![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
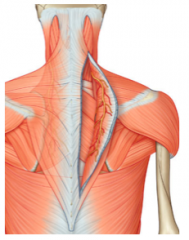
What are the superficial muscles of the back?
Where do they originate from in development? |
trapezius, latissimus dorsi, rhomboid minor, rhomboid major, levator scapulae
locations other than the back |
|
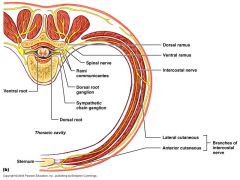
Where do the superficial (extrinsic) muscles of the back generally recieve their innervations from?
What is the exception?
|
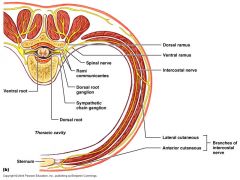
anterior rami of spinal nerves
trapezius receives innervation from CNXI that comes from the posterior rami |
|
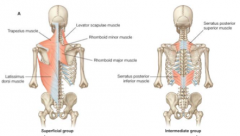
What is the general function of the superficial back muscles? AKA?
What is the general function of the intermediate back muscles? AKA? |
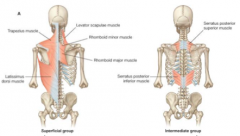
move the upper limbs
appendicular group
move the ribs
respiratory group |
|
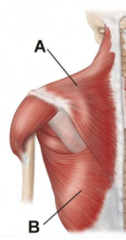
What does the first layer of the back consist of? |
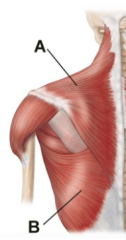
Trapezius & Latissimus Dorsi |
|
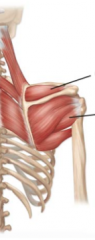
What does the second layer of the back consist of? |
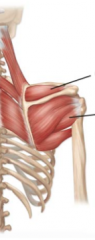
levator scapulae, rhomboid minor, rhomboid major |
|
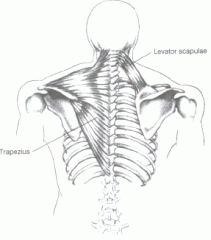
Where is the attachment of the Trapezius? |
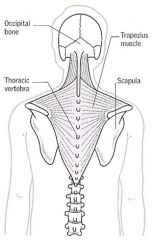
Proximal - external occipital protuberance, superior nucheal line, ligamentum nuchae, C7-T12 spinous processes
Distal - spine of scapula, acromion, lateral 1/3 or clavicle |
|
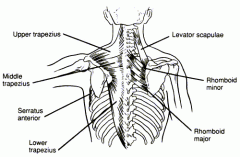
TRAPEZIUS:
What is the action? |
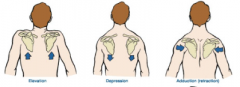
adduct scapula, upwards & outward scapular rotation, elevates scapula, depresses scapula |
|
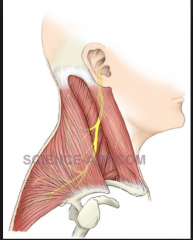
TRAPEZIUS:
What is the motor innervation?
What is the sensory/proprioceptive innervation? |
spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
C3 & C4 |
|
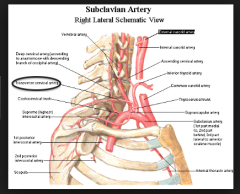
TRAPEZIUS:
What is the blood supply? |
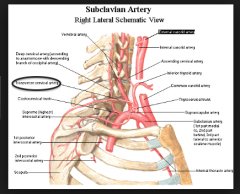
MAJOR: superficial branch of the transverse cervical artery |
|
|
What could damage to the spinal accessory nerve (CN XI) cause? |
trapezius muscle atrophy --> shoulder droop, weakness/inability to shrug shoulder, difficulty raising upper limb above head (no upward/outward rotation) |
|
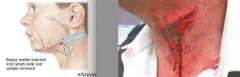
What is the majority of the causes of spinal accessory nerve (CN XI) damage? |
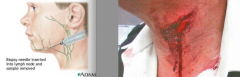
penetrating trauma (stab/bullet)
surgery in the lateral cervical region - cervical lymph node biopsy/removal of cancerous nodes |
|
|
What are physical signs of CN XI damage or trapezius atrophy? |
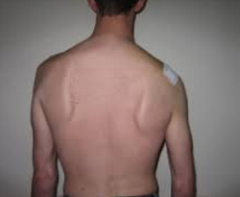
shoulder droop
diminished shoulder elevation, inability to shrug shoulders against resistance
inability to raise arm above head |
|
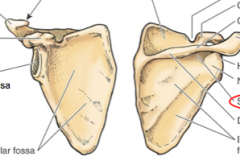
Where is the acromion and spine of scapula? |
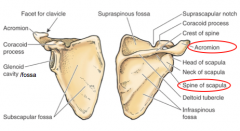
|
|
|
What landmarks of the scapula are easily palpable? |
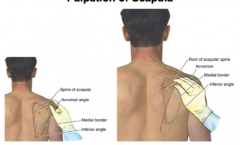
spine of scapula, acromial angle, medial border, inferior angle |
|
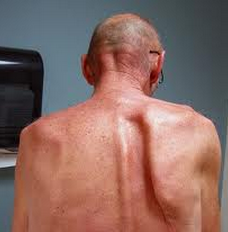
Damage to which nerve causes a winged scapula?
