![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Joint between head and jaw (mandible)?
|

Temporomandibular joints
Hyoid apparatus |
|
|
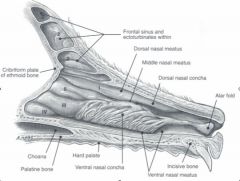
______ passes through the Ventral Nasal Meatus (VNM)
- leads to nasopharynx |
Nasogastric Tube
|
|
|
between nares
|
philtrum
|
|
|
For drainage of excess tears
Opens below alar fold |
Nasolacrimal duct
|
|
|
For detecting phermones
(identify opening in oral cavity) |

vomeronasal organs
- located off incisive duct, which opens into oral cavity @ incisive papillae |
|
|
Deciduous teeth erupt by?
what time is this? |
6 weeks
Time for vaccinations |
|
|
6 months (what time is this?)
|
Time to spay
|
|
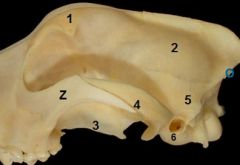
Identify bones
|
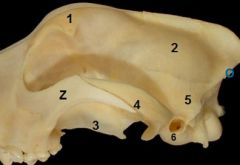
1. Frontal
2. Temporal 3. palantine bone 4. Zygomatic process of temporal bone 5. Parietal 6. Tympanic bulla |
|
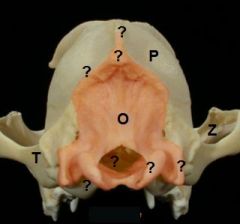
identify
|
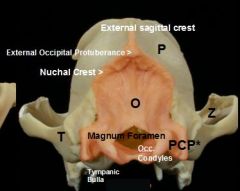
answers
*Paracondylar (jugular) process |
|
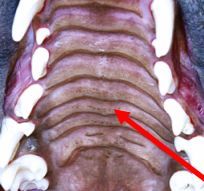
identify
|
palantine ridges (line hard palate)
|
|
|
dental formula for dogs?
|
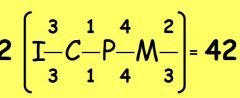
dental formula for dogs
|
|
|
inner side of teeth (facing medially)?
outer side of tooth? |
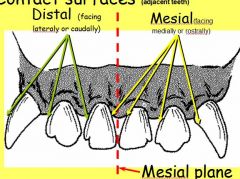
mesial
distal |
|
|
Sectorial or Carnassial
what empties here? |
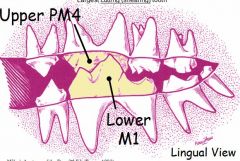
Upper PM4
Lower M1 Parotid duct empties near upper carnassial More specifically, in vestibular space opposite the upper 4th Pm |
|
|
How many roots do upper molars do dogs have?
How many roots do upper premolars do dogs have? |
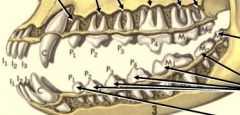
upper molars have 3 roots!
varies... UPM1 has 1 UPM2 and UPM3 have 2 roots Carnassial (upper PM4) has 3 roots like the molars |
|
|
feline permant dental formula
|

