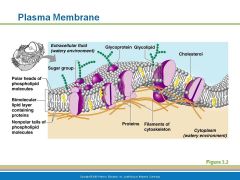
|
|
|
|
Function of plasma membrane aka cell membrane
|
barrier between cell's contents and the surrounding environment; selectively permeable to most water-soluble molecules. Cholesterol helps keep the membrane fluid
|
|
|
|
Structure of plasma membrane
|
2 lipid (fat) layers arranged tail to tail; heads are hydrophilic - water loving; nonpolar tails are hydrophobic -hate water. sugars attach to membrane
|
|
|
|
Specializations of the plasma membrance
Microvilli |
little shaggy hairs/projections that increase the cell's surface area of absorption
|
|
|
|
Membrane Junctions
|
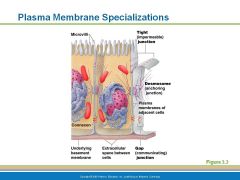
|
|
|
|
Plasma Membrane - Tight Junctions
|
impermeable junctions prevent
adjacent plasma membranes fuse tightly like a zipper (in small intestine to prevent digestive enzymes from seeping into the bloodstream) |
|
|
|
Plasma Membrane - Desmosomes Junctions
|
anchoring junctions prevent cells from being pulled apart (skin cells)
|
|
|
|
Plasma Membrane - Gap Junctions
|
allows communication between cells (heart or embryonic cells) connexons are hollow cylinders tha span the width of the two attached membrane
|
|
|
|
Structure of generalized cell
|
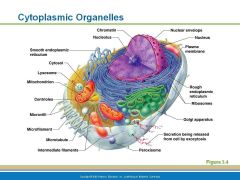
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Mitochondria |
Cytoplasmic organelles responsible for ATP generation for cellular activities.
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Ribosomes |
Cytoplasmic organelles that float free at which proteins are synthesized in the cell - Ribosomes also can attach to the Endoplasmic Reticulum called rough ER
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) |
2 forms smooth and rough
provides a network of channels to carry substances (mostly proteins) around the cell |
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) |
studded with ribosomes, protein is made on the ribosomes then migrate into the ER to be folded into their functional shapes, then dispatach by transport vesicle out into the cell
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) |
Lipid metabolism (cholesterol, fat synthesis, and breakdown and detoxification of drugs and pesticides) liver is chock-full of smooth ER
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Golgi Apparatus |
traffic directer for cellular proteins - it modifies and package proteins received from the rough ER via transport vesicles.
Exports in secretory vesicles that 1. fuse with cell membrane and ejects contents outside cell 2. fuses and becomes part of the membrane 3. packages enzymes for use in the cell - Lysosomes |
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Lysosomes |
packaged by smooth ER - enzymes that digest worn-out cell structures, foreign substances; phagocytes
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Peroxisomes |
sacs of oxidase enzymes that detoxify harmful or poisonous substances (alcohol and formaldehyde)converts free radicals, found in liver and kidney cells
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Cytoskeleton |
internal framework that determines cells shape made of filaments
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Filaments of Cytoskelton |
Intermediate filaments - forms desmosomes anchoring junctions
Microfilaments - mortility and in producing changes in shape Microtubules - determines shape of cell and distribution or organelles |
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Centrioles |
rod shape, made of microtubules, direct the formation of mitotic spindles
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Cilia |
little hairs that move substances along the cell surface - in respiratory lining that move mucus away from lungs
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Flagella |
the sperm tail
|
|
|
|
Besides fuel, what does the mitochondrion need to regenerate ATP?