What can cause this? |
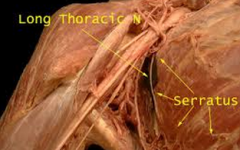
long thoracic nerve
removal of axillary lymph nodes, mastectomy
*atrophy of serratus anterior muscle |
|
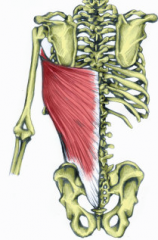
LATISSIMUS DORSI:
Attachment? |
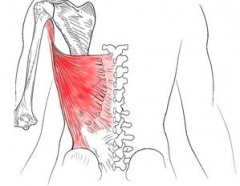
Proximal - T7-T12 & lumbar spinous processes, sacrum, iliac crest, ribs 10-12
Distal - floor of bicipital groove (intertubercular groove) |
|
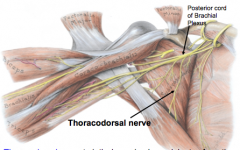
LATISSIMUS DORSI:
Innervation?
Where does this nerve originate from? |
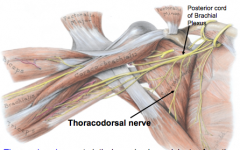
Thoracodorsal nerve (C6-8)
posterior cord of brachial plexus |
|
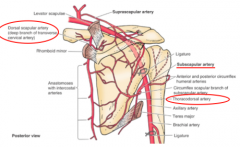
LATISSIMUS DORSI:
What is the blood supply?
What is the derivation of that artery? |
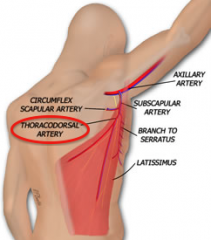
thoracodorsal artery
(subclavian --> axillary --> subscapular --> thoracodorsal) |
|
|
Where is the intertubercular (bicipital) groove of the humerus? |
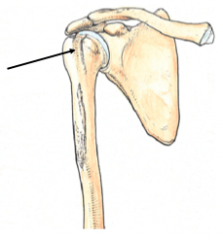
between the greater and lesser tubercles of the proximal humerus
*medial to insertion of pectoralis major |
|
|
LATISSIMUS DORSI:
What is the action? |
extend, medially rotates, adduct THE HUMERUS
pulls body toward arm in climbing and chin exercise
* HANDCUFF MUSCLE |
|
|
What can cause damage to the thoracodorsal nerve? |
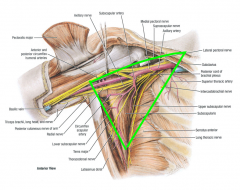
surgery involving the axilla - breast cancer surgery |
|
|
What are the physical signs of thoracodorsal nerve injury? (C6-C8) |

difficulty in adducting arm, rotation of humerus, extension of humerus
inability to adduct against resistence, inability to do chin up, inability to pull body toward arm in climbing |
|
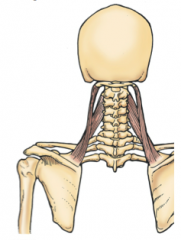
LEVATOR SCAPULAE:
Attachment? |
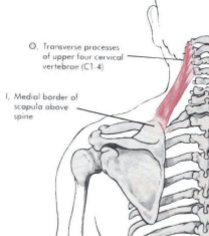
Proximal - C1-C4
Distal - medial border of scapula superior to scapular spine |
|
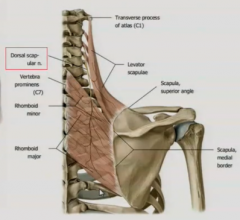
LEVATOR SCAPULAE:
Innervation? |
C4,C4 anterior rami (from cervical plexus)
lower portion recieves dorsal scapular nerve (C4-C5) |
|
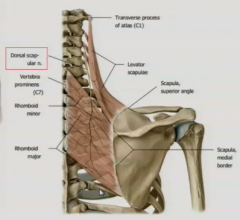
LEVATOR SCAPULAE:
What is the action? |
elevate & draw medially scapula
tilt gelnoid fossa inferiorly
laterally flex neck |