attached
|
|
|
Salivary Glands of head?
(one has 2 parts, name these parts) |
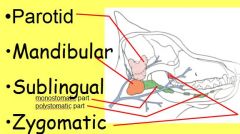
All are paired, all empty into oral cavity
Sublingual Salivary Gland 2 parts: Monostomatic (little guy attached to mandibular) Polystomatic: (below oral submucosa lateral to tongue) |
|
|
what clinically significant vein located in tongue
|
lingual vein
|
|
|
Mandibular & Sublingual salivary gland ducts travel together to empty on the ________ ?
|
Sublingual Caruncle
|
|
|
Cranial edge of the soft palate
Caudal edge of the soft palate |
Palatoglossal arch
Palatopharyngeal Arch |
|
|
Palatine tonsils located where?
|
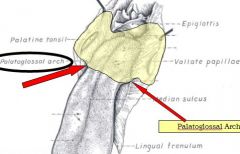
oropharynx
|
|
|
3 branches of trigeminal nerve? (dorsal to ventral), also mention if any goes thr. foramen
Where is trigeminal in relation to facial nerve? |
1. ophthalmic br.
2. maxillary br. (infraorbital foramen) 3. mandibular br. (out mental foramen as mental n.) DEEP - sensor, which is why it surfaces thr. foramen also does motor to muscles of mastification ( |
|
|
Largest bone (most recognizable bone in head)?
|
frontal bone
|
|
|
3 branches of facial nerve?
(dorsal to ventral), also mention if any goes thr. foramen Where is facial in relation to trigeminal nerve? |
1. auriculopalpebral br.
2. dorsal buccal br. 3.. ventral buccal br. facial is superficial |
|
|
Blood supply (arteries) to head?
|
Common carotid artery splits into external carotid a. and internal carotid a. (back of head)
ext.carotid a. splits into (1) maxillary a. (2) facial a. and (3) lingual a. which goes to tongue with hypoglossal nerve |
|
|
Which artery travels behind (medial side of) top of jaw and then through infraorbital foramen?
|
maxillary artery
|
|
|
Which is more lateral strap muscle?
|
sternothyroideus m.
|
|
|
Diifferentiate between choanae, nasopharynx, and ventral nasal meatus...and nasogastric tube
(if any of these are tagged, how to tell apart?) |
Nasopharynx extents from choanae to soft palate
Ventral nasal meatus is cranial to soft palate (i think?) Nasogastric Tube passed through the Ventral Nasal Meatus |
|
|
inner surface of teeth ?
outer surface of teeth? |
lingual surface
labial surface |
|
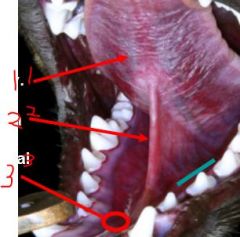
identify
|
1. lingual vein
2. frenulum 3. sublingual caruncle |
|
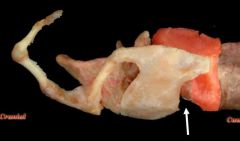
identify structure
|
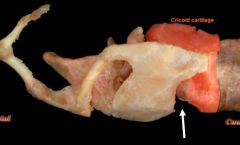
cricoid cartilage
|
|
|
name 3 main processes of arytenoid cartilage
|
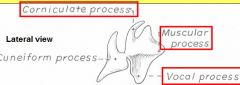
Corniculate,
Muscular & Vocal |
|
|
Which process of aryt.cartilage attaches to muscular process of arytenoideus dorsalis?
|
arytendois cartilage
|
|
|
4 signs of HORNER'S SYNDROME
|
1. Ptosis - (from Greek Ptosis or πτῶσις, to "fall") (drooping) of upper or lower eyelid.
2. Enopthalmos - protruding eyeball anteriorly out of orbit (eye socket). Greek word ophthalmos means "eye" and ex means "out". 3. Protruding 3d Eyelid 4. Miosis (or myosis): is constriction of the pupil All stem from interruption of sympathetic innervation to the eye. note: important to distinguish ptosis caused by Horner's syndrome from ptosis caused by lesion to oculomotor nerve. According to wiki, former b/c loss of sympathetic to eye and later ptosis occurs with dilated pupil (due to a loss of innervation to the sphincter pupillae). But I think it's the other way around! "Horny PAMELa" |
|
|
Opposite of miosis
|
Mydriasis, which is excessive dilation of the pupil
|
|
|
pupillary light reflex
|
controls diameter of pupil, in response to intensity (luminance) of light that falls on retina of eye
Afferent fibers via optic nerve, while oculomotor nerve is responsible for efferent limb of pupillary reflex - driving muscles that constrict pupil. Loss of reflex on same side (ipsilateral) as lesion. |
|
|
Ptosis
|
“toe-sis”, drooping of eyelid
One sign of Horners! |
|
|
Skip until know everything else!
CHOROID CILIARY BODY |
Along w/ iris (most anterior) these are parts of vascular tunic (mid tunic) of eye!
- vascular supply to optical retina. Contains pigment (iris also has), and TAPETUM LUCIDUM - suspends lens, contains smooth muscle for accommodation; has PROCESSES covered by secretory epithelium. |
|
|
Miosis
|
(or myosis, from Ancient Greek μύειν, mūein, "to close the eyes") is CONSTRICTION of the pupil
Part of papillary light reflex |
|
|
Most extrinsic eye mm. innervated by ________.
|
3rd Cranial Nerve = Oculomotor Nerve!
exceptions DO4(LrRb)6Rest3? |
|
|
Cricothyroideus m.
|
Bowtie muscle!
to identify midline! |
|
|
What innervates most of the muscles of mastification?
|
Mandibular division of CrN5
|
|
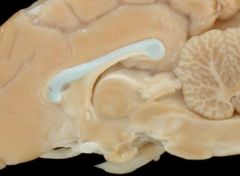
Identify this structure
what is part below it? |
corpus callosum: connects the 2 hemispheres
fornix |
|
|
nasopharynx extends from what to what?
|
-part of pharynx above soft palate
-extends from choanae and palatopharyngeal arch. |