|
Oxygen
|
|
|
|
Three main regions of all cells
|
Nucleus
Cytoplasm Plasma membrane |
|
|
|
Nucleus is the Control center of the cell has three regions
|
Nuclear envelope or Nuclear membrane with pores
Nucleolus - site of ribosome production Chromatin - DNA and protein |
|
|
|
Nucleus - Chromatin is
4 things |
Composed of DNA and protein
Present when the cell is not dividing Scattered throughout the nucleus Condenses to form Chromosomes when the cell divide |
|
|
|
Plasma Membrane
|
Barrier to cell contents
Double phospholipid layer with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails Also contains, proteins, cholesterol and glycoproteins |
|
|
|
Plasma cell Membrane is double phospholipid layer one side has hydrophilic polar heads and one has hydrophobic non-polar tails
|
hydrophilic - water loving and are attracted to water
hydrophobic - hates water are lined up toward center of membrane layers |
|
|
|
Plasma Membrane - specializations
Microvilli are |
finger-like projections that increase surface area for absorption ( is folded up)
|
|
|
|
Plasma Membrane junctions
3 types are |
Tight junctions
Desmosomes Gap junctions |
|
|
|
Plasma Membrane junctions
Tight junctions are |
like a ziplock bag
Impermeable junctions Bind cells together into leak-proof sheets |
|
|
|
Plasma Membrane junctions
Desmosomes |
anchoring junctions that prevent cells from being pulled apart - skin - bottonlike
|
|
|
|
Plasma Membrane junctions
Gap Junctions |
small hole that allow communication between cells - heart - nutrients or ions can pass directly from one cell to another cell
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasm is where most cellular activities take place its the factory area
|
outside the nucleus and held inside the cell by the plasma membrane
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasm contains three major elements
|
Cytosol
Organelles Inclusions |
|
|
|
Contain in the cytoplasm is Cytosol which is
|
fluid that suspends other elements
|
|
|
|
Contain in the cytoplasm are Organelles that
|
Metabolic machinery of the cell
Little organs that perform functions for the cell |
|
|
|
Contain in the cytoplasm are Inclusions that are
|
chemical substances such as stored nutrients or cell products
|
|
|
|
Structures of the cell
Nuclear envelope or Nuclear membrane is |
a double membrane barrier that holds the nucleoplasm inside
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Mitochondria |
Powerhouse of the cell
Generates ATP for cellular energy reactions use oxygen to breakdown food - cellular respiration |
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Ribosomes is made up of and does what, and is found |
made of protein and RNA
Sites of protein synthesis Found at two locations; free in the cytoplasm and a part of the rough endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
protein synthesis takes place in the |
Ribosomes
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
The ribosomes attached to the membrane combination is called |
the rough endoplasmic reticulum where protein synthesis takes place
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum |
function is lipid metabolism (cholesterol and fat/lipid synthesis and breakdown, detoxification of drugs and pesticides - liver cells have lots
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Rough Endoplasmic reticulum is studded with ribosomes |
site of protein synthesis
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Rough Endoplasmic sends protein off in |
transport vesicles
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Golgi Apparatus does |
Modifies and packages proteins (folds and shapes)
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Golgi Apparatus produces 3 different types of packages |
Secretory vesicles
Cell membrane components Lysosomes |
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Golgi Apparatus - secretory vesicles |
vesicles that are to be secreted from the cell
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Golgi Apparatus - cell membrane components |
fuse with the cells plasma membrane to repair
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Golgi Apparatus Lysosomes |
vesicle containing digestive enzymes become lysosomes - worn out nonusable materials in cells - trash recycle
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
Peroxisomes membranous sacs of oxidase enzymes do what |
Detoxify harmful substances like alcohol and formaldehyde
Break down free radicals - highly reactive chemicals |
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
How does the Peroxisomes reproduce |
replicates by pinching itself in half forming 2 cells from one
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
What is cytoskeleton |
network of protein structures throughout the cytoplasm
Provides the cell an internal framework |
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Organelles
What are the 3 types of cytoskeleton? |
Microfilaments - smallest
Intermediate filaments Microtubules - largest |
|
|
|
CYTOPLASMIC ORGANELLES
Centrioles directs |
the formation of the mitotic spindle during cell division
|
|
|
|
CYTOPLASMIC ORGANELLES
Microvilli are |
finger like projections that increase the cells surface area for absorption
|
|
|
|
CYTOPLASMIC ORGANELLES
Microfilament like actin and myosin |
producing changes in the cells shape
|
|
|
|
CYTOPLASMIC ORGANELLES
Microtubule determine the |
overall shape of a cell and the distribution of organelles
|
|
|
|
CYTOPLASMIC ORGANELLES
Intermediate filaments help form |
desmosomes - button like junctions to prevent cells form be torn apart - skin
|
|
|
|
Cellular Projections - 2 types are
|
Cilia - to move materials in respiratory system to move mucus
Flagella - tail of sperm to propel |
|
|
|
Cell Diversity - Types
2 types of cells that connect body parts |
Fibroblast and Erythrocytes
|
|
|
|
Cells that over and line the body
|
Epithelial cells
|
|
|
|
Cells that move organs and body parts
|
Skeletal muscle and smooth muscle cells
|
|
|
|
Cells that fight disease
|
Macrophage
|
|
|
|
Cells that gather information and controls body functions
|
Nerve Cells
|
|
|
|
Cells of reporduction
|
Oocyte -egg
Sperm with flagellum |
|
|
|
3 functions of body Membranes
|
Cover body surfaces
Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs |
|
|
|
Nuclear Envelope aka Nuclear Membrane
Location Function |
double membrane barrier that has a fluid filled space between the layers, surrounds the jellylike fluid called nucleoplasm around the nucleus. Keeps DNA save
|
|
|
|
What are the stages of cell division?