|
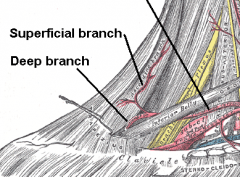
LEVATOR SCAPULAE:
What is the blood supply? |
![transverse cervical artery (deep branch) [subclavian]](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/05/03/51/6050351_m.png)
transverse cervical artery (deep branch) [subclavian --> thyrocervical trunk --> TCA --> deep/superficial] |
|
RHOMBOID MINOR:
Attachment?
RHOMBOID MAJOR:
Attachment |
Proximal - C7-T1 spinous processes Distal - Root of scapular spine
Proximal - T2-T5 Distal - medial border of scapula |
|
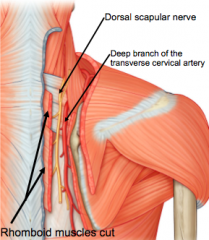
RHOMBOID MINOR:
Innervation?
RHOMBOID MAJOR:
Innervation?
|
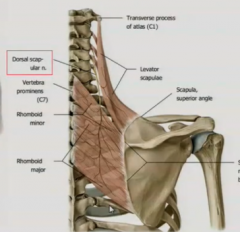
dorsal scapular nerve (C4-C5)
dorsal scapular nerve (C4-C5) |
|
|
RHOMBOID MINOR & RHOMBOID MAJOR:
Action? |
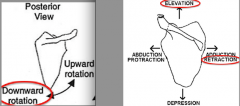
retracts & elevates scapula
w/ assistance from other muscles, rotates the lateral aspect of the scapula inferiorly |
|
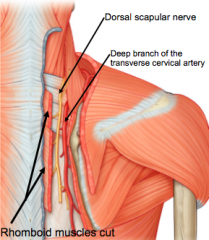
RHOMBOID MINOR AND RHOMBOID MAJOR:
Blood supply? |
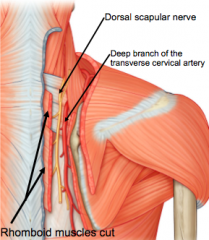
Deep branch of transverse cervical artery |
|
|
What is a common variation of the blood supply of the rhomboids? |
the descending scapular artery, coming right off of the subclavian, will supply this area
there is no TCA - the artery arising from the thyrocervical trunk and following the path similar to the TCA (w/o a deep branch) is named the superficial cervical artery |
|
|
What is a physical sign of dorsal scapular nerve damage? |
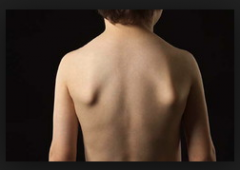
affected scapula will be further from the midline than the unaffected scapula
weakness in retraction/adduction/elevation of scapula
*weakness bc the function is not completely lost due to functioning trapezius
**Rhomboids AND levator scapulae are affected |
|
|
Derivation of transverse cervical artery?
Derivation of thoracodorsal artery? |
subclavian artery --> thyrocervical trunk --> transverse cervical artery --> deep & superficial branches
** deep is sometimes called dorsal scapular artery
subclavian --> axillary --> subscapular --> thoracodorsal |
|
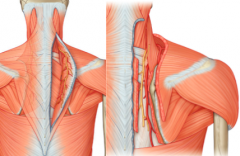
Where is the superficial transverse cervical artery located?