I popped my apple turnover croissant |
Interphase - not included in mitosis
Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase and cytokinesis |
|
|
|
Mitosis does what?
|
Process during which the chromosomes are redistributed to two daughter nuclei; nuclear division. Consists of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
|
|
|
|
3 stages of cell division are?
|
Interphase
Mitosis Cytokinesis |
|
|
|
Interphase
|
the cell grows and carries on metabolic activities; prepares for cell division by duplicating DNA
|
|
|
|
Prophase
|
chromosomes considting of 2 sister chromatids are held together by centromere; mitotic spindle starts forming; nuclear envelope disolves; spindle move to opposite poles
|
|
|
|
Metaphase
|
Chromosome, consisting of 2 sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate
|
|
|
|
Anaphase
|
Sister chromatids divide and move toward opposite poles and are now called daughter chromosomes
|
|
|
|
Telophase
|
chromosomes uncoil at opposite poles, spindle breaks down, nuclear envelope forms, nucleoli appear
|
|
|
|
Cytokinesis
|
is the division of the cytoplasm, cleavage furrow forms at the midline and eventually pinches the cytoplasmic mass into 2 cells
|
|
|
|
STAGES OF MITOSIS
|
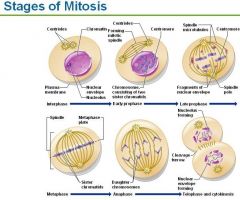
|
|
|
|
What are the 4 types of tissue?
|
Epithelial Tissue
Connective Tissue Muscle Tissue Nervous Tissue |
|
|
|
Characteristics and Examples of
Epithelial Tissue |
Epithelial Tissue:
Lining, covering and glandular tissue fit closely together to form continuous sheets membranes have on free surface called apical surface lower surface rests on a basement membrane Do not have their own blood supply depend on diffusion from capillaries in connective tissue for food and oxygen Samples: Skin, air sacs of lungs, lines the entire length of the digestive tract Functions protection, absorption, filtration and secretion |
|
|
|
Classification of epithelia based on
|
arrangement or layers and the cell shape
|
|
|
|
What are the 2 classifications of cells based on arrangement or layers
|
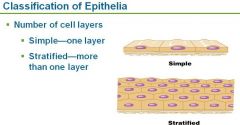
|
|
|
|
What are the 3 classifications based on cell shapes?
|
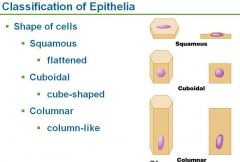
|
|
|
|
Characteristics and Examples of
Connective Tissue |
connects body parts
Bone, cartilage, tendons, ligaments and blood Functions - protecting, supporting and binding together |
|
|
|
Characteristics and Examples of
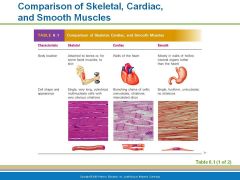
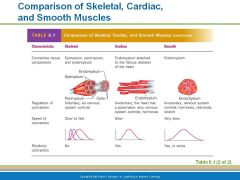
Name the 3 kinds of muscle tissue? |
Skeletal muscles - can be controlled voluntarily for movement
Cardiac Muscles - non-voluntarily only in the heart Smooth Muscle - non-voluntary lines walls of hollow organs stomach, blood vessels |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nervous Tissue
|
neurons receive and conduct electrochemical impulses
irritability (chemical, electron, heat) and conductivity Transmit, implulses communicate to other cells |
|
|
|
Tissue Repair (wound healing)
name 2 types |
Regeneration - replacement of destroyed tissue by the same kind of cells
Fibrosis - repair by dense fibrous connective tissue or scar tissue |
|
|
|
What is regeneration of tissue repair?
|
Regeneration - replacement of destroyed tissue by the same kind of cells - BEST REPAIR
|
|
|
|
What is fibrosis tissue repair?
|
Fibrosis - repair by dense fibrous connective tissue or scar tissue
|
|
|
|
Where are of mucous membranes?
|
wet or moist
line body cavities that are open to the exterior Mucosa of nose, mouth esophagus and of Mucosa of lung bronchi |
|
|
|
Where are serious membranes?
|
occur in pairs
lines ventral body cavities that are closed to the exterior the parietal layer lines the wall of the ventral body cavity the visceral layer covers the outside of an organ in the cavity |
|
|
|
Describe Serous Fluid
|
Serous membranes ooze their materials to an interior surface, it serves to lubricate and reduce friction.