Where is the deep transverse cervical artery located? |
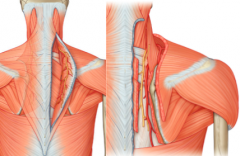
beneath the trapezius with the spinal accessory nerve
beneath the rhomboids to supply them and levator scapulae |
|
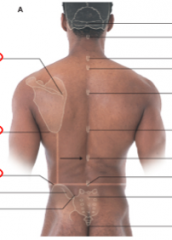
What is the vertebrae level of:
root of the spine of the scapula
inferior angle of scpaula
iliac crest |
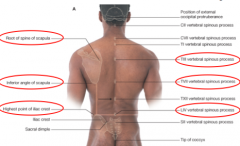
T3 spinous sprocess
T7 spinous process
L4 spinous process - L4/L5 intervertrbral disc |
|
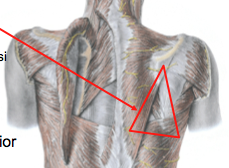
What are the borders of the triangle of auscultation? |
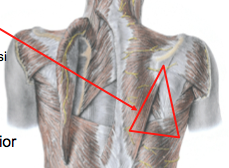
Floor - rhomboid major
Medial border of scapula
Superior border of latissimus dorsi
lateral border of trapezius |
|
|
What is heard in the triangle of auscultation?
What intercostal space is located deep to the traingle of auscultation? |
breath sounds from the posterior lung segments
6th intercostal space |
|
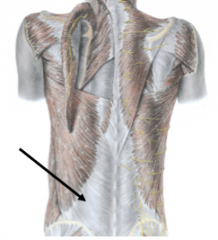
What does the thoracolumbar fascia cover?
What does the thoracolumbar fascia provide attachment for? |
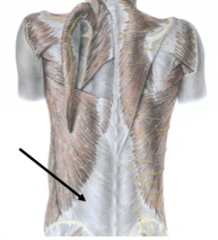
deep muscles of the back
attachment for latissimus dorsi |
|
|
What is aponeurosis?
What is fascia?
What is its function?
|
a fibrous sheet or flat expanded tendon, giving attachment to muscular fibers and serving as the means of origin or insertion of a flat muscle, it sometimes serves as fascia for other muscles
connective tissue
wrap, insulate and support deep structures of the body; permit passage for nerves and vessels ; limit the spread infection or malignancy to a fascial compartment |
|
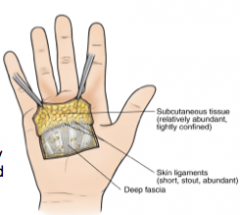
Describe superficial fascia
Describe deep fascia |
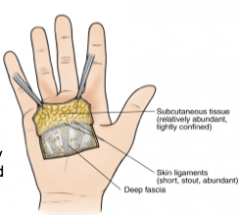
mostly fatty tissue; attached to the dermis of the skin
dense, more organized, connective tissue |
|
|
What are the intermediate back muscles? |
serratus posterior superior
serratus posterior inferior |
|
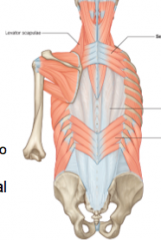
What is the attachment of serratus posterior superior?
What is the attachment of serratus posterior inferior? |
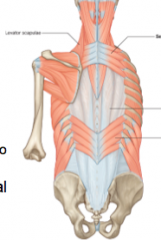
C7-T3 to ribs 2/3/4/5
T11-L3 to lower 3 or 4 ribs |
|
|
What is the function of serratus posterior superior?
What is the function of serratus posterior inferior? |
elevate ribs during forced inspiration
depress & stabilize ribs against diaphragm contraction |
|
|
What is the innervation of serratus posterior superior and serratus posterior inferior? |
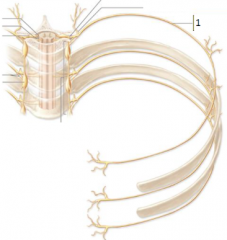
intercostal nerves T2-T5
last 4 intercostal nerves (T9/T10/T11/T12) |
|
|
Dorsal rami nerves pass through the superficial back muscles to innervate ____ |
the overlying skin
**do not innervate the superficial back muscles |
|
|
Each spinal nerve innervates a region of skin called a _____ |
dermatome |