|
|
|
|
Describe Mucus
|
mucous membrane has mucus secreting cells in it (often called goblet cells) - sticky mass (usually clear). These membranes line surfaces that are in potential contact with the environment. Foreign material will stick to the mucous- it is an effective and important defense barrier. Mucous membranes can be found lining the digestive, respiratory, reproductive, and urinary tracts. The epithelial surfaces are kept moist at all times.
|
|
|
|
What are the 2 biggest concerns with a severe burn?
|
dehydration and infection
|
|
|
|
Benign tumors are
|
not cancer
|
|
|
|
Metastasize
|
spread to other body areas
|
|
|
|
maligment tumors are
|
Cancerous tumors
|
|
|
|
How do tumors occur?
|
a cell starts reproducing uncontrollably,
|
|
|
|
What are the 2 kinds of tissue that make up the skin?
|
Outer epidermis - made of 5 layers of stratified squamous epithelium - strong
Underlying dermis - dense connective tissue - strong and stretchy |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
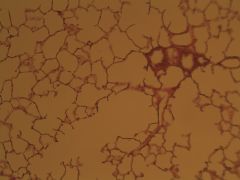
Simple Squamous epithelium
|
|
|
|
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Function and Location |
Function - thin, allows diffusion and filtration
Location - air sacs of lungs, lining of heart, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, lining of ventral body savity (serosae) |
|
|
|
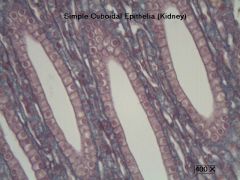
Simple Cubodidal Epithelium
Structure: Single layer of cubed cells, lare, spherical central nuclei |
|
|
|
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Function and Location |
Function - secretion and absorption
Location - Kidney tubules, ducts of secretory portions of glands, surface of the ovary |
|
|
|
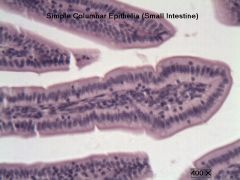
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Structure - Single layer of columns with round or oval nucleus |
|
|
|
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Function and Location |
Function - secretes mucous, has Microvilli extensions increasing surface area
Location - digestive tract, portions of uterus and uterine tubes |
|
|

|
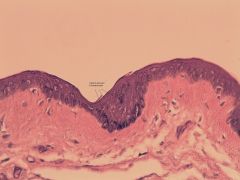
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
single layer of cells of different heights - CILIATED |
|
|
|
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Function and Location |
Function - ciliated to move secreted goblets and clean
Location - Trachea and most of the upper respiratory tract |
|
|
|
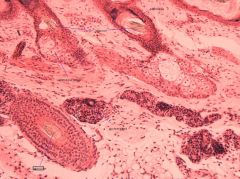
Integument Pigmented Skin
|
|
|
|
Integument scalp long section
|
|
|
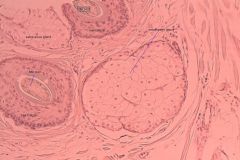
|
Integument scalp xsection
|
|
|
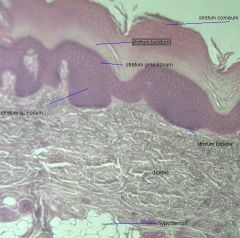
|
integument thick skin
|
|
|
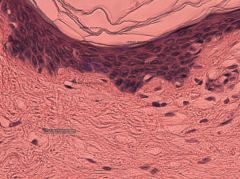
|
integument thin skin
|
|
|
|
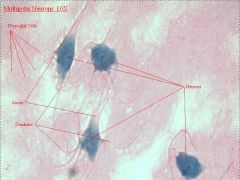
neuronal tissue
|
|
|
|
skeletal muscle
|
|
|
|
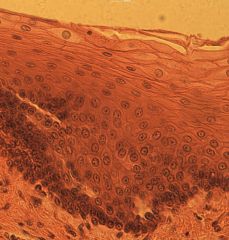
stratified squamous epithelium
|
|
|
|
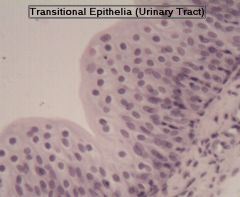
transitional epithelium
|
|
|
|
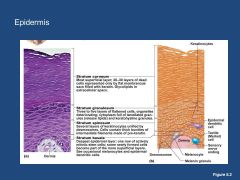
Layers of Epidermis
|
top down
Stratum Corneum Granulosum Spinosum Germinativum/basale |
|
|
|
Epidermis
|
|

